
How do you know if hepatitis B is acute or chronic?
If you test positive for HBsAg for longer than six months, it means you have a chronic hepatitis B infection. But, if you no longer test positive (or “reactive”) for HBsAg after six months and you develop hepatitis B surface antibodies (HBsAb), then you have cleared hepatitis B after an “acute” infection.
Is hepatitis B considered chronic?
For some people, hepatitis B infection becomes chronic, meaning it lasts more than six months. Having chronic hepatitis B increases your risk of developing liver failure, liver cancer or cirrhosis — a condition that permanently scars of the liver.
Which hepatitis is acute and chronic?
If you have the hepatitis C virus in your blood for anywhere from a few weeks to a few months, you have “acute” hep C. After 6 months, it's called “chronic.” Without diagnosis and treatment, chronic hep C can remain for many years and lead to serious symptoms like liver damage.
Which hepatitis is chronic?
Long-term infection with the hepatitis C virus is known as chronic hepatitis C. Chronic hepatitis C is usually a "silent" infection for many years, until the virus damages the liver enough to cause the signs and symptoms of liver disease.
Does acute hepatitis B go away?
The acute illness most often goes away after 2 to 3 weeks. The liver most often returns to normal within 4 to 6 months in most people. Almost all newborns and about one half of children who get hepatitis B develop the chronic condition. Very few adults who get the virus develop chronic hepatitis B.
How long does acute hepatitis B last?
When symptoms of acute hepatitis B occur, how long do they usually last? Symptoms typically last for several weeks but can persist for up to 6 months (6,12).
How do you get acute hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is spread when blood, semen, or other body fluid infected with the hepatitis B virus enters the body of someone who is not infected or has not been vaccinated. People can become infected with the virus from: Birth (spread from a mother who has hepatitis B to her baby during birth)
Can hepatitis B become negative?
Sometimes a negative test result can indicate a mutant hepatitis B virus is present. So, the absence of e-Antigen does not always mean there is little or no active viral replication. The doctor can confirm with additional tests.
How long does hepatitis B take to damage the liver?
Seventy percent of carriers develop chronic persistent hepatitis B. Most do not appear to be ill. The remaining 30 percent of carriers experience continuous liver disease. This condition often progresses to cirrhosis and then, after 30 to 40 years, possibly to liver cancer.
Can chronic hepatitis B cured?
Currently there is no complete cure for chronic hepatitis B. However, several effective treatment options can reduce the risk of liver damage and slow down or stop the virus from spreading.
How do you get chronic hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is spread when blood, semen, or other body fluids from a person infected with the virus enters the body of someone who is not infected. This can happen through sexual contact; sharing needles, syringes, or other drug-injection equipment; or from mother to baby at birth.
How is chronic hepatitis B treated?
Current treatments for chronic hepatitis B fall into two general categories: Immunomodulator Drugs - These are drugs that boost the immune system to help control the hepatitis B virus. They are given as injections over 6 months to 1 year.
Can hepatitis B be cured totally?
There's no cure for hepatitis B, but there are several treatments that can help you with managing your symptoms and lowering your risk of long-term health problems, such as cirrhosis. If you have hepatitis B, try to get in for a blood test every 6 months or so to monitor your viral load and liver health.
Will I always test positive for hepatitis B?
Most adults who acquire HBV clear the virus within a few months, and their hepatitis B surface antigen test result will be negative after that time. Some people remain infected and continue to test positive for hepatitis B surface antigen.
How do you know if you have chronic hepatitis?
People who test positive for the hepatitis B virus for more than six months (after their first blood test result) are diagnosed as having a chronic infection.
How is chronic hepatitis B diagnosed?
Blood tests can detect signs of the hepatitis B virus in your body and tell your doctor whether it's acute or chronic. A simple blood test can also determine if you're immune to the condition. Liver ultrasound. A special ultrasound called transient elastography can show the amount of liver damage.
What is it called when you get hepatitis B?
When a person is first infected with the hepatitis B virus, it is called an " acute infection " (or a new infection). Many people are able to naturally get rid of an acute infection.
How long does hepatitis B last?
If you are newly infected with hepatitis B, your infection is considered acute. An acute hepatitis B infection may last up to six months and you may pass the virus to others during this time.
What is the rarest condition that can occur with a new acute infection?
