What is Fischer esterification?
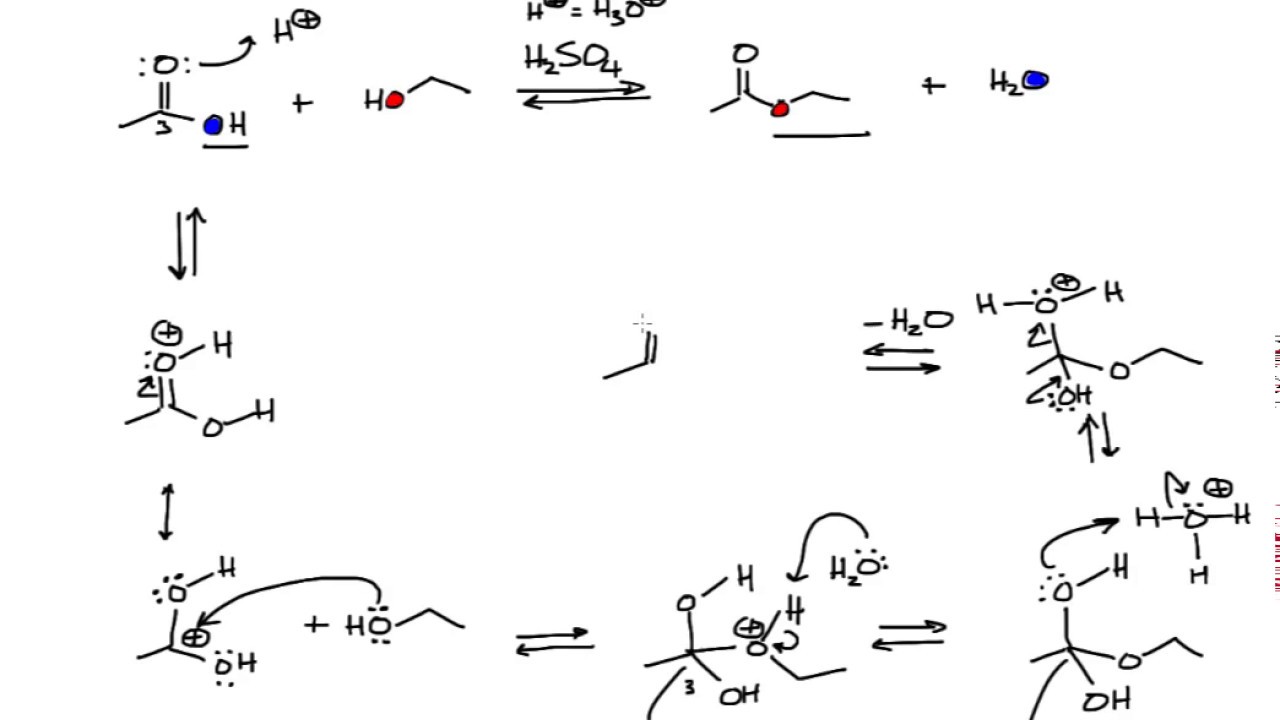
Fischer Esterification Fischer esterification is the acid-catalyzed reaction of carboxylic acids and alcohols: Before we go into the details of this reaction, remember that there are other ways of preparing esters.
What are the limitations of Fischer esterification of tertiary alcohol?
Again, this makes it even a weaker nucleophile than other alcohols which is especially true in acidic conditions. Another limitation of Fischer esterification is the fact that tertiary alcohols undergo a “fast” dehydration in presence of strong acids:
How are esterification reactions made?
Another common way of making esters is the reaction of acyl chlorides with alcohols or alkoxides: Each of these can be classified as an esterification reaction, however, the Fischer esterification is specifically referred to the acid-catalyzed reaction of carboxylic acids and alcohols.
Does Fischer ester inherit oxygen from the alcohol?
And it is confirmed experimentally, using the isotope label method, that the ester does inherit the oxygen from the alcohol. For the isotope label method, you simply use an 18O-containing alcohol and if the molecular mass of the ester corresponds to this change, it proves the suggested mechanism of Fischer esterification:

How do you reverse Fischer esterification?
