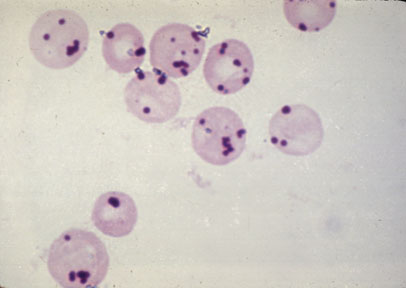
Can G6PD deficiency be cured?
Thus, in the vast majority of cases, someone has a variant such as G6PD deficiency because they have inherited it from one or sometimes both parents. As an inherited genetic disorder, G6PD deficiency (G6PDd) is not a disease that one can acquire or be cured of; it is part of the inherent genetic makeup that is with you for your whole life.
How long does it take for G6PD to go away?
However, some may develop symptoms when they’re exposed to the medication, food, or infection that triggers the early destruction of red blood cells. Once the underlying cause is treated or resolved, symptoms of G6PD deficiency usually disappear within a few weeks.
What is the G6PD test?
The G6PD test is a blood test that measures how much of this enzyme you have in your blood. If you have low amounts, you have a condition called G6PD deficiency.

Is G6PD life-threatening?
Certain triggers can cause red blood cells to be destroyed faster than they can be replaced. In this case, a person with G6PD deficiency can develop acute haemolytic anaemia (AHA), which can be life-threatening, especially in children.
What happens when you have G6PD?
G6PD is a genetic disorder that happens when your body doesn't have enough glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) enzyme. G6PD helps red blood cells work and protects them from harmful substances. G6PD can cause life-threatening hemolytic anemia that requires blood transfusions.
How do you fix G6PD?
Treating G6PD deficiency symptoms is usually as simple as removing the trigger. Often, this means treating the infection or stopping the use of a drug. A child with severe anemia may need treatment in the hospital to get oxygen and fluids. Sometimes, a child also needs a transfusion of healthy blood cells.
What foods to avoid if you have G6PD deficiency?
Your child should not eat fava beans. Some people should also avoid red wine, all beans, blueberries, soya products, tonic water and camphor.
Does G6PD affect brain?
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiencies are globally prevalent. Brain deficiencies enhance G6pd gene dose-dependent oxidative DNA damage. Deficient brains exhibit lower Purkinje cell numbers and synaptic dysfunction. G6PD-deficient mice exhibit cognitive and motor abnormalities.
Is G6PD inherited from father?
G6PD deficiency is inherited. This means it is passed down from parents through their genes. Women who carry one copy of the gene can pass G6PD deficiency to their children. Men who get the gene have G6PD deficiency.
What foods trigger G6PD?
Some foods, medications, and other substances can trigger a hemolytic crisis in individuals with G6PD. A hemolytic crisis refers to the rapid breakdown of red blood cells....falafel.chickpeas.broad beans.green peas.peanuts.lentils.black eye peas.
What happens to baby with G6PD?
Clinical. Babies with G6PD deficiency appear normal at birth. They may experience neonatal jaundice and hemolysis that can be so serious as to cause neurologic damage or even death. Barring such severe complications in the newborn period, infants with G6PD deficiency generally experience normal growth and development.
Is G6PD a disability?
The criteria for a disability rating of 70 percent for G6PD deficiency with hemolytic anemia, renal glycosuria, and Fanconi's syndrome from December 23, 1969 under the provisions of 38 C.F.R. § 3.321(b)(1) have been met. 38 C.F.R. § 3.321 (2014).
Can G6PD drink milk?
Despite its good nutritional and functional qualities, milk products containing Soy ingredients are unsuitable for children with G6PD deficiency.
Can G6PD patients take Covid vaccine?
Like routine vaccines, COVID-19 vaccines can be safely administered to people with G6PD deficiency. Clinical trials and real-world evidence have not identified any specific concerns regarding COVID-19 vaccines and people with G6PD deficiency.
Can G6PD eat peanuts?
Based on study and data, all types of nuts SHOULD NOT BE EATEN by G6PD Deficients.
What happens to baby with G6PD?
Clinical. Babies with G6PD deficiency appear normal at birth. They may experience neonatal jaundice and hemolysis that can be so serious as to cause neurologic damage or even death. Barring such severe complications in the newborn period, infants with G6PD deficiency generally experience normal growth and development.
What food is good for G6PD?