A rare, life-threatening condition called “fulminant hepatitis” can occur with a new acute infection and requires immediate, urgent medical attention since a person can go into sudden liver failure.
Can you live with hepatitis B?
The good news is that most people with chronic hepatitis B should expect to live a long and healthy life.
Can chronic liver infections cause cancer?
Acute infections have few, if any, lasting effects. People with chronic infections are at greater risk for developing serious liver diseases, including cirrhosis and liver cancer, and should take precautions to keep their liver healthy.
How long does hepatitis B last?
Chronic hepatitis B infection lasts six months or longer. It lingers because your immune system can't fight off the infection. Chronic hepatitis B infection may last a lifetime, possibly leading to serious illnesses such as cirrhosis and liver cancer.
How long does hepatitis B go undetected?
Chronic infection may go undetected for decades until a person becomes seriously ill from liver disease.
What are the complications of HBV?
Complications. Having a chronic HBV infection can lead to serious complications, such as: Scarring of the liver (cirrho sis). The inflammation associated with a hepatitis B infection can lead to extensive liver scarring (cirrhosis), which may impair the liver's ability to function. Liver cancer.
How does HBV spread?
Sharing of needles. HBV easily spreads through needles and syringes contaminated with infected blood. Sharing IV drug paraphernalia puts you at high risk of hepatitis B. Accidental needle sticks.
How to avoid HBV?
Other ways to reduce your risk of HBV include: Know the HBV status of any sexual partner. Don't engage in unprotected sex unless you're absolutely certain your partner isn't infected with HBV or any other sexually transmitted infection.
What to do if you think you have hepatitis B?
If you think you have signs or symptoms of hepatitis B, contact your doctor.
Can hepatitis B be recovered?
Most adults with hepatitis B recover fully, even if their signs and symptoms are severe. Infants and children are more likely to develop a chronic (long-lasting) hepatitis B infection.
How long does hepatitis B last?
Hepatitis B is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus. Some people with hepatitis B are sick for only a few weeks (known as “acute” infection), but for others, the disease progresses to a serious, lifelong illness known as chronic hepatitis B.
How long does hepatitis B last outside the body?
The hepatitis B virus can survive outside the body for at least 7 days. During that time, the virus is still capable of causing infection.
How many people have hepatitis B in 2018?
CDC estimates the actual number of acute hepatitis B cases was closer to 21,600 in 2018. Many more people (about 862,000 ) are estimated to be living with chronic, long-term hepatitis B.
How long does it take for hepatitis B to show symptoms?
Acute hepatitis B is a short-term illness that occurs within the first 6 months after someone is exposed to the hepatitis B virus. Some people with acute hepatitis B have no symptoms at all or only mild illness. For others, acute hepatitis B causes a more severe illness that requires hospitalization.
When should the next hepatitis B shot be given?
If the hepatitis B vaccine series is interrupted, the next dose should be given as soon as possible. The first dose (s) does not need to be repeated.
What is the most common cause of hepatitis?
Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. When the liver is inflamed or damaged, its function can be affected. Heavy alcohol use, toxins, some medications, and certain medical conditions can all cause hepatitis. However, hepatitis is often caused by a virus. In the United States, the most common hepatitis viruses are hepatitis A virus, hepatitis B virus, and hepatitis C virus.
Can you take hepatitis B medication indefinitely?
However, not every person with chronic hepatitis B needs medication, and the drugs may cause side effects in some patients. People who start hepatitis B treatment may need to take medication indefinitely because these medications do not lead to a cure.
Background
Hepatitis B is a disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) that can be self-limited for some and lifelong for others. HBV is transmitted through the blood or bodily fluids of an infected person.
Cases and Clusters of Potential Public Health Importance
Jurisdictions should review and analyze hepatitis B data regularly to identify cases and clusters of hepatitis B that merit further investigation. When resources are limited, these should be prioritized for investigation based on the degree of public health importance. The following are examples of high priority cases and clusters:
Interpretation of Laboratory Test Results
A description of hepatitis B laboratory markers can be found in Appendix B.
Recommended Reportable Laboratory Markers
The following laboratory markers are recommended for reporting to public health, as they can aid in case ascertainment, case classification, and monitoring care continua for hepatitis B:
Case Reporting and National Notification
Cases of acute, chronic, and perinatal hepatitis B, and hepatitis B during pregnancy should be reported to HDs as specified by state, territorial, or local regulations. Acute, chronic, and perinatal hepatitis B are nationally notifiable conditions ( 5 ).
