How do you determine the phenotype of an individual?
The phenotype is determined by an individual’s genotype and expressed genes or by visible trait, for instance, hair colour or type, eye colour body shape, and height. It depends on the genotype but also influenced by the factors in the environment.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
The genotype is the genetic basis of an organism. It consists of all the genetic information that determines the characteristics of organisms. The phenotype is the observable expression of these genes. The environment influences the phenotype.
What is an example of genotype in biology?
Genotype refers to the genetic basis of an organism. The DNA that we are born with is an example of a genotype. The genotype is critical to developing the phenotype, but the environmental forces that determine the phenotype can often cause even genetically identical people (like identical twins) to have significant differences.
What is the genotype of human pigmentation?
Genotype versus phenotype: human pigmentation The natural range of hair and skin colour is a continuous spectrum, controlled by multiple genes in a complex fashion. Many of these genes are as yet unknown, but several key pigmentation genes have been characterised, in particular the melanocortin 1 receptor gene (MC1R).

Is hair type a phenotype?
A phenotype is your version of a trait. Like curly vs straight hair. An allele is the term geneticists use to refer to a version of a gene. For example, a hair texture gene might come in two versions: curly or straight.
Is hair an example of genotype?
Other examples of genotype include: Hair color. Height.
Is hair color a phenotype or genotype?
phenotypeHair color is a genetic and physiologically complex phenotype, which represents one of the most visible variations within humans and between populations [1].
What is a phenotype vs genotype?
A person's genotype is their unique sequence of DNA. More specifically, this term is used to refer to the two alleles a person has inherited for a particular gene. Phenotype is the detectable expression of this genotype – a patient's clinical presentation.
What are 3 examples of phenotypes?
In humans, phenotype examples include earwax type, height, blood type, eye color, freckles, and hair color. And phenotypes aren't just physical traits. Behavior is also considered a phenotype.
What are the 3 phenotypes?
Polygenic inheritance can be explained by additive effects of many loci: if each "capital" allele contributes one increment to the phenotype. With one locus and additive effects we have three phenotypic classes: AA, Aa and aa.
What's an example of a phenotype?
Examples of phenotypes include height, wing length, and hair color. Phenotypes also include observable characteristics that can be measured in the laboratory, such as levels of hormones or blood cells.
What are the 3 types of genotypes?
There are four hemoglobin genotypes (hemoglobin pairs/formations) in humans: AA, AS, SS and AC (uncommon)....There are four blood GROUPS:Type A (marker A)Type B (marker B)Type AB (blood cells have both A and B markers)Type O (blood cells have neither A or B markers)
Which of the following is a phenotype?
Phenotype refers to an individual's observable traits, such as height, eye color and blood type. A person's phenotype is determined by both their genomic makeup (genotype) and environmental factors.
What's an example of a genotype?
Definition. A genotype is a scoring of the type of variant present at a given location (i.e., a locus) in the genome. It can be represented by symbols. For example, BB, Bb, bb could be used to represent a given variant in a gene.
What are the 5 types of genotype?
A blood genotype indicates the genetic makeup of an individual's blood in its entirety. Typically, there are five (5) distinct types of blood genotype. They are AA, AS, AC, SS, and SC.
How do you determine a phenotype?
To find a phenotypic ratio, we look at the alleles of the parent organisms and estimate how often those genes will be exhibited by the offspring. Most times, we know what the alleles will express and how they will look.
What is an example of genotype?
Definition. A genotype is a scoring of the type of variant present at a given location (i.e., a locus) in the genome. It can be represented by symbols. For example, BB, Bb, bb could be used to represent a given variant in a gene.
What are the 5 types of genotype?
A blood genotype indicates the genetic makeup of an individual's blood in its entirety. Typically, there are five (5) distinct types of blood genotype. They are AA, AS, AC, SS, and SC.
What are the 4 types of genotypes?
