What is a glomus tumor?
Glomus tumors, or paragangliomas, are slow-growing, usually benign tumors in the carotid arteries (major blood vessels in your neck), the middle ear or the area below the middle ear (jugular bulb). Glomus tumors are most often benign; however, they can cause significant damage to surrounding tissues as they grow.
Can glomus tumors be removed without surgery?
Unfortunately, due to the nature of glomus tumors and what they are made of, as well as where they are and how they are connected to the body’s surrounding tissues, surgery is the only viable option when it comes to having them removed.
How common are glomus tumors in young adults?
Abnormal growth of a glomus body results in Glomus Tumors. Glomus Tumors usually occur in people 20 to 50 years of age but are more frequent in young adults. More common in women, 70% of Glomus Tumors present in the hand with the clear majority occurring underneath the nail bed. Most of the nodules are solitary but can occur in clusters.

Are glomus tumors cancerous?
What is a Glomus Tumor? Glomus tumors — also known as paragangliomas — of the head and neck are benign (noncancerous) but locally invasive tumors that arise from glomus cells. In the head and neck, glomus tumor tissue is found in the jugular bulb, middle ear, and carotid artery.
Do glomus tumors spread?
Malignant glomus tumor, or glomangiosarcoma, is a very rare mesenchymal neoplasm that, when seen, occurs in visceral organs. Despite having histologic features of malignancy, these tumors usually do not metastasize. However, when metastasis occurs, this disease is often fatal.
Should glomus tumor be removed?
A glomus tumor is typically treated with surgical intervention. Because this condition can affect the patient's quality of life, a definitive diagnosis is necessary to evaluate the extent of the condition. However, because this condition is benign, recurrence is uncommon. Multiple growths in the area may occur.
What causes a glomus tumor?
The cause of a glomus jugulare tumor is unknown. In most cases, there are no known risk factors. Glomus tumors have been associated with changes (mutations) in a gene responsible for the enzyme succinate dehydrogenase (SDHD).
Can a glomus tumor burst?
Additionally, subungual glomus tumors have been reported to rupture and have also been reported to result in various nail changes, including color change, erythronychia, splitting, and thickening of the nail bed.
How common is a glomus tumor?
The glomus tumor is a rare benign neoplasm that arises from the neuroarterial structure called a glomus body1, which accounts for 1 % to 4.5 % of tumors in the hand.
Can a glomus tumor grow back?
The glomus tumor may recur in 4–15% of cases. Its recurrence is usually observed within a year of surgery and indicates an incomplete excision, or the presence of another tumor that was not diagnosed and excised earlier. Uncommonly, the recurrence may present after one year of the index surgery.
How do you get rid of a glomus tumor?
How are Glomus Tumors treated? Surgical excision of the tumor is the only treatment modality. During a 15-minute outpatient procedure the nail is removed, an incision is made into the nail bed exposing the tumor, and the tumor is removed.
How painful are glomus tumors?
Glomus tumors are painful subungual lesions. They produce a throbbing or lancinating local discomfort, cold-sensitivity, and severe pain following minor trauma. The diagnosis is confirmed by histology, but the clinical diagnosis is highly suggestive. Complete excision will usually relieve pain.
What does glomus mean?
Medical Definition of glomus : a small arteriovenous anastomosis together with its supporting structures: as. a : a vascular tuft that suggests a renal glomerulus and that develops from the embryonic aorta in relation to the pronephros. b : carotid body.
Are glomus tumors hereditary?
Multiple glomus tumours are rare, often asymptomatic lesions, with a familial tendency and found in a more proximal location than their solitary counterparts.
How do you know if you have a glomus tumor?
Glomus jugulare tumors grow on the jugular bulb, while glomus tympanicum tumors grow in the middle ear space. Distinguishing these tumors can typically be done through a detailed ear microscope exam or with a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) scan.
How do you get rid of a glomus tumor?