Surveillance of Acute and Chronic Hepatitis B
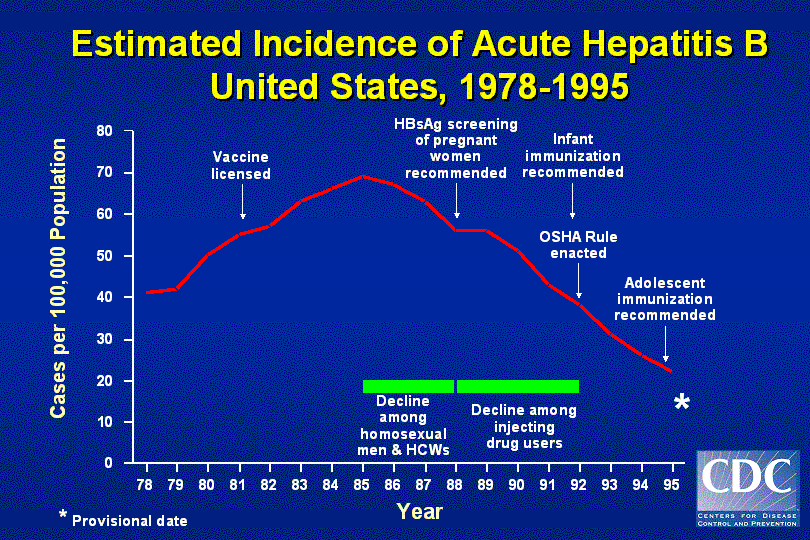
The national incidence of acute hepatitis B dramatically declined after incremental recommendations for vaccinating people at-risk for infection and severe outcomes were released beginning in 1982 ( 47) and for infants and children in 1991 ( 53 ).
Surveillance of Hepatitis B During Pregnancy and Perinatal Hepatitis B
Knowledge of a pregnant person’s HBV infection status is essential for preventing perinatal hepatitis B.
What is the acute form of hepatitis B?
When people get infected by the hepatitis B virus, they first contract the acute form of the infection, also referred to as the new infection. In some cases, symptoms may not even show up at the start, and the infected individual may be able to get relief from the virus without any complications. However, for some adults, the infection is not fully treated even with long-term medications, causing a more severe form of the infection, also known as chronic hepatitis B.
What is hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is an infection that could cause irreparable damage to the liver.
How long does it take for a hepatitis B shot to work?
If you have not received the necessary vaccines to protect you against the infection or if you are unsure whether you have received the vaccine or not, you need to have an injection that protects you against the hepatitis B virus called immune globulin, which works best when administered within 12 hours of being exposed to the virus.
How long does hepatitis B last?
The acute form of hepatitis B normally lasts up to six months, and it can be present in a person with or without any symptoms.
What are the three types of hepatitis?
The hepatitis viruses have three types, namely, A, B, and C. While all three can cause complications of the liver, hepatitis B and C are considered to be the most severe. Hepatitis B can cause a potentially fatal infection if left untreated.
What is the best diet for hepatitis?
Diet plays a key role in the recovery process. A good, light diet is often recommended for patients suffering from hepatitis. It is important to take care of your diet since the liver is already weak due to the infection and should not be further stressed.
Is junk food good for hepatitis?
Hence, when recovering from a hepatitis infection, it is unhealthy to further strain the liver by consuming harmful products. You should stick to a junk-free diet until you completely recover from the infection.
Overview
- Hepatitis B is a serious liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). For some people, hepatitis B infection becomes chronic, meaning it lasts more than six months. Having chronic hepatitis B increases your risk of developing liver failure, liver cancer or cirrhosis — a condition that permanently scars of the liver. Most adults with hepat...
Symptoms
- Signs and symptoms of hepatitis B range from mild to severe. They usually appear about one to four months after you've been infected, although you could see them as early as two weeks post-infection. Some people, usually young children, may not have any symptoms. Hepatitis B signs and symptoms may include: 1. Abdominal pain 2. Dark urine 3. Fever 4. Joint pain 5. Loss of app…
Causes
- Hepatitis B infection is caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). The virus is passed from person to person through blood, semen or other body fluids. It does not spread by sneezing or coughing. Common ways that HