What is glutamic acid?
Glutamic acid is an acidic amino acid that is essential for the biosynthesis of different kinds of proteins in living beings. Glutamic acid is one of the non-essential amino acids that can be synthesized in the body, but it is the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter in the vertebrate nervous system.
Is glutamic acid ionic or cation?
Glutamic acid is a zwitterionic amino acid with pKa values of 2.19, 4.25 and 9.67 (3) which indicates glutamic acid will exist almost entirely in ionic form (anion, cation or both) at pH values of 5 to 9 and, therefore, volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process (SRC).
What are aspartic acid and glutamic acid?
These are aspartic acid or aspartate (Asp) and glutamic acid or glutamate (Glu). Their side chains have carboxylic acid groups whose pKa's are low enough to lose protons, becoming negatively charged in the process.
Are amino acids acidic or basic?
Acidic and Basic Amino Acids. There are three amino acids that have basic side chains at neutral pH. These are arginine (Arg), lysine (Lys), and histidine (His). Their side chains contain nitrogen and resemble ammonia, which is a base.
See more

Is glutamic acid Basic?
At a pH inferior to their pK, the lysine, arginine and histidine side chains accept an H+ ion (proton) and are positive charged. They are therefore basic....Charged side chains.Amino acidpK of the side chain groupGlutamic acid4.2Lysine10.5Arginine12.5Histidine6.01 more row
Is glutamic acid an acid or base?
Two amino acids have acidic side chains at neutral pH. These are aspartic acid or aspartate (Asp) and glutamic acid or glutamate (Glu). Their side chains have carboxylic acid groups whose pKa's are low enough to lose protons, becoming negatively charged in the process.
What is glutamic acid pH?
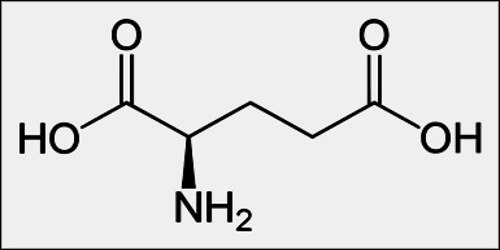
The Glutamic Acid Molecule. Symbol: Glu E. Molecular Weight: 147.13. Isolectric point (pH) 3.22. Molecular Formula: C 5H9NO4.
Is glutamic a basic amino acid?
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is non-essential in humans, meaning that the body can synthesize it....Glutamic acid.NamesSignal wordWarningHazard statementsH315 , H319 , H33543 more rows
Is glutamic acid glutamine?
Glutamine is a derivative of glutamic acid and is formed in the body from glutamic acid and ammonia in an energy requiring reaction catalyzed by glutamine synthase. It also possesses anticancer activity.
Is glutamic acid positive or negative?
There are four of them, two basic amino acids, lysine (Lys) and arginine (Arg) with a positive charge at neutral pH, and two acidic, aspartate (Asp) and glutamate (Glu) carrying a negative charge at neutral pH.
Which amino acid is most basic?
Histidine is the most basic amino acid in the given compound. This can be attributed to the fact that the histidine contains the most number of a basic nitrogen atom.
Which is more acidic aspartic acid or glutamic acid?
Glutamic Acid E (Glu) The pKa of the γ carboxyl group for glutamic acid in a polypeptide is about 4.3, significantly higher than that of aspartic acid. This is due to the inductive effect of the additional methylene group.
Which amino acid is a basic amino acid?
Amino acids with positively charged side chains include the basic amino acids histidine, lysine, and arginine. Histidine is only weakly charged at physiologic pH. In contrast, amino acids with negatively charged side chains are acidic, and include glutamic and aspartic acids (which exist as glutamate and aspartate).
Is glutamic acid charged?
Substitutions: Glutamate (or Glutamic acid) is a negatively charged, polar amino acid.
What is the difference between acidic and basic amino acids?
In conclusion and to summarize: the difference between acidic and basic amino acids is the same as between any acid and base in chemistry and chemical substances. Their similarities still include being polar amino acids, as well as hydrophilic amino acids, and, of course, the biggest thing they have in common is that they're all still amino acids, ...
What are some examples of acidic acid?
Acids lose their acidity when combined with alkalis. Examples are: citric acid (lemon juice), acetic acid (vinegar), stomach acid, and battery acid. Bases. pH level: greater than (>7) Bases that can dissolve in water are also known as alkalis, or alkaline substances. Alkalis are caustic.
What are the nonessential amino acids?
Your nonessential amino acids are the amino acids your body can create on its own as a byproduct of normal functioning. There are 11 of these amino acids, and they include the following: Alanine (ala) Arginine (arg) Asparagine (asn) Aspartic acid (asp) Cysteine (cys) Glutamic acid (glu) Glutamine (gln)
Why are amino acids classified as basic amino acids?
These basic amino acids are so classified because they have basic side chains containing nitrogen, which resemble ammonia (a base). The pKa values of basic amino acids are high enough to bind protons and give them a positive charge.
What are the three molecular structures of amino acids?
