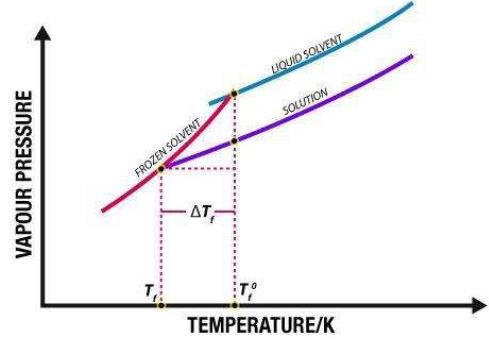
The change in freezing point is proportional to the amount of solute added. This phenomenon is called freezing point depression. The freezing point variation is defined by: ∆Tf = Tf,solution − Tf,solvent. ∆Tf is negative because the temperature of the solution is lower than that of the pure solvent.
What is freezing point depression and how does it work?
Freezing point depression is the phenomenon by which the freezing point of a pure solvent is lowered when a solute is added to it. Freezing point depression is a colligative property, meaning the effect is determined by how many solute particles are added - regardless of what molecule the solute is.
How do you calculate freezing point depression?
Strategy:
- Calculate the freezing point depression of benzene. Tf = (Freezing point of pure solvent) – (Freezing point of solution)
- Calculate the molal concentration of the solution. molality = moles of solute / kg of solvent.
- Calculate Kf of the solution. Tf = (Kf) (m)
How do you solve freezing depression?
How do you solve for freezing point depression? The freezing point depression ∆T = KF·m where KF is the molal freezing point depression constant and m is the molality of the solute. Rearrangement gives: mol solute = (m) x (kg solvent) where kg of solvent is the mass of the solvent (lauric acid) in the mixture. This gives the moles of the solute.
What is the formula for freezing point depression?
With the help of this knowledge, one can also conclude that the freezing point formula is: ΔTf= i x Kf x m In this freezing point depression formula, ΔTf is the freezing point depression, i is the Van’t Hoff factor, Kf is the cryoscopic constant, and m is the molality.
Can freezing point depression be positive?
(Note: This equation assumes the freezing point depression constant has a positive value.) The freezing point of the solvent in a solution containing a nonvolatile nonelectrolyte, Tsolution, may be found from the following information: The freezing point of the pure solvent, Tpure solvent.
What does freezing point depression tell us?
Freezing Point Depression. The freezing point of a solution is less than the freezing point of the pure solvent. This means that a solution must be cooled to a lower temperature than the pure solvent in order for freezing to occur.
What does a low freezing point depression mean?
Freezing point depression occurs when the freezing point of a liquid is lowered or depressed by adding another compound to it. The solution has a lower freezing point than that of the pure solvent.
What are the effects of freezing point depression?
The effect of adding a solute to a solvent has the opposite effect on the freezing point of a solution as it does on the boiling point. A solution will have a lower freezing point than a pure solvent.
What should be true about the freezing point depression per particle or ion?
Correct answer: Freezing point depression is a colligative property, meaning that it depends on the amount of particles present in solution. The more ions that a solute dissociates into, the larger the magnitude of freezing point depression.
What is the difference between freezing point and freezing point depression?
The key difference between freezing point and freezing point depression is that freezing point is the temperature at which a liquid becomes a solid, whereas freezing point depression is the decrease of the freezing point of a solvent due to the addition of a solute into the solvent.
Is freezing point depression constant positive or negative?
This phenomenon is called freezing point depression. The change in the freezing point is defined as: ∆Tf = Tf,solution − Tf,solvent. ∆Tf is negative because the temperature of the solution is lower than that of the pure solvent.
Which has highest depression in freezing point?
Depression in freezing point is a colligative property which depends on number of particles. Among given choices K2SO4 gives maximum number of ions, so it will have maximum depression in freezing point.
How does freezing point depression determine purity?
If the freezing point depression constant is known you can calculate the molal concentration of solute from a measured freezing point depression, assuming the concentration is dilute enough to be considered an ideal solution.
What is meant by freezing point depression quizlet?
Freezing point depression. The difference in temperature between the freezing point of a solution and that of it's pure solvent.
How does freezing point depression determine purity?
If the freezing point depression constant is known you can calculate the molal concentration of solute from a measured freezing point depression, assuming the concentration is dilute enough to be considered an ideal solution.
How is freezing point depression used in real life?
A very common example of this phenomenon in everyday life is salting of the roads in water. Pure water freezes at 0°C. However, by mixing in salt the freezing point of this mixture of water and salt will drop well below zero.
How does freezing point depression also explain the behavior of ocean water?
As a result, the ambient temperature must reach a lower point in order to freeze the ocean than to freeze freshwater lakes. This freezing-point depression effect is the same reason we throw salt on icy sidewalks in the winter. The salt lowers the freezing point of the ice below the ambient temperature and it melts.
1. Is there any difference between freezing and melting point?
Most liquids have a characteristic temperature at which those liquids become solids. This temperature is known as the freezing point. According to...
2. Is freezing an exothermic reaction or an endothermic reaction?
No, the phenomenon of freezing, like condensation, is an exothermic process. This is because, during the phase transition from a liquid to a solid-...
3. How quickly can water freeze at 00C?
Generally, as it is known, water freezes at 32 0F or 0 0C. But it is not as simple as it seems. Water behaves differently under different condition...
