
Is facet syndrome a permanent condition? There is no way to “cure” facet joint syndrome with non-surgical treatments because it develops with age. The vast majority of people, on the other hand, have been able to manage their symptoms for years without surgery.
Is facet joint syndrome a permanent disability?
When a facet joint is damaged through normal deterioration, injury, or repetitive trauma, it may cause long-lasting or permanent disability. The most common causes of facet joint syndrome include:
What is “facet syndrome?
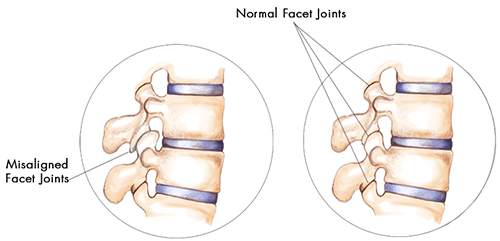
They also can become restricted in movement or develop too much movement resulting in pain. The facet joints are shaped and angled differently in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine. This allows for all of the available motion within the spine. Pain stemming from the facet joints is termed “facet syndrome.”
Where is facet joint syndrome most likely to occur?
The facet joints located in your lumbar spine (low back) are most susceptible to facet joint syndrome, as the lumbar spine bears the most weight and endures the greatest amount of strain. However, facet joints located in your cervical (neck) and thoracic (midback) spine may also cause chronic pain.
What is the treatment for facet joint syndrome?
For chronic cases of facet joint syndrome, where the pain relief from the injections is short-lived a procedure called Radiofrequency Rhizotomy can be performed.
Does facet joint pain go away?
While facet joint arthritis can't be reversed, there is evidence that exercise, lifestyle changes and careful management of your back pain can contribute to better quality of life. If conservative therapies fail to help you manage and control the pain, your doctor may recommend injections, ablations or surgery.
How long does it take for facet syndrome to heal?
How long does it take to heal a facet joint? As with any injuries healing times can change depending on numerous factors, such as age, weight, work and ability to avoid/manage aggravating activities. But typically, an acute sprain can take anywhere from 2-4 weeks if managed and treated correctly.
How do you fix facet joint syndrome?
Your doctor may recommend any of the following pain management treatment options:Heat and Cold Therapy. Heat and cold therapy can help ease pain caused by facet joint syndrome. ... Medications. ... Physical Therapy and Exercise. ... Proper Posture. ... Back Brace. ... Epidural Steroid Facet Injections. ... Medial Branch Injections.
Is facet syndrome acute or chronic?
They described the characteristics of an acute, uncomplicated facet syndrome as follows: local, ipsilateral pain, occasionally extending into the thigh with pain and decreased range of motion in extension and rotation both standing and sitting.
Is facet syndrome progressive?
It's important to note that while the degeneration of the facet joints is known as facet disease, it is not necessarily a progressive or degenerative disease. On the contrary, much like degenerative disc disease, the title actually represents wear and tear that occurs naturally over time within every spine.
What kind of doctor treats facet joint syndrome?
Physiatrists: These rehabilitation physicians specialize in treating injuries or illnesses that affect movement. They manage non-surgical approaches to back pain, including the pain of facet joint syndrome.
Does facet syndrome show up on MRI?
The accuracy of MRI in assessing facet joint osteoarthritis against CT was 94%. Under 40 years of age, the degree of disc degeneration varied among individuals. Over the age of 60, most of the discs were markedly degenerated.
Can facet disease be cured?
While there is no cure for facet arthropathy, there are ways to effectively manage the pain. Your orthopaedic specialist will work with you to find the least invasive treatment plan to manage your pain. Nonsurgical treatment options include: NSAIDs to fight pain and reduce inflammation.
How common is facet joint syndrome?
While facet arthrosis is a common radiographic finding, which has been suggested to be a potential cause of spinal pain, nearly 10% of all adults show signs of degeneration by the time they reach age 30.
How do you get facet syndrome?
What Causes Facet Syndrome?Being overweight or obese.Fractures of the spine.Poor posture.Repetitive bending or twisting.Sedentary lifestyle.Sudden, vigorous stretching.Torn ligaments.Trauma, such as an accident, fall, or sports injury.
Is facet syndrome considered a disability?
Have you been diagnosed with facet joint syndrome or facet disease? Disability benefits may be available to you if your condition has made it impossible for you to earn a living. Below is an overview of this potentially debilitating disease and what is necessary to apply for disability benefits in such circumstances.