Eating antioxidants with plenty of suitable fats and chewing fewer refined carbohydrates can help in minimizing risks. antioxidants. These include tomatoes, berries, pomegranates, apples, oranges, grapes, dates, spinach, sunflower seeds, walnuts, apricots and prunes.
Is G6PD a disability?
The criteria for a disability rating of 70 percent for G6PD deficiency with hemolytic anemia, renal glycosuria, and Fanconi's syndrome from December 23, 1969 under the provisions of 38 C.F.R. § 3.321(b)(1) have been met. 38 C.F.R. § 3.321 (2014).
What can trigger G6PD?
In people with G6PD deficiency, hemolytic anemia can occur after eating fava beans or certain legumes. It may also be triggered by infections or by certain drugs, such as: antimalarials, a type of medication used to prevent and treat malaria. sulfonamides, a medication used for treating various infections.
How is G6PD passed down?
G6PD deficiency is inherited. This means it is passed down from parents through their genes. Women who carry one copy of the gene can pass G6PD deficiency to their children. Men who get the gene have G6PD deficiency. Women who get the gene are carriers. They often don’t have symptoms.
What is G6PD deficiency?
G6PD deficiency is an inherited condition. It is when the body doesn’t have enough of an enzyme called G6PD (glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase). This enzyme helps red blood cells work properly. A lack of this enzyme can cause hemolytic anemia. This is when the red blood cells break down faster than they are made.
How is G6PD deficiency diagnosed?
Your healthcare provider can diagnose G6PD deficiency with a simple blood test. You may need this test if:
How to treat G6PD?
Treatment of G6PD deficiency. Most people don't need any treatment — they manage their condition by avoiding the triggers. If you develop anaemia, it will need to be treated — potentially with a blood transfusion. Babies with jaundice are treated by being placed under special lights called 'bili lights'.
What happens if you have a G6PD?
When to seek help. If people with G6PD deficiency are exposed to a trigger, they can very quickly develop acute haemolytic anaemia, which requires medical attention . If you or your child develops jaundice (yellow skin and eyes), dark-coloured urine, pale skin or lethargy, see your GP as soon as possible.
What are some medicines that help with G6PD?
medicines such as some antibiotics, malaria medications (both for the prevention and treatment of malaria), aspirin, some anti-cancer drugs and large doses of vitamin C. some chemicals, including mothballs (naphthalene) some foods, particularly fava beans (broad beans) certain infections. G6PD deficiency is a lifelong genetic condition ...
What happens if you don't have enough G6PD?
People with G6PD deficiency do not have enough of an enzyme called glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD). This enzyme helps protects red blood cells from damage. The condition can cause the red blood cells to break down too easily (called 'haemolysis'). This can lead to anaemia (lack of red blood cells) and jaundice ...
How to know if you have G6PD?
Most people with G6PD live without symptoms most of the time. But the common signs and symptoms include: 1 dark-coloured urine 2 very pale skin 3 breathlessness 4 an enlarged spleen 5 very fast heart rate 6 low back pain 7 fever 8 diarrhoea, nausea or abdominal pain
What tests are used to diagnose G6PD?
The condition is diagnosed with blood tests, which are used to rule out other conditions, as well. It’s recommended that if one child in the family is diagnosed with G6PD deficiency, other children should be tested.
Can G6PD cause anaemia?
In this case, a person with G6PD deficiency can develop acute haemolytic anaemia (AHA), which can be life-threatening, especially in children. Triggers can include:
What is the treatment for G6PD?
This sometimes includes oxygen therapy and a blood transfusion to replenish oxygen and red blood cell levels.
How long does it take for G6PD to go away?
Once the underlying cause is treated or resolved, symptoms of G6PD deficiency usually disappear within a few weeks.
What is the role of G6PD in the body?
G6PD is also responsible for keeping red blood cells healthy so they can function properly and live a normal life span. Without enough of it, red blood cells break down prematurely. This early destruction of red blood cells is known as hemolysis, and it can eventually lead to hemolytic anemia.
How to diagnose G6PD?
How’s G6PD deficiency diagnosed? Your doctor can diagnose G6PD deficiency by performing a simple blood test to check G6PD enzyme levels. Other diagnostic tests that may be done include a complete blood count, serum hemoglobin test, and a reticulocyte count.
What is G6PD in genetics?
G6PD deficiency is a genetic condition that is passed along from one or both parents to their child. The defective gene that causes this deficiency is on the X chromosome, which is one of the two sex chromosomes. Men have only one X chromosome, while women have two X chromosomes. In males, one altered copy of the gene is enough to cause G6PD ...