How are Glomus Tumors treated? Surgical excision of the tumor is the only treatment modality. During a 15-minute outpatient procedure the nail is removed, an incision is made into the nail bed exposing the tumor, and the tumor is removed.
Where on the skin are glomus tumors most likely to be found?
Glomus tumors occur most commonly in the subungual region of the fingers, but may also occur in areas of the body that are not richly endowed with glomus apparatus (e.g., muscle, bone, blood vessels, and nerves).
Do glomus tumors show on MRI?
Glomus tumors are often evaluated with MRI, which has a positive predictive value of 97%.
How to diagnose glomus tumor?
First, you’ll meet with your doctor for a physical exam and to discuss your symptoms. Then your doctor may order imaging tests, such as an MRI, CT scan or angiogram.
Where is the glomus tumor located?
Glomus tumors, or paragangliomas, are slow-growing, usually benign tumors in the carotid arteries (major blood vessels in your neck), the middle ear or the area below the middle ear (jugular bulb).
What are the symptoms of a glomus tumor?
Paraganglioma symptoms depend on where the tumor is located. A tumor in the carotid arteries (carotid body tumor) can cause: A mass in the neck. Hoarseness.
What is the best treatment for a glomus tumor?
Your team may recommend a combination of treatments for glomus tumors, including surgery and radiation.
What is a glomus jugulare tumor?
Glomus Jugulare Tumor. A glomus jugulare tumor is a tumor within the skull cavity. The area of the skull affected by this type of tumor is called the jugular foramen. The jugular foramen is on the temporal bone. The temporal bones are on the sides of your skull, or your temples.
How to diagnose glomus jugulare?
How Are Glomus Jugulare Tumors Diagnosed? A physical examination is the first step towards diagnosing a glomus jugulare tumor. The symptoms, as well as an examination of the ear and throat area, can indicate that a tumor may be present. There may be a lump on the neck, and the tumor may even be visible inside the ear.
What is the tumor on the top of the skull called?
The underside region of the temporal bone in the skull contains many nerve bundles with glomus cells. Tumors that grow in this area are called glomus jugulare tumors because they form at the top of the jugular vein. This is the vein that takes blood from the brain back to the heart.
What are the symptoms of a tumor on the neck?
ear pain. dizziness. If the tumor is large enough and grows towards the face or neck, it can cause other symptoms. These may include: weakness in facial muscles. facial paralysis. difficulty swallowing. hoarseness. drooping shoulders.
What is the sound of a tumor in the middle of the ear called?
These can include: partial or complete hearing loss. a ringing or pulsing sound, which is called tinnitus. ear pain.
What is the treatment for a tumor that can't be removed?
In some cases, traditional surgery to remove most of the tumor is combined with follow-up radiation. The radiation targets the remains of the tumor that the surgeon couldn’t physically remove.
Where does a tumor grow?
Glomus tumors, although not often cancerous, can grow extensively and may spread throughout the inside of nerves, along veins and arteries, and inside the ear and the Eustachian tube, which is the connection between the ear and the nose.
What are Glomus Tumors?
A Glomus Tumor is rare, usually benign, soft tissue neoplasm. The glomus apparatus (or glomus body) is a part of the dermal layer of the skin and is thought to aid in temperature regulation. When exposed to cold temperatures, the glomus body moves blood away from the skins surface to reduce heat loss. While they are located all over the body, glomus apparati are found in higher concentrations in the fingers and toes. Abnormal growth of a glomus body results in Glomus Tumors.
How common are glomus tumors?
Glomus Tumors usually occur in people 20 to 50 years of age but are more frequent in young adults. More common in women, 70% of Glomus Tumors present in the hand with the clear majority occurring underneath the nail bed. Most of the nodules are solitary but can occur in clusters. Glomus Tumors represent 1 to 5% of all soft tissue tumors in ...
What are the symptoms of Glomus Tumors?
These lesions are usually quite small, less than 7mm in diameter. They can be extremely painful, are sensitive to temperature change, and tender on palpation. The pain is often worse at night and can be relieved by applying a tourniquet. The mass can cause the nail bed to grow irregularly with ridging possible.