What aggravates facet joint?
What aggravates facet joint pain? Facet pain is usually heightened with activities that cause excess movement of the spine such as rotating or bending the spine backward, twisting, and lifting. Conversely, bending forward may relieve the pain.
What aggravates facet joint?
What aggravates facet joint pain? Facet pain is usually heightened with activities that cause excess movement of the spine such as rotating or bending the spine backward, twisting, and lifting. Conversely, bending forward may relieve the pain.
Can damaged facet joints be repaired?
It involves the removal of your damaged facet joints via the posterior approach (from the back) and replacing them with a set of artificial facet joints, designed to restore your vertebra to the safe and correct position, while removing pain and retaining healthy movement.
Is walking good for facet joint pain?
Lumbar (lower spine) facet joint pain can present as low back pain, buttock pain, and pain in the back of the thighs. Prolonged walking and standing can make the pain worse. Sitting usually relieves the pain as stress is taken off the facet joints.
Is facet syndrome considered a disability?
Have you been diagnosed with facet joint syndrome or facet disease? Disability benefits may be available to you if your condition has made it impossible for you to earn a living. Below is an overview of this potentially debilitating disease and what is necessary to apply for disability benefits in such circumstances.
What is the best radiographic assessment for lumbar pain?
The initial radiographic assessment of patients presenting with lumbar facet-mediated pain includes AP, lateral, and oblique views [18]. Oblique radiographs are the best projections for assessing FJs of the lumbar spine because of their oblique position (“Scottie dog”). Lateral films, however, may provide useful information from the isthmus profile such as the pars interarticularis defect. Because of its ability to provide cross-sectional images and to provide a higher contrast between bony structures, CT improves anatomic evaluation of the FJs and is the preferred method for imaging FJ osteoarthritis [46]. However, standard radiographs can also show pathological changes especially in severe disease. Degeneration is characterized by joint space narrowing, sclerosis, subchondral sclerosis and erosions, cartilage thinning, calcification of the joint capsule, hypertrophy of articular processes and of the ligamentum flavum causing impingement of the foramina and osteophytes. Secondary signs include vacuum joint phenomenon (intra-articular gas), joint effusion and associated degenerative spondylolisthesis. Synovial and subchondral cysts can extend posterior to the FJ but also anterior in the spinal cord or neuroforamen. Kalichman et al. showed 24% of X-rays FJOA before 40 years and 89% in the 60–69 years population, but once again with no correlation between abnormal morphology on radiologic findings and back pain [4].
What are the classifications of FJ degeneration?
Two classifications of FJ degeneration are recommended for clinical use. Radiographically, Pathria’s classification classifies FJ arthropathy as well: Facets with joint space narrowing are classified as grade 1, facets with narrowing and sclerosis or hypertrophy as grade 2, and facets with severe degenerative disease encompassing narrowing, sclerosis, and osteophytes as grade 3 [57]. Standard radiographs (Meyerding or Taillard classification) [33] also evaluate motion-related abnormalities in flexion or extension, and assess instability in cases of spondylolisthesis, thanks to dynamic studies. In the setting of degenerative spondylolisthesis, a weight-bearing lateral flexion-extension radiograph is most effective for grading spondylolisthesis and may be needed in addition to MRI and CT imaging. Anteroposterior translation of more than a few millimetres is suggestive of lumbar spine instability in the sagittal plane, which in the appropriate clinical setting may require surgical arthrodesis. In addition to Pathria’s classification, Weishaupt’s grading scheme, based on the agreement between MRI and CT imaging, has been proposed. Facets were again graded from 0 to 3 depending on the degree of joint space narrowing, hypertrophy, sclerosis, and osteophyte formation. The authors recommended against the routine use of CT imaging in the presence of an adequate MRI scan [49]. Fujiwara et al. is credited with developing the standard MRI-based classification system for lumbar FJ osteoarthritis. An additional grading system for foramen stenosis, caused by disc and FJ degeneration can be used as well, based on the depiction of the foraminal components: nerve, vessels and fat [58]. First stage, the non stenotic stage: no modifications depicted. Second stage corresponds to stenosis without evidence of root compression. Third stage, compression of the spinal nerve in the intervertebral foramen caused by either intervertebral disc, flaval ligament or osseous stenosis. In this stage, the content of the foramen is not well identified. A grading scale has also been proposed for lumbar canal stenosis as follows [59]: A) cerebro-spinal fluid (CSF) is clearly visible inside the thecal sac, but its distribution is inhomogeneous. B) Some CSF is still present, giving a grainy appearance to the thecal sac. The rootlets occupy the whole of the dural sac, but they can still be individualized. C) the dural sac demonstrates a homogeneous grey signal with no CSF. No rootlets can be recognized. D) In addition to no rootlets being recognizable, there is no epidural fat posteriorly.
