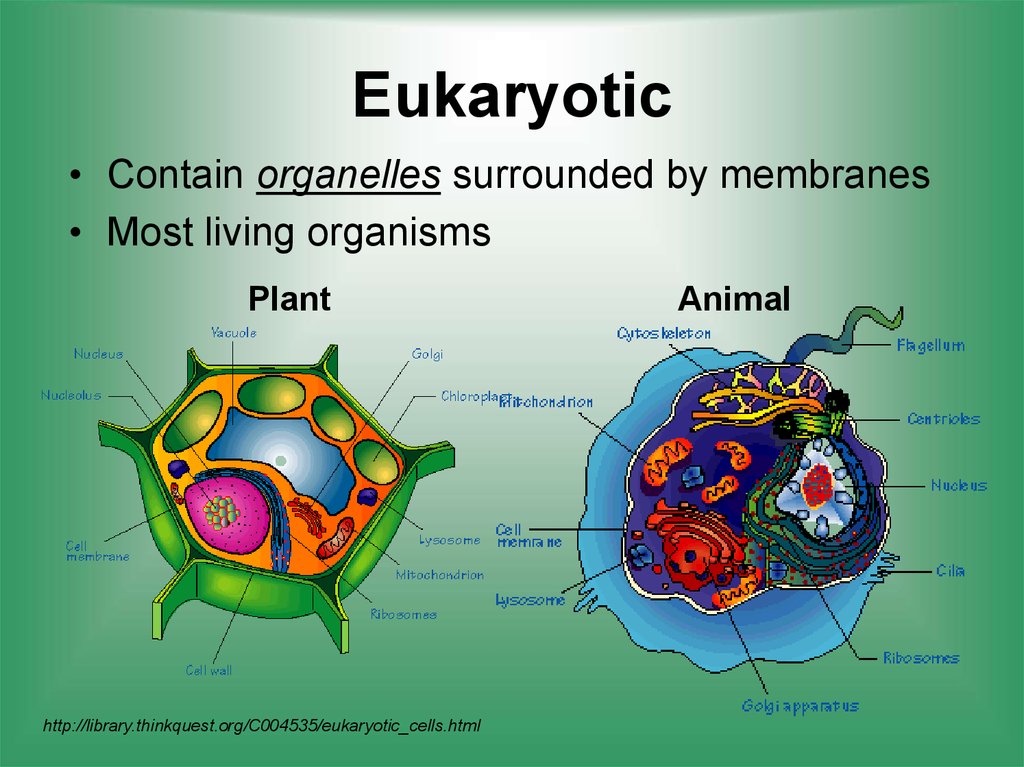
What are facts about plant and animal cells?
Animal cells do not have a cell wall or chloroplasts but plant cells do. Animal cells are round and irregular in shape but plants cells are rectangular and have a fixed shape. Animal cells contain lysosomes which are absent in plant cells. Animal cells have one or more small vacuoles but plant cells have only one big vacuole. 2.
Are mitochondria in plant and animal cells?
The mitochondrion is a double-membraned, rod-shaped structure found in both plant and animal cell. Its size ranges from 0.5 to 1.0 micrometre in diameter. The structure comprises an outer membrane, an inner membrane, and a gel-like material called the matrix.
Is a plant cell prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
plant cells are eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells do not contain a membrane bound nucleus, mitochondria or other membrane bound cell structures (organelles), the DNA of prokaryotic cells are located in the cytoplasm of the cell. Since plant cells contain membrane bound organelles this makes them eukaryotic. Click to see full answer.
What is the function of plant and animal cells?
plant & animal cells vacuole -stores . water, wastes & other materials-helps provide shape & structure. in plant cells-larger in . plant. cells since they may have to go for long periods without . rain. plant & animal cells cell membrane -controls what . moves. in & out of the cell (takes in food/ gases & removes wastes)-outermost layer of an animal. cell

Is prokaryotic animal or plant?
Only the single-celled organisms of the domains Bacteria and Archaea are classified as prokaryotes—pro means before and kary means nucleus. Animals, plants, fungi, and protists are all eukaryotes—eu means true—and are made up of eukaryotic cells.
Is eukaryotic a animal cell?
Plant and animal cells are eukaryotic, meaning that they have nuclei. Eukaryotic cells are found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists. They generally have a nucleus—an organelle surrounded by a membrane called the nuclear envelope—where DNA is stored.