What are the risks of G6PD?
You may have a higher risk of having G6PD deficiency if you: 1 are male 2 are African-American 3 are of Middle Eastern descent 4 have a family history of the condition
How to tell if you have G6PD?
Symptoms of G6PD deficiency can include: rapid heart rate. shortness of breath. urine that is dark or yellow-orange. fever. fatigue. dizziness. paleness. jaundice, or yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes.
How do i cure a g6pd deficiency?
You don't: This is genetic, where your genetic code does not carry the information for you to make g6pd in normal amounts. This enzyme problem only effects those cells where this becomes an issue like the red cells.The enzyme helps the red cell maintain its cell wall integrity by assisting energy production.Without it the red cells can break down.
What is G6PD deficiency?
Heereditary disease: Glucose -6- phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-PD) deficiency is a hereditary condition in which red blood cells break down when the body is exposed to certain drugs or the effect of infection.
How to avoid G6PD?
1. Avoid Taking Certain Medications . The best way to avoid symptoms due to G6PD deficiency is to limit exposure to the triggers. It’s very important for people with G6PD deficiency to avoid taking a number of “high risk”medications, which can potentially cause severe reactions.
How long does it take for G6PD to go away?
When symptoms do occur, the symptoms will usually disappear within several weeks once the trigger is removed.
What is the cause of G6PD deficiency?
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency is a genetic disorder — meaning it’s passed down from parents to their offspring — that is characterized by an enzyme defect due to a mutated G6PD gene.
How many variants of G6PD are there?
There are more than 400 genetic variants of the G6PD deficiency that have been identified.
Why do people with G6PD have hemolytic anemia?
Hemolytic anemia in people with G6PD deficiency is usually due to reactions caused by a bacterial or viral infection. It can also be due to side effects caused by taking certain medications or drugs, such as antibiotics or medications used to treat malaria.
What does G6PD stand for?
G6PDs stands for g lucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. G6PD deficiency is a genetic disorder that affects an erythrocyte (red blood cell) enzyme and may contribute to anemia. The severe form of the deficiency is called favism, which causes more symptoms and poses more risks than other types of G6PD deficiency.
What happens if you don't have enough G6PD?
As mentioned above, people who have G6PD deficiency develop hemolytic anemia, which, according to the U.S. Department of Health & Human Service’s Genetics Home Reference page, o ccurs when “red blood cells are destroyed faster than the body can replace them.” ( 4) Anemia is defined as “a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells.” (5) There are a number of different types of anemia depending on what’s causing it. When someone has hemolytic anemia their red blood cells, which are produced inside bone marrow, are destroyed more rapidly than usual. In people without anemia, this is normally about 120 days after they are produced.
What happens if you don't have G6PD?
When your body can’t make up for the quick loss, you can get hemolytic anemia . . Hemolytic anemia can be dangerous because it causes a loss of oxygen to your organs and tissues.
What Is G6PD?
G6PD is an enzyme called glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. It is a type of housekeeping protein that has many different activities in the body. It is responsible for stopping your cells from being damaged by compounds called reactive oxygen species.
What Is G6PD Deficiency?
G6PD deficiency is a hereditary condition caused by a mutation, or a change, in your G6PD gene. This gene tells your body to make the G6PD enzyme, so a mutation will lower the amount of this useful protein in your body.
What is the normal G6PD level?
A normal test result means you have enough of the enzyme and don’t have G6PD deficiency. A normal measurement is 5.5 to 20.5 units/gram of hemoglobin for adults. Moderate deficiency. A moderate deficiency means the amount of G6PD enzyme in your blood is at 10% to 60% of the normal range. Someone with a moderate deficiency might have hemolytic ...
What is the name of the drug that causes fava beans to turn into free radicals?
Malaria medicines. Acetylsalicylic acid, or Aspirin. Acetaminophen. Fava beans have certain chemicals that quickly turn to free radicals. People who have G6PD deficiency can have a reaction to fava beans that causes sudden onset hemolytic anemia. This is called favism.
Where is G6PD most common?
Men are more likely than women to have G6PD deficiency. It’s more common in some areas like Africa, Asia, and the Mediterranean. In the United States, African-American men are most commonly affected.
Can G6PD cause anemia?
Not everyone who has G6PD deficiency has other health problems. The deficiency alone is not enough to cause anemia or problems with your red blood cells. However, individuals who already have this mutation can have new symptoms triggered by outside sources.