What is degenerative spondylolisthesis?
Degenerative spondylolisthesis is the displacement of one vertebra to another in the sagittal plane , which is related in the majority of cases to FJ osteoarthritis and failure of the motion segment. It occurs as a result of subluxation of the FJs, related to an important and progressive loss of cartilage and articular remodelling, with segmental instability causing capsule tension [22]. Spondylolisthesis most often occurs at the L4–5 level, which is predominantly affected by osteoarthritis [33]. In younger populations (30–40 years old), spondylolisthesis can be due to congenital abnormalities, acute or stress-related fractures or isthmic spondylolisthesis. As opposed to its degenerative counterpart, L5–1 is the most affected level, and related instability seems to be more frequent [34].
What is the most common form of back pain?
Lumbar facet joints (FJ) constitute a common source of pain, accounting for 15–45% of LBP. Facet joint degenerative osteoarthritis is the most frequent form of facet joint pain. History and physical examination may suggest but not confirm facet joint syndrome. Although imaging (radiographs, MRI, CT, SPECT) for back pain syndrome is very commonly performed, there are no effective correlations between clinical symptoms and degenerative spinal changes. Diagnostic positive facet joint block can indicate facet joints as the source of chronic spinal pain. These patients may benefit from specific interventions to eliminate facet joint pain such as neurolysis, by radiofrequency or cryoablation. The purpose of this review is to describe the anatomy, epidemiology, clinical presentation, and radiologic findings of facet joint syndrome. Specific interventional facet joint management will also be described in detail.
Which spondyloarthropathies are seronegative?
Rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis, which are seronegative spondyloarthropathies, may also involve the lumbar FJs, as FJs are synovial joints [18].
Is MRI good for FJ?
MRI is a noninvasive and nonionizing modality that provides excellent soft tissue resolution. The role of MRI in the evaluation of FJ degeneration is not proven. Osteoarthritis may be present in both symptomatic and asymptomatic patients (from 8 to 14%) [47, 48]. Superior sensitivity of MRI compared to CT imaging is controversial [8]. CT and MRI are equally useful in demonstrating morphological changes in FJ. One of the two examinations is thus sufficient for assessing degenerative changes [49]. MRI, however, clearly presents advantages of better assessing the immediate consequences of FJ degeneration, such as surrounding neural structure impingement [50]. Chronic degenerative osteoarthritis processes in these structures involve active synovial inflammation or adjacent bone edema, which can be detected using MRI with a fat saturation technique [51]. Exaggerated fluid in the facets and FJ synovial cysts seen on axial MRI seems to be significantly suggestive of spondylolisthesis and its instability, but is not specific of FJ origin of pain [52]. Recent studies using fat-suppressed MRI sequences have demonstrated that subchondral bone edema is present in the lumbar FJ articular processes in 14 to 41% of patients with back pain [53, 54]. Enhancement of the FJ rim after gadolinium administration will establish a diagnosis of synovitis. Fujiwara et al. proposed a four-grade classification from 1 to 4 [55]: grade 1, normal; grade 2, joint space narrowing or mild osteophyte; grade 3, sclerosis or moderate osteophyte; and grade 4, marked osteophyte. They additionally described the wraparound bumper osteophyte formations which provides an additional stabilizing effect in segmental degenerative disease. An important observation from the Fujiwara study is that MRI tends to underestimate the severity of osteoarthritis of the FJs as compared to CT. The fluid-sensitive sequences on MRI are generally preferred over CT for imaging FJ effusions and juxta-facet cysts; however, they are less sensitive in depicting the joints’ bony cortices and are less accurate in quantifying the amount of sclerosis present. An additional limitation of MRI is that it cannot accurately measure cartilage thinning secondary to the partial volume effect and chemical-shift artefact inherent in this type of imaging. CT is better able to demonstrate the degenerative changes of the FJs because of the high contrast between bony structures and the surrounding soft tissues [18]. However, some authors suggest that TSE T2 fat saturation sequences and, when indicated, gadolinium administration with T1 fat saturation sequences enhance the sensitivity and diagnostic specificity of MR scans. In particular, gadolinium will disclose the active inflammatory stage of a degenerative process thereby identifying new therapeutic targets for percutaneous treatment [51].