How are Glomus Tumors diagnosed?
Glomus Tumors often require a specialist for accurate diagnosis. Upon examination the mass may appear as a bluish lesion under the nail or in the fingertip pulp. There may be an abnormal ridge in the nail, swelling at the tip and the nodule will be tender to touch. X-rays may show deformity or erosion in the distal phalanx if the mass is long standing, otherwise the films may appear normal. MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) is the gold standard for diagnosis.
How can Dr. Knight help you with a glomus tumor?
When it comes to this rare and complex finger tumor, it is important to find a surgeon who is well-versed in their treatment and who has seen many cases. Dr. Knight is one such surgeon, and he will bring his expertise to bear in your case, which will, no doubt, lead to a quick diagnosis after a long period of pain that has been difficult to diagnose.
What percentage of glomus tumors are solitary?
Most of the nodules are solitary but can occur in clusters. Glomus Tumors represent 1 to 5% of all soft tissue tumors in the hand and fingers.
Do you have to have surgery to remove a glomus tumor?
Do I have to have surgery to get rid of a glomus tumor?#N#Unfortunately, due to the nature of glomus tumors and what they are made of, as well as where they are and how they are connected to the body’s surrounding tissues, surgery is the only viable option when it comes to having them removed. In the case of fingers, where they most commonly occur on hands, it is very important that the doctor carefully outline the area of the tumor so that the incision is done precisely and carefully, and the surrounding tissues are not excised in addition to the body of the tumor. Complete removal of the glomus body is key to making sure that the tumor doesn’t recur.
What is a glomus tumor?
Glomus tumors (also called paragangliomas) are a rare, slow-growing, and usually benign type of skull base tumor that often develop near the inner ear. Without treatment, they can harm surrounding tissue, damage nerves, and cause other serious problems. Duke’s skull base tumor experts collaborate to diagnose your tumor and offer a range of the most effective and advanced therapies available. Our goal is to treat the tumor while minimizing any injury to the surrounding structures.
How to diagnose a glomus tumor?
Glomus tumors are usually diagnosed with MRI or CT scans. These scans also help identify additional glomus tumors that may be present.
What are the symptoms of a glomus tumor?
One of the most common symptoms of glomus tumors is hearing your heartbeat in your ears, which doctors call pulsatile tinnitus. Other symptoms include hearing loss, voice changes, and problems with swallowing.
How to embolize a tumor?
If your tumor is large, you may need an endovascular procedure a few days before surgery to embolize -- cut off the blood supply to -- the tumor. During this minimally invasive procedure, a surgeon makes a small incision and inserts a thin catheter into a major artery (usually in the groin). The catheter is threaded to the tumor site. Then, through the catheter, your surgeon uses tiny tools to block key blood vessels that feed the tumor.
Where is Glomus tympanicum located?
Glomus tympanicum, located in the middle ear. These are usually very small.
What is the treatment for a tumor?
Radiation oncologists use radiation treatments and stereotactic radiation therapy to target the tumor and shrink it. Radiation may be recommended before surgery, after surgery, or alone.
Where are glomus tumors found?
Glomus tumors are usually solitary and small lesions. The vast majority are found in the hand, wrist, foot, and under the fingernails. They are often painful, and the pain is reproduced when the lesion is placed in cold water. Multiple tumors are less likely to be painful.
What is the size of a glomus tumor?