What does G6PD protect?
G6PD protects oxygen-rich RBCs from chemicals called reactive oxygen species (ROS). ROS build up in your body:
What is G6PD in men?
A G6PD deficiency is an inherited disorder. It’s most common in men of African, Asian, or Mediterranean descent. It’s the result of X-linked recessive transmission, which means it’s much more likely to affect men as opposed to women. The deficiency can lead to a certain type of anemia known as hemolytic anemia.
What are the triggers for G6PD?
Triggers related to a G6PD deficiency hemolytic episode include: Other potential triggers include taking aspirin (Bayer) and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), such as ibuprofen (Advil). There are other substances that your doctor will know to avoid, as they may cause complications.
Why is my G6PD test delayed?
Your G6PD test may be delayed if you’re experiencing a hemolytic episode. Many cells with low levels of G6PD are destroyed during an episode. As a result, your test results may show falsely normal G6PD levels. Your doctor will give you complete instructions on how to prepare for your blood draw.
Why is G6PD important for RBCs?
A lack of G6PD may make RBCs more vulnerable to breaking down in a process called hemolysis. A G6PD test is a simple test that requires a blood sample.
When is a G6PD test ordered?
A G6PD test is most often ordered after a doctor has ruled out other causes of anemia and jaundice. They’ll perform the test once a hemolytic episode has subsided.
Can G6PD be inherited?
Your doctor will discuss the results from your G6PD test at a follow-up appointment. Low levels of G6PD in your blood indicate an inherited deficiency. There’s no cure for this disorder. However, you can prevent hemolytic episodes and anemic symptoms by avoiding certain triggers. Triggers related to a G6PD deficiency hemolytic episode include:
Overview
A G6PD test is a blood test to measure G6PD levels. G6PD is short for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. G6PD is an enzyme (protein) that helps your red blood cells work correctly.
Test Details
Healthcare providers test your G6PD levels by taking a small blood sample. During the blood test, your healthcare provider:
Results and Follow-Up
Low levels of G6PD can indicate a G6PD deficiency. You may have a deficiency without having hemolytic anemia. If you have a G6PD deficiency, it’s important to avoid triggers of symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
Not always. Many people have a G6PD deficiency that never leads to hemolytic anemia. Unless you have hemolytic symptoms, a G6PD deficiency typically won’t interfere with your usual activities.
Why is G6PD a variant?
Thus, in the vast majority of cases, someone has a variant such as G6PD deficiency because they have inherited it from one or sometimes both parents. As an inherited genetic disorder, G6PD deficiency (G6PDd) is not a disease that one can acquire or be cured of; it is part of the inherent genetic makeup that is with you for your whole life.
How often does a child get G6PD?
The frequency of new spontaneous mutations of the G6PD gene is about one in one million. Thus, whenever a child is diagnosed with G6PD deficiency it almost always because he or she has inherited it from one or both parents. As the diagrams of inheritance show, the variant may be present in either or both parents. Screening of family members, parents and siblings, may be desirable, both to identify possible unrecognized cases and also to indicate the likelihood of future offspring inheriting the trait. This is an option that should be discussed with your healthcare provider.
What is the mutation of the enzyme G6PDD?
Chromosomes. Mutations. Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase deficiency (G6PDd) is a metabolic disorder caused by a mutation in the gene for the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase. Although many mutations of many different genes are known, the probability of any given individual spontaneously acquiring a new deleterious mutation is actually very ...
Where is the G6PD gene located?
The gene that codes for the enzyme glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) is located on the X chromosome and is quite near the genes for coagulation Factor VIII (a variant of which causes Hemophilia) and for colorblindness. The location on the X chromosome has particular consequences for its pattern of inheritance.
Can a male inherit G6PD?
All female children of a G6PD deficient (hemizygous) male will inherit the trait but none of his male children can inherit the trait from him. Thus, a male can only inherit this enzyme deficiency from his mother.
Is G6PD a heterozygous or homozygous trait?
This means that when a trait such as G6PD deficiency is located on the X chromosome, a female can still be heterozygous or homozygous depending if she has one or both chromosomes bearing the variant gene. A male, on the other hand, is said to be hemizygous if his single X chromosome carries the variant gene.
Is G6PD a disease?
As an inherited genetic disorder, G6PD deficiency (G6PDd) is not a disease that one can acquire or be cured of; it is part of the inherent genetic makeup that is with you for your whole life.