Is chronic pain a health problem?
Chronic and recurrent pain has been defined as a specific health care problem and is considered a disease in its own right [10]. A recent survey showed a high prevalence of chronic pain of moderate to severe intensity in adult Europeans, affecting the quality of their social and working lives and is therefore a major health care problem in Europe [1]. Low back pain (LBP) is one of the most common pain syndromes and is an enormous burden and cost generator for society. The high health care costs may be attributed to multiple factors, including lack of an accurate diagnosis [2], imaging overuse, unwarranted surgery and working stoppages. LBP is responsible for functional limitations and causes difficulty in performing common daily life tasks, especially among the elderly [11]. Therefore, LBP is the most expensive disease in industrialized countries, as has been reported in Germany at a total cost of 48.960 billion euros per year [12]. In the USA, the prevalence of LBP is reportedly between 15 and 45% according to cross-sectional studies [13]. Most spinal structures may be source of LBP, including intervertebral discs, FJs, sacroiliac joints and nerve roots, and may be accessible to diagnostic tests including imaging. Some disorders, particularly disc-related impairments, are reasonably easily diagnosed and lead to definitive treatments. However, discogenic LBP without disc herniation, lumbar FJ, and sacroiliac joint pain are difficult to diagnose with imaging only [2]. The literature focuses on intervertebral discs as the source of LBP; however, FJ pain also seems to play a major role in generating LBP [8]. Among LBP patients, there are wide discrepancies in the reported prevalence of FJ pain. Reviews implicate FJs as the primary pain generator in 10–15% of young adult patients with chronic LBP and higher in older populations (15% among injured workers, 40% in older population without pre-existing trauma, 45% in a more heterogeneous population) [14]. Controlled diagnostic studies have shown a prevalence of lumbar FJ pain of 27–40% in patients with chronic LBP [15].
How are facet joints formed?
The facet joints are formed by the superior and inferior processes of each vertebra. The first cervical vertebra has an inferior articulating surface but, as it does not restrict lateral or posterior translation, is not always considered a proper zygoma ( zygoma is Greek for "yoke," i.e. something that restrains movement). In the lumbar spine, facets provide about 20 percent of the twisting stability in the low back. Each facet joint is positioned at each level of the spine to provide the needed support especially with rotation.
What is the name of the condition where the facet joints are painful?
Facet syndrome. Facet syndrome is a syndrome in which the facet joints ( synovial diarthroses, from L2 to S1) cause painful symptoms. In conjunction with degenerative disc disease, a distinct but functionally related condition, facet arthropathy is believed to be one of the most common causes of lower back pain.
What causes lumbar spine pain?
Affected persons usually feel dull pain in the lumbar spine that can radiate into the buttocks and legs. Typically, the pain is worsened by stress on the facet joints, e.g. by lumbar extension and loading (the basis of the Kemp Test) or lateral flexion but also by prolonged standing or walking.
How to diagnose facet arthropathy?
Facet arthropathy or 'facet syndrome' can typically be diagnosed through a physical examination, MRI, x-rays and/or a diagnostic block into the suspected joint.
What is facet arthropathy?
In conjunction with degenerative disc disease, a distinct but functionally related condition, facet arthropathy is believed to be one of the most common causes of lower back pain.
How do you know if you have facet joint arthropathy?
The symptoms of facet joint arthropathy depend entirely on the location of the degenerated spinal joint, the severity of the damage and the amount of pressure that is being placed on the surrounding structures. It's important to note that the amount of pain a person experiences does not correlate well with the amount of degeneration that has occurred within the joint. Many people experience little or no pain while others, with exactly the same amount of pathology, experience chronic pain.
Why are facet joints positioned at each level of the spine?
Each facet joint is positioned at each level of the spine to provide the needed support especially with rotation. Facet joints also prevent each vertebra from slipping over the one below. A small capsule surrounds each facet joint providing a nourishing lubricant for the joint.
What causes a twisting spine?
Any twisting of the spine has the potential for injury. A few of the known culprits are: golf. over-extending. leaning backward. Another option is to explore several pain management treatments. The key is to work your way up, starting with the less aggressive treatments first.