4. Mention the six types of phase changes?
Following are the six types of phase changes observed in substances at various temperature and pressure conditions:(i) Phase change from solid to l...
5. What is the difference between the phenomena of boiling point elevation and freezing point depres...
Boiling point elevation refers to the phenomenon of rising in the boiling point of a substance due to the addition of a solute. In the same manner,...
Why does freezing point depression occur?
There are many reasons why the freezing points of solvents tend to depress upon the addition of a solute . Some of those reasons are mentioned below. At the freezing point of a solvent, there is an equilibrium that is present between ...
What is the freezing point of seawater?
The freezing point depression examples are mentioned below. The freezing point of seawater is below zero Celsius. Seawater remains liquid at temperatures lower than that of the freezing point of pure water. This is due to the salts that are dissolved in the seawater.
What happens to the vapour pressure of a nonvolatile solvent?
According to Raoult’s law, the vapour pressure of any pure solvent will decrease after the addition of a solute. This further means that if the vapour pressure of a non-volatile solvent is zero, then the overall vapour pressure of the solution will be lesser than that of the pure solvent.
Why do organisms survive in freezing climates?
Did you know that many organisms can survive in freezing climates because their bodies tend to produce compounds like sorbitol and glycerol? The secretion of these compounds helps in decreasing the freezing point of the water in their bodies.
Is the vapour pressure of a liquid or solid equal?
This means that the vapour pressures of both the solid and liquid phase are equal. Once a nonvolatile solute is added to the solvent, the vapour pressure of the solution will be lower than the vapour pressure of the pure solvent.
Is the melting point of a solid the same as the freezing point of a liquid?
This temperature is known as the freezing point. According to the theories, the melting point of a solid should be the same as the freezing point of a liquid. However, during the actual action, it is possible that small differences might be observed between these values. 2.
When does water freeze?
Water usually freezes when it hits 00C, but the amount of time it takes for the water to freeze depends on various variables.
Why does the freezing point depression occur?
The explanation for the freezing point depression is then simply that as solvent molecules leave the liquid and join the solid, they leave behind a smaller volume of liquid in which the solute particles can roam. The resulting reduced entropy of the solute particles thus is independent of their properties. This approximation ceases to hold when the concentration becomes large enough for solute-solute interactions to become important. In that case, the freezing point depression depends on particular properties of the solute other than its concentration.
What is the phenomenon of freezing point depression?
Freezing-point depression is a drop in the temperature at which a substance freezes, caused when a smaller amount of another, non- volatile substance is added.
Why does a solvent freeze to a very nearly pure crystal?
This typically occurs simply because the solute molecules do not fit well in the crystal , i.e. substituting a solute for a solvent molecule in the crystal has high enthalpy. In this case, for low solute concentrations, the freezing point depression depends solely on the concentration of solute particles, not on their individual properties. The freezing point depression thus is called a colligative property.
How does elevated concentration of solute affect the freezing point of water?
This elevated concentration of solute decreases the freezing point of the water inside them, prevent ing the organism from freezing solid even as the water around them freezes , or as the air around them becomes very cold.
What is the freezing point of a liquid?
Explanation. The freezing point is the temperature at which the liquid solvent and solid solvent are at equilibrium, so that their vapour pressures are equal. When a non-volatile solute is added to a volatile liquid solvent, the solution vapour pressure will be lower than that of the pure solvent. As a result, the solid will reach equilibrium ...
Why does a solution have a lower freezing point than a pure solution?
The resulting liquid solution or solid-solid mixture has a lower freezing point than the pure solvent or solid because the chemical potential of the solvent in the mixture is lower than that of the pure solvent, the difference between the two being proportional to the natural logarithm of the mole fraction. In a similar manner, the chemical potential of the vapor above the solution is lower than that above a pure solvent, which results in boiling-point elevation. Freezing-point depression is what causes sea water, (a mixture of salt and other compounds in water), to remain liquid at temperatures below 0 °C (32 °F), the freezing point of pure water.
What is the effect of salting ice?
Road salting takes advantage of this effect to lower the freezing point of the ice it is placed on. Lowering the freezing point allows the street ice to melt at lower temperatures, preventing the accumulation of dangerous, slippery ice.
Why does freezing point depression occur?
The solute must be non-volatile. The reason is that freezing point occurs when the vapor pressure of the liquid and solid solvent are at equilibrium.
How to calculate freezing point depression?
Key Takeaways: Calculate Freezing Point Depression 1 Freezing point depression is a property of solutions where the solute lowers the normal freezing point of the solvent. 2 Freezing point depression only depends on solute concentration, not its mass or chemical identity. 3 A common example of freezing point depression is salt lowering the freezing point of water to keep ice from freezing on roads in cold temperatures. 4 The calculation uses an equation called Blagden's Law, which combines Raoult's Law and the Clausius-Clapeyron Equation.
Can a solvent be any phase?
In fact, the solvent can be any phase, too. Freezing point depression also occurs in solid-solid mixtures. Freezing point depression is calculated using Raoult's Law and the Clausius-Clapeyron Equation to write an equation called Blagden's Law. In an ideal solution, freezing point depression only depends on solute concentration.
Does freezing point depression depend on solute concentration?
Freezing point depression only depends on solute concentration, not its mass or chemical identity.