Are eukaryotic a plant cell?
plant cell, the basic unit of all plants. Plant cells, like animal cells, are eukaryotic, meaning they have a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles.
Are animal and plant cells eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic, so they contain membrane-bound organelles like the nucleus and mitochondria.
What is meant by eukaryotic?
eukaryote, any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus. The eukaryotic cell has a nuclear membrane that surrounds the nucleus, in which the well-defined chromosomes (bodies containing the hereditary material) are located.
What kind of organism is eukaryotic?
Eukaryotes are organisms whose cells contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. There is a wide range of eukaryotic organisms, including all animals, plants, fungi, and protists, as well as most algae. Eukaryotes may be either single-celled or multicellular.
Why plant cell is a eukaryotic cell?
Animal cells and plant cells are eukaryotic. Both of them contain a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, vacuole, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, etc. In addition, another membrane-bound cell organelle called chloroplast is only found in plant cells.
What is an example of eukaryotic?
AnimalFungusProtozoaParameciumEuglenaDinosaurEukaryote/Lower classifications
Why is the animal cell eukaryotic?
Animal cells and plant cells are eukaryotic. Both of them contain a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, vacuole, Golgi bodies, lysosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, etc. In addition, another membrane-bound cell organelle called chloroplast is only found in plant cells.
How are eukaryotic cells classified?
Eukaryotic cells may be classified into two groups based on the number of cells that make an individual organism: (1) unicellular eukaryotic cells and (2) multicellular eukaryotic cells. Unicellular eukaryotes include the protists. Multicellular eukaryotes include a variety of plant, fungal, and animal species.
What cells are in animal cells?
Animal cells are typical of the eukaryotic cell, enclosed by a plasma membrane and containing a membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Unlike the eukaryotic cells of plants and fungi, animal cells do not have a cell wall.
Why human cell is eukaryotic?
The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope. For more information on DNA, see section “DNA Definition.” Cells that contain these features (ie, cytoskeleton, organelles surrounded by cytoplasm and nucleus surrounded by nuclear envelope) are called eukaryotic cells. Human cells are eukaryotic cells.
What is the nucleus of an eukaryotic cell?
A eukaryotic cell has a membrane-bound nucleus and other components, including the plasma membrane, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, chloroplast, mitochondria, cytoplasm and several rod-shaped chromosomes.
What is a prokaryotic cell?
A prokaryotic cell is a single-celled, also called a unicellular organism, which doesn't contain a nucleus and other membrane-bound components. This cell is a bit different from the eukaryotes cell.
What is the term for the chromosomes of animal cells?
The term diploid cell means: the chromosomes of animal cells are present in homologous pairs. In the period of sexual reproduction, the cellular division process called meiosis is essential to produce the haploid daughter cells or gametes.
What is an animal cell?
Animal cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane, which is also termed as cell membrane that contains a membrane-bounded nucleus and other organelles. The plasma membrane is a layer that separates the interior of the cell from its outside environment. These cell's features raise the kingdom of Animalia.
What is the outer cover of a cell?
Plasma membrane: It is an outer cover that separates the cell's interior parts from the surrounding environment. Cytoplasm: It is a jelly-like region inside the cell in which other cellular components exist. DNA: It is the genetic component of a cell. Ribosomes: It is a particle that synthesis proteins.
What are the two types of cells that are used to exchange genetic material?
Some of these cells have pili, flagella, or fimbriae. Most pili are used to exchange genetic material at the time of reproduction, known as conjugation. Flagella are used for movement, and fimbriae are used by the cell to attach to the host cell.
How big are animal cells?
Most animal and plant cells range in size between 1 to 100 micrometers, unicellular between 0.1 to 5.0 micrometer s, and they are only visible via microscope. Animals are multicellular and diploid. Multicellular means multiple cells combine to form a complete organism. The term diploid cell means: the chromosomes of animal cells are present in ...
What are some examples of eukaryotic cells?
Protists and fungi are two other types of eukaryotic organisms. Examples of protists include algae, euglena, and amoebas. Examples of fungi include mushrooms, yeasts, and molds.
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotes are usually single-celled organisms, while animal and plant cells are generally multicellular. Eukaryotic cells are more complex and larger than prokaryotic cells. Animal and plant cells contain many organelles not found in prokaryotic cells.
How are animal cells and plant cells similar?