Acid-catalyzed ester hydrolysis is literally just the reverse of Fischer esterification. It's literally just the reverse reaction of producing an ester. You could then hydrolyze that ester back to a carboxylic acid.
Is an esterification reaction reversible?
Esterification is a reversible reaction. Hydrolysis- literally "water splitting" involves adding water and a catalyst (commonly NaOH) to an ester to get the sodium salt of the carboxylic acid and alcohol.
What type of reaction is Fischer esterification?
Fischer esterification reactions The reaction is an example of a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction. The substitution is based on the nucleophilicity of the alcohol and electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon.
What is a disadvantage of Fischer esterification reaction?
The primary disadvantages of Fischer esterification routes are its thermodynamic reversibility and relatively slow reaction rates—often on the scale of several hours to years, depending on the reaction conditions.
What is the difference between esterification and Fischer esterification?
The key difference between Fischer esterification and Steglich esterification is that Fischer esterification involves the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of a strong acid as the catalyst whereas Steglich esterification involves the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in ...
Why is Fischer esterification in equilibrium?
The Fischer esterification reaction takes advantage of Le Chatelier's principle to increase the amount of carboxylic acid that is esterified. The equilibrium is shifted towards products by using a large excess of the alcohol (it is used as the reaction solvent), and (in some cases) also removing water as it it formed.
Does esterification go to completion?
The ester is heated with a large excess of water containing a strong-acid catalyst. Like esterification, the reaction is reversible and does not go to completion.
Why are esterification reactions reversible?
In esterification, a carboxylic acid reacts with an alcohol, in presence of acid to form ester and water. The reaction is reversible since ester and water can react to form the carboxylic acid and alcohol again.
Is Fischer esterification harmful?
Relatively simple compared to other esterification mechanisms. As compared to other esterifications, the chemicals used and the byproducts released in this mechanism are non-toxic to the environment.
Why is sulfuric acid used in Fischer esterification?
Esterification Reaction Fisher esterification is a reversible reaction that proceeds very slowly. An acid catalyst, typically in the form of sulfuric acid, is added to increase the rate of the reaction while also acting as a dehydrating agent.
Why is ester hydrolysis reversible?
2.10. Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis of ester is reversible and occurs by SN1 pathway. Acid catalysts speed up the reaction by protonating carbonyl oxygen and thus rendering carbonyl carbon more susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
Why is saponification the reverse of esterification?
Saponification is the cleavage of an ester into carboxylic acid and alcohol. This is the backward reaction of esterification. This reaction needs the presence of a base and water. Due to the basic condition provided by the base, the carboxylate ion becomes more stable than the carboxylic acid form.
What is an esterification reaction?
Esterification is the process of combining an organic acid (RCOOH) with an alcohol (ROH) to form an ester (RCOOR) and water; or a chemical reaction resulting in the formation of at least one ester product.
Which of the following is the reverse of an esterification reaction quizlet?
Hydrolysis is the reverse of an esterification reaction.
What is Fischer Esterification Reaction?
The Fischer Esterification Mechanism must include the continuous removal of water from the system or the usage of a large excess of alcohol since the overall reaction is reversible. Fischer Esterification is an organic reaction which is employed to convert carboxylic acids in the presence of excess alcohol and a strong acid catalyst to give an ester as the final product. This ester is formed along with water. A few examples of Fischer Esterification reactions are given below.
What are the disadvantages of Fischer esterification?
3. What is a disadvantage of Fischer esterification? Ans: The equilibrium existence of the reaction is a major disadvantage in Fischer esterification. When the reaction is conducted in a closed vessel, it is even more difficult because it is necessary to remove either the product or the water generated to drive the reaction to completion. 4.
What is the esterification reaction of Fischer?
Ans: The esterification of Fischer is one of the most common carboxylic acid reactions. Treatment with alcohol of carboxylic acids in the presence of acid catalyst contributes to the formation with esters along with the removal of a water molecule. 3.
How to remove water from the system during esterification?
The techniques used to remove water from the system during this esterification include the removal of water by azeotropic distillation or adsorption by molecular sieves. The reaction is an example of a nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction. The substitution is based on the nucleophilicity of the alcohol and electrophilicity of the carbonyl carbon.