What is the best treatment for facet joint syndrome?
When a more permanent solution is needed, surgery can help. There are two different surgical options to consider: Spinal Fusion, and something called Facet Debridement.
Where are facet joints located?
Unlike spinal conditions caused by acute injury, facet joint syndrome develops with age. Facet joints are located in the spine, and help with normal range of motion like twisting from side to side. Each joint is lined with a nerve-rich substance called “ synovial tissue “.
How long does a rfa last?
Next, you might consider prescription drugs (cortisone, novocaine, etc.) Finally, RFA (or radiofrequency ablation) can also be used to manage pain for up to 12 months.
Why does my lower back hurt?
Specifically, suffers will experience pain in the lower back region. The sensation of pain is caused by tiny nerves and tissues that get compressed . Other symptoms occur at the anatomical level, and are less likely to be “felt”. These symptoms include: less water volume in the joints.
Can facet joint syndrome be treated without surgery?
However, the vast majority of people are able to manage their symptoms without surgery for many years. One option is to avoid activities that are known to aggravate the facet joins. Any twisting of the spine has the potential for injury.
Is spinal fusion surgery risky?
Spinal fusion is the more dramatic and risky of the two surgical options. Because of the invasiveness of this approach, recovery time is quite long and complications are not uncommon. Studies show that the success-rate of this surgery is only 66%.
How to treat facet joint pain?
Treatment. Injection of steroids into the facet joints can help relieve pain for a long period of time. Other conservative approaches include anti-inflammatory drugs, and physical therapy. For long-term relief and in more severe cases, a rhizotomy (burning the anterior or posterior spinal nerve roots) may be done.
What is it called when your facet is pinched?
This condition is called facet hypertrophy.
What is the facet joint?
The facet joints are the connections between the bones of the spine. The nerve roots pass through these joints to go from the spinal cord to the arms, legs and other parts of the body.
Why do my knee joints hurt?
The joints are lined with the synovium and have lubricating joint fluid. When these joints get swollen because of injury or arthritis, it causes pain.
How to diagnose facet joint syndrome?
A diagnosis of facet joint syndrome is confirmed by injecting an anesthetic and an anti-inflammatory in the joint. If there is immediate relief of pain after the injection, the condition is facet joint syndrome.
What causes facet pain?
Causes of Facet Syndrome. Facet syndrome can be caused by trauma, such as a whiplash injury of the neck. Abnormal postures can overload spinal tissues, including the facet joints, and cause inflammation and pain in these joints. More commonly, degenerative changes in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine can lead to abnormal stress and strain.
What is the name of the joint that causes pain in the lumbar spine?
The facet joints are shaped and angled differently in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine. This allows for all of the available motion within the spine. Pain stemming from the facet joints is termed “facet syndrome.”. The facet joints become inflamed and may cause pain, soreness and stiffness. Patients often report increased pain ...
How to diagnose facet syndrome?
At your initial consultation your spinal specialist will diagnose your pain or symptoms. The visit will begin with a physical exam and collection of health history. In addition you will be asked to share the timeline and triggers of your pain and discomfort. Diagnosis of facet syndrome is made primarily from the history and physical exam. If facet syndrome is suspected, diagnostic imaging can be obtained. Imaging includes but is not limited to X-Rays, MRI, and CT scan. X-Rays will be done in-house at our facility during your initial consultation. These studies might show facet hypertrophy (enlargement of the joint) which would indicate the joint is under excessive stress.
What are the two joints in the back of the body?
This tripod creates great stability, supports all your weight above each level and provides support for you to move in all directions. The posterior facet joints are synovial joints, similar to other joints in the human body.
Why does my facet hurt?
The facet joints become inflamed and may cause pain, soreness and stiffness. Patients often report increased pain with extension or prolonged periods of inactivity like sitting or standing too long. Changing positions often improves pain. Facet syndrome pain may feel worse in the morning and improve after moving around as the day progresses.
How does massage help with osteoarthritis?
Therapeutic massage can help reduce osteoarthritis pain by improving circulation and reducing stress and muscle tension.
What is the treatment for facet syndrome?
Most conservative treatments for facet syndrome involve postural correction, soft tissue massage and manipulation of the affected areas . Spine-specialized physical therapists and osteopathic clinicians are adept at restoring movement and normal function in restricted and painful facet joints.
What Are The Symptoms Of Facet Joint Syndrome?