Animal cells and plant cells are similar in that they are both eukaryotic cells. These cells have a true nucleus, which houses DNA and is separated from other cellular structures by a nuclear membrane. Both of these cell types have similar processes for reproduction, which include mitosis and meiosis. Animal and plant cells obtain the energy they ...
How do animal and plant cells obtain energy?
Animal and plant cells obtain the energy they need to grow and maintain normal cellular function through the process of cellular respiration. Both of these cell types also contain cell structures known as organelles, which are specialized to perform functions necessary for normal cellular operation. Animal and plant cells have some of the same cell ...
What is the difference between animal cells and plant cells?
Shape. Animal cells come in various sizes and tend to have round or irregular shapes. Plant cells are more similar in size and are typically rectangular or cube shaped.
What are the components of an animal cell?
Animal and plant cells have some of the same cell components in common including a nucleus, Golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, mitochondria, peroxisomes, cytoskeleton, and cell (plasma) membrane. While animal and plant cells have many common characteristics, they are also different.
Which type of cell does not have plasmodesmata?
Plasmodesmata. Animal cells do not have plasmodesmata. Plant cells have plasmodesmata, which are pores between plant cell walls that allow molecules and communication signals to pass between individual plant cells.
What are the organelles of animal and plant cells?
[In this figure] The cell anatomy of animal and plant cells.#N#The animal cell and plant cell share many organelles in common, such as a nucleus, ER, cytosol, lysosomes, Golgi apparatus, cell membrane, and ribosomes. The organelles unique for plant cells are vacuole, cell wall, and chloroplast (shown in orange text).
What are the characteristics of plants?
Plants are multicellular organisms of the kingdom Plantae. Their features include: 1 Autotroph – can produce its own food using light, water, carbon dioxide, or other chemicals 2 Both consume and produce oxygen 3 Generally, do not move 4 Reproduce sexually and asexually
What is the membrane of a cell?
Also known as the plasma membrane, a phospholipid bilayer that surrounds the entire cell and encompasses the organelles within.
What are some examples of plant-like protists?
For example, protozoans are grouped as animal-like protists, and algae are referred to as mixed groups of plant-like protists. Interestingly, some species confuse the scientists by exhibiting both characteristics of animal and plant. The best example is Euglena, a single-celled microorganism that can harvest solar energy by its chloroplasts like a plant, but also swim around using its flagellum like an animal.
What are the tiny structures inside a cell called?
Tiny structural parts inside the cell, called organelles, are involved in various specialized functions to keep the cell alive and active. [In this figure] Left: The compound microscope used by Robert Hooke to discover “cells.”. Right: Cell structure of cork illuminated by Robert Hooke in Micrographia, 1665.
Why do plant cells have a fixed shape?
Due to the cell wall, many plant cells have a rectangular fixed shape.
Which process occurs in both plant and animal cells to separate the parent cell from the daughter cell?
Cytokinesis occurs in mitosis and meiosis in both plant and animal to separate the parent cell from daughter cells.
Why are plants eukaryotic cells?
We have already said that All plant cells are eukaryotic. Now if this is true then why are plant eukaryotes. You should ask why should we consider plants as eukaryotic.
Which is better, eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Eukaryotic cells have better organization than prokaryotes. These cells can coordinate and work as a group. A group of eukaryotic cells can fulfill specific tasks for the plant. Hence Eukaryotes are more developed than prokaryotic cells.
Are seedless plants Eukaryotic?
Definitely, All seedless or seeded plants are Eukaryotic. In fact, A seed itself has millions of cells with specific features. Each of the cells in the seed has a distinct cell wall and cell membrane.
How are prokaryotes and eukaryotes differentiated?
They are differentiated based on their shape both internally and externally. The presence or absence of specific cell organelles makes them different.
What is the membrane of a plant cell?
The eukaryotic plant cell is covered with a thin soft cell membrane which is again protected by a semi-permeable hard cell wall. The multi-layer protection in a plant cell is a feature of eukaryotic cells.
What is the opposite of prokaryotic?
As an opposite companion of prokaryotes, A Eukaryotic has a well-developed cellular structure. These cells have a multi-layer membrane for the cell organelles as well as the entire cell covering.
What organelles are separate from each other in plants?
You can observe separate Nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast, Vacuoles, and ER floating in the cytoplasm of a plant cell. All of these cell organelles have membrane cover that separates them from others.