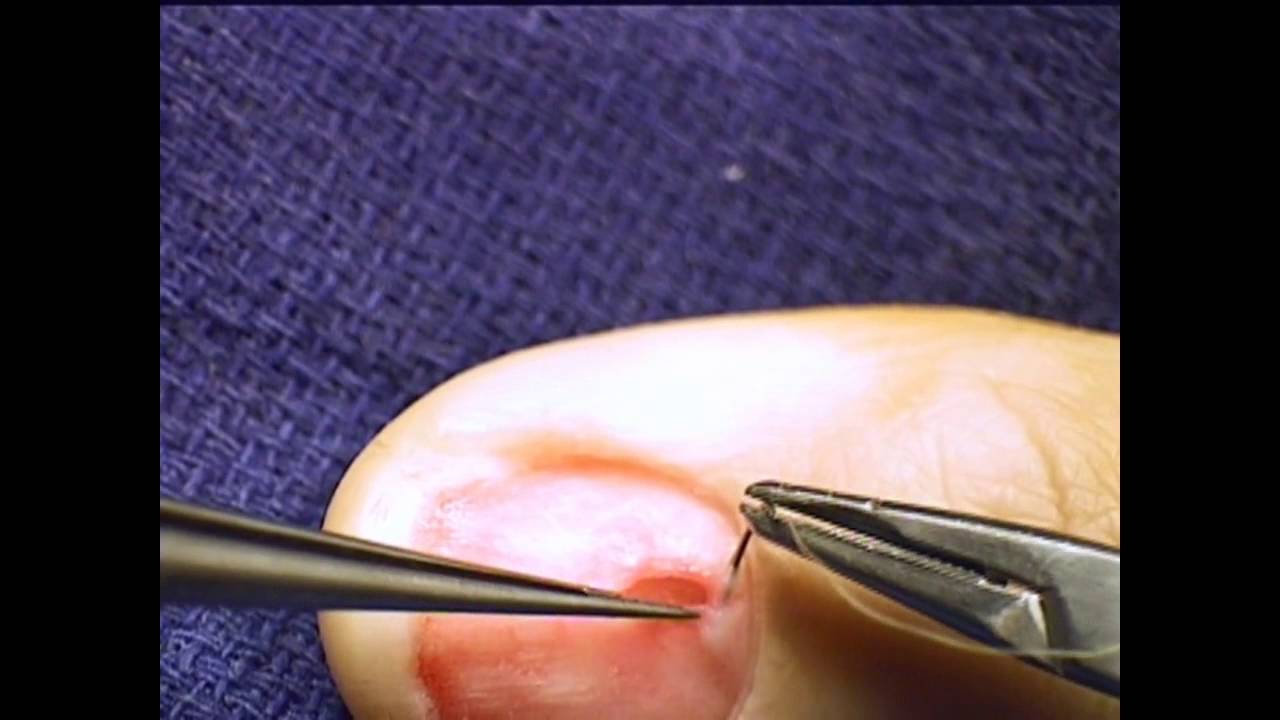
The tumor is the translucent oblate spheroid in the center of the incision, approximate horizontal dimension is 4 millimeters. Surgical excision is the preferred treatment for benign glomus tumors.
What are the criteria for glomus tumor diagnosis?
Criteria for the diagnosis of malignancy in glomus tumors are: Tumor size of more than 2 centimeters and subfascial or visceral location. Atypical mitotic figures. Marked nuclear atypia and any level of mitotic activity. Pericytes of Zimmerman.
How often do glomus tumors occur?
Solitary glomus tumors are more frequent in adults than in others. Multiple glomus tumors develop 11–15 years earlier than single lesions; about one third of the cases of multiple tumors occur in those younger than 20 years. Congenital glomus tumors are rare; they are plaguelike in appearance and are considered a variant of multiple glomus tumors.
Where does a malignant glomus tumor come from?
Another report of a malignant glomus tumor ( glomangiosarcoma) with metastases from the skin. A malignant glomus tumor one arose from the kidneys.
What is glomangioma inherited?
Familial glomangiomas have been associated with a variety of deletions in the GLMN ( glomulin) gene, and are inherited in an autosomal dominant manner, with incomplete penetrance.
Is a glomus tumor benign?
The majority of glomus tumors are benign, but they can also show malignant features. Glomus tumors were first described by Hoyer in 1877 while the first complete clinical description was given by Masson in 1924. Histologically, glomus tumors are made up of an afferent arteriole, anastomotic vessel, and collecting venule.