Each amino acid is made of a central alpha carbon atom (Cα), and attached to that central atom are three molecular structures, also known as functional groups: one is a carboxyl group (-COOH), the second is an amino group (-NH2), and the third is a single hydrogen atom (H). This is the same structure of all amino acids, ...
Why do amino acids matter?
Though some are essential and some nonessential, the reason amino acids matter, and the reason that all these tiny permutations matter, is because without each of them working together, our health and well-being would fail. We at Amino Co. have developed amino acid supplements specifically because we understand their vital importance to human life. The chemistry behind each person's daily concert of amino acids is the science that drives our passion.
How are amino acids delivered?
Amino acids can be delivered either by intravenous infusion or oral ingestion. Both routes support protein metabolism in the body, as well as provide amino acids for other purposes. But what are the advantages and disadvantag ...
What are acidic amino acids?
Acidic amino acids are those amino acids that have a carboxylic acid group on their side chains at neutral pH, resulting in acidic properties in the molecule. Acidic amino acids have an additional carboxylic group (COOH) in addition to the one present on the linear chain. These types of amino acids have acidic properties and, thus, ...
What is the amino acid?
The amino acid consists of two carboxylic acid groups and a single amino group. The amino acid can lose a proton from the carboxylic group present on the side chain to form a glutamate anion. Glutamic acid is involved in the biosynthesis of proteins, and it can be tasted when present in an unbound form.
What is aspartic acid?
Aspartic acid is essential for the synthesis of other amino acids that play essential roles in processes like urea and citric acid cycles. Amino acids like lysine, methionine, isoleucine, and arginine are synthesized from aspartic acid.
What are the amino acids that have a carboxylic acid group on their side chains?
Acidic amino acids are those amino acids that have a carboxylic acid group on their side chains at neutral pH, resulting in acidic properties in the molecule. Basic amino acids are those amino acids that have an amino group on their side chains at neutral pH, resulting in basic or alkaline properties in the molecule. Side Chain.
What are the three amino acids that make up the arginine group?
There are three amino acids that belong to this group; arginine, histidine, and lysine.
What is the charge of amino acids at pH?
This results in the overall charge of -1.
Which amino acid has a negative charge?
Acidic amino acids have a negative charge in their side chain. Basic amino acids have a positive charge in their side chain. Examples of acidic amino acids are aspartic acid and glutamic acid. Examples of basic amino acids are histidine, lysine, and arginine.
Which amino acids have acidic side chains?
Two amino acids have acidic side chains at neutral pH. These are aspartic acid or aspartate (Asp) and glutamic acid or glutamate (Glu). Their side chains have carboxylic acid groups whose pKa's are low enough to lose protons, becoming negatively charged in the process.
What pH do deprotonated amino acids predominate?
For these amino acids, the deprotonated forms predominate at physiological pH (about 7). Click on the Protein 1 icon at left to see a chart of all the amino acids, classified according to the chemistry of their side chains. See if you can tell why each amino acid has been sorted in that way.
What are the basic amino acids?
Basic amino acids are those with a positive R Group or chain and the include Arginine, histidine and Lysine acid. Below are more details on these three (3) Acidic Amino acids:
What are the two amino acids that have a negative R group?
Acidic amino acids are those with a negative R Group or chain and the include aspartic acid and glutamic acid. Below are more details on these two (2) Acidic Amino acids:
Why are amino acids important?
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins and thus, are very important for the overall health and survival of an individual. Amino acids can be classified based on a number of different types and classifications. These different types or classifications of amino acids are determined by their specific functional groups and these functional groups gives the amino acids their unique properties such as being polar, aromatic, charged or aliphatic. Another property determined by the functional groups of amino acids would be whether or not they are acidic or basic. In this article, we will look at the different acidic and basic amino acids and how they affect the overall health of individuals.
Does amino acid help with hypertension?
Health Benefits: This amino acid has been shown to help protect the heart, decrease blood pressure for better management of hypertension, serve as the body’s antioxidant, decrease the inflammation being experienced by the body, help patients with type 2 diabetes, decrease chances of being obese through the suppression of appetite, protect the skin against the harmful effects of the sun, enhance brain function, aid in preventing blood clots, assist in possibly lessening the instances of seizures and even protect the eyes.
Is aspartic acid safe to take?
Things to Consider: Individuals who wish to take aspartic acid as a form of supplement should be aware that there are limited to no studies available for the safe dosage and drug interactions of aspartic acid supplements. As such, it is best to first coordinate the regular use of aspartic acid with a medical professional.
Does glutamic acid help with irritable bowel syndrome?
Health Benefits: Glutamic acid has been shown to improve gastrointestinal health and address issues such as IRS or irritable bowel syndrome, helps in addressing ulcers and leaky gut, may aid in boosting brain health, promote muscle growth and prevent muscle breakdown, enhance athletic performance, enables the body’s recovery from injuries and physical activities, aid the body in burning fat and help manage sugar levels.
Is amino acid acidic or acidic?
Amino acids can generally be either positively charged, negatively charged or neutral/ uncharged. In addition, amino acid side chains can also have a specific charge and those with a positive charge tend to be basic such as arginine, histidine and lysine. Side chains with a negative charge such as aspartic acid and glutamic acid, tend to be acidic.