There are four hemoglobin genotypes (hemoglobin pairs/formations) in humans: AA, AS, SS and AC (uncommon)....There are four blood GROUPS:Type A (marker A)Type B (marker B)Type AB (blood cells have both A and B markers)Type O (blood cells have neither A or B markers)
What are the 3 types of genotypes?
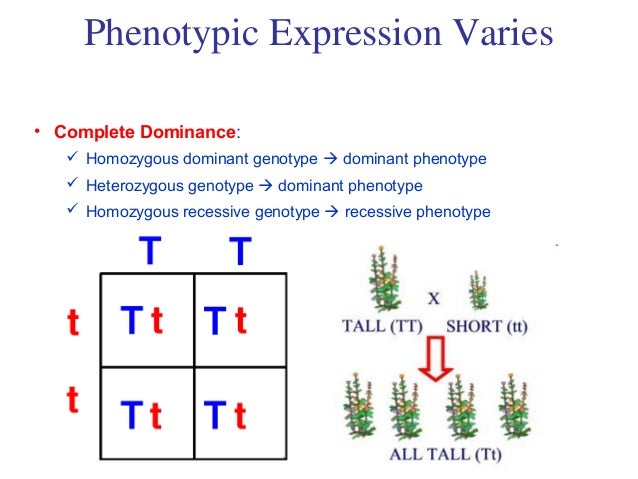
The different types of genotypes are- homozygous recessive (pp), homozygous dominant (PP), and heterozygous (Pp).
What are the genes that control hair and skin color?
Many of these genes are as yet unknown, but several key pigmentation genes have been characterised, in particular the melanocortin 1 receptor gene (MC1R). Here, the function and known mutations of MC1R and other human pigmentation genes including ASIP, MATP, SLC24A5, TYR, TYRP1 and OCA2 are outlined, and a forensic test based on MC1R SNPs presented. The forensic utility of this and potential future genetic tests for phenotypic traits are discussed, in the light of the extensive debate on the ethics of predicting phenotypic traits from crime scene samples.
What is the natural range of hair and skin color?
The natural range of hair and skin colour is a continuous spectrum, controlled by multiple genes in a complex fashion. Many of these genes are as yet unknown, but several key pigmentation genes have been characterised, in particular the melanocortin 1 receptor gene (MC1R). Here, the function and kno …
How are genotype and phenotype related?
Genotype and phenotype are two different concepts but are closely related to each other. Phenotype refers to the physical traits that are observed in an organism which are the outcome of the expression of the genes of an individual. The genotype determines the phenotype of an individual.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
The genotype is a set of genes in DNA responsible for unique trait or characteristics while the phenotype is the physical appearance or characteristic of an organism.
What is the phenotype of an organism?
What is meant by phenotype? The physical characteristics of an organism which are the outcome of the interaction of the genotype with the environment are known as the phenotype. It depends upon the genes which are dominant. Shape. size, colour, the behaviour is the phenotype of an organism.
How is phenotype determined?
The phenotype is determined by an individual’s genotype and expressed genes or by visible trait, for instance, hair colour or type, eye colour body shape, and height. It depends on the genotype but also influenced by the factors in the environment.
What are the different types of genotypes?
The different types of genotypes are- homozygous recessive (pp), homozygous dominant (PP), and heterozygous (Pp). The homozygous dominant and the heterozygous genotypes show the same phenotypes.
What is the hereditary information of an organism in the form of gene in the DNA and remains the same throughout the?
Phenotype. The hereditary information of the organism in the form of gene in the DNA and remains the same throughout the life. The characters of an organism which are visible are known as phenotypes. Same genotype produces same phenotype. Same phenotype may or may not belong to same genotype. Present inside the body as genetic material.
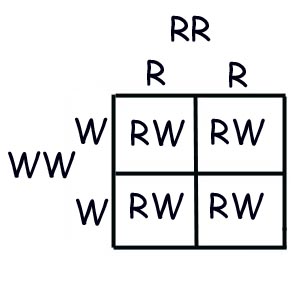
How to identify genotype?
A genotype can be identified by a Punnet square. It helps in determining the probability of the genotype of an offspring based on the genotype of the parents.