Neck, shoulder and low back and buttock pain are more commonly caused by facet joint disease. There are many painful symptoms that can be linked to the facets joints of your spine. The following symptoms are associated with facet joint syndrome:
Why is the thoracic spine more rigid than the lumbar and cervical areas?
Because the thoracic spine is more rigid than the lumbar and cervical areas it is less likely to develop facet joint disease. Age-related Wear and Tear: The most common cause and progression of this condition appear to be aging.
What are the factors that contribute to facet joint syndrome?
Being overweight is also considered a contributing factor. Also, to lesser degree arthritis, gout and some infections can contribute to facet joint syndrome
Can sitting in a car flare up facets?
Riding or sitting in the car for a long period can flare up facets
How are Facet Joint Syndrome Symptoms Treated?
A conservative nonoperative approach is often the starting course of action, and this may include physical therapy and anti-inflammatory medication. Core strengthening exercises (eg, abdominals) and low back stretching are key to alleviate and prevent facet syndrome.
What is the role of the intervertebral disc in the facet joints?
Like any other joint in your body, each facet joints’ job is to promote healthy movement and—along with the intervertebral disc—provide stability for each motion segment. The disc functions as a spacer and to support motion between the vertebral bodies.
Why do my facet joints hurt?
Trauma—like whiplash from a car accident—is a common cause of facet joint syndrome in the neck. While aging is the leading cause of facet joint pain in the lumbar spine, trauma from a sports injury or auto accident can cause chronic low back joint pain too. Rarely do spinal tumors affect the facet joints and cause pain.
Why does my facet hurt?
The cause of facet joint syndrome is largely dependent on the region of the spine affected. For example, facet pain in the low back is typically caused by the degenerative effects of aging. Like the knee or hip joints, the facet joints are true synovial joints (fluid filled).
What is the most common site of facet joint pain in the lumbar spine?
The most common site of facet joint pain in the lumbar spine is at the L4-L5 level followed by L5-S1. Some researchers estimate that facet joint syndrome accounts anywhere from 15% of all low back pain complaints to 59.6% in men and 66.7% in women. 1. While facet joint syndrome most often affects the lumbar spine, ...
What is the name of the joint that connects two or more bones in your body and functions to promote motion?
Facet Joint Syndrome. A joint connects two or more bones in your body and functions to promote motion. In your spine, the joints connecting each of your vertebrae are known as facet joints. Other names for facet joints include zygapophyseal or apophyseal joints, or your doctor may refer to them as simply facets.
How does RFA work?
RFA blocks the nerve’s pain signals by heating the nerves with radiofrequency waves. RFA may be an appropriate treatment if your spinal joint pain isn’t responding well to injection therapy. RFA provides extended pain relief—possibly up to a year.
What is facet syndrome?
Facet Syndrome: Symptoms and Underlying Causes. Facet syndrome is a degenerative condition in which the facet joints of the spine deteriorate. This causes pain and may greatly reduce mobility and flexibility. A patient may experience intense muscle spasms.
How to qualify for degenerative medical assistance?
To qualify for either form of assistance you must prove that your degenerative condition has limited your functional capacity. You can do this by presenting substantial medical documentation from your treating physicians and other qualified witnesses.
What is the procedure that involves severing nerve roots?
surgery (such as a rhizotomy – which includes severing certain nerve roots).
What are the benefits of disability?
Disability benefits are provided via the Social Security Administration and are available in two forms: 1 Supplemental Security Income (SSI) – based on the applicant’s financial need; and 2 Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) – based on the applicant’s work history.
Where are the facet joints located?
The facet joints can be found on both sides of the lumbar spine and help with twisting movements. A compromised facet joint cannot provide sufficient rotation. This may cause a person to have to turn his or her entire body to look to one side. Meanwhile, facet joints are packed with nerves.
How long can a witness sit without changing positions?
witness statements about how your condition impacts your daily activities (such as “Mr. Smith cannot sit for more than 10 minutes at a time without changing positions”).
Can you get disability if you have facet joint disease?
Have you been diagnosed with facet joint syndrome or facet disease? Disability benefits may be available to you if your condition has made it impossible for you to earn a living. Below is an overview of this potentially debilitating disease and what is necessary to apply for disability benefits in such circumstances.
What is Facet Syndrome?
Facet joints, which are the flat surfaces of the vertebrae that interlock, are located at each vertebral level, lending stability, flexibility and movement to the spine . If these joints become irritated or inflamed they can generate pain down the spine into the buttocks and legs. Facet disease is commonly caused by the deteriorating of cartilage and can be caused by aging, overuse, normal wear and tear and injury.
What is SSA 1.00?
The SSA does have a listing for disorders of the spine which is found under 1.00 Musculoskeletal System, Section 1.04 Disorders of the spine. Under this section is included the following conditions: herniated nucleus pulposus, spinal arachnoiditis, spinal stenosis, osteoarthritis, degenerative disc disease, facet arthritis, vertebral fracture, resulting in compromise of a nerve root (including the cauda equina) or the spinal cord.
What does it mean when you have a back injury?
If you have a severe back condition the Social Security Administration (SSA) will evaluate if your condition is as severe as a condition outlined in their SSA Listing of Impairments. Also known as the Blue Book, this listing contains conditions and related symptoms that the SSA acknowledges are generally so severe a claimant cannot work and may qualify for SSI or SSDI.
What are the symptoms of facet syndrome?
Common symptoms of facet syndrome occur in either the cervical, lumbar or thoracic spine and can include: Severe headaches. Radiating pain into the upper or lower back. Limited neck movement. Severe neck pain. Lower back pain.
What does it mean if your condition does not meet or exceed a listing?
If your condition does not meet or exceed a listing the SSA will determine if you have the residual capacity to work through a process called a medical vocational allowance. Through this process the SSA will consider not only your condition but also your age, work history, work skills and education and decide if you can work your current job, past job or retrain for new work. Under this process it will be easier for older claimants to prove they cannot retrain for new work and prove they qualify for SSI or SSDI.
What causes a facet to deteriorate?
Facet disease is commonly caused by the deteriorating of cartilage and can be caused by aging, overuse, normal wear and tear and injury. There are a variety of names used to describe facet syndrome including degenerative joint disease, facet arthritis, facet hypertrophy, and facet joint syndrome. Regardless of the cause of the name ...
Can facet syndrome qualify for SSDI?
Through medical evidence you may be able to prove that your facet syndrome is as severe as one of these conditions and qualify for SSI or SSDI. The main thing the SSA will determine is whether your condition is causing nerve root compression characterized by neuro-anatomic (or nervous system) distribution of pain, limitation of motion of the spine, motor loss (atrophy with associated muscle weakness) accompanied by sensory or reflex loss and, if there is involvement of the lower back, positive straight-leg raising test (sitting and supine).

Overview
Facet syndrome is a syndrome in which the facet joints (synovial diarthroses, from L2 to S1) cause painful symptoms. In conjunction with degenerative disc disease, a distinct but functionally related condition, facet arthropathy is believed to be one of the most common causes of lower back pain.
Signs and symptoms
The symptoms of facet joint arthropathy depend entirely on the location of the degenerated spinal joint, the severity of the damage and the amount of pressure that is being placed on the surrounding structures. It's important to note that the amount of pain a person experiences does not correlate well with the amount of degeneration that has occurred within the joint. Many people experience little or no pain while others, with exactly the same amount of pathology, experience …
Cause
Like many other joints throughout the human body, facets can experience natural degeneration from normal aging. Over time, the cartilage within the joints can naturally begin to wear out, allowing it to become thin or disappear entirely which, in turn, allows the conjoining vertebrae to rub directly against one another with little or no lubricant or separation. A result of this rubbing is often swelling, inflammation causing pain.
Pathophysiology
55% of facet syndrome cases occur in cervical vertebrae, and 31% in lumbar. Spinal osteoarthritis is known as spondylosis. Pathology of the C1-C2 (atlantoaxial) joint, the most mobile of all vertebral segments, accounts for 4% of all spondylosis.
The facet joints are formed by the superior and inferior processes of each vertebra. The first cervical vertebra has an inferior articulating surface but, as it does not restrict lateral or posterio…
Diagnosis
Facet arthropathy or 'facet syndrome' can typically be diagnosed through a physical examination, MRI, x-rays and/or a diagnostic block into the suspected joint.
Treatment
In general, anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed initially. This medical treatment is usually accompanied by physiotherapy to increase back and stomach muscles. Thus, the spine can be both relieved and stabilized. If these conservative measures do not bring about betterment, minimally invasive procedures such as a facet infiltration can be conducted to offer relief. In this procedure, a local anesthetic is injected directly into the respective joint, usually in combination …
See also
• Facet joint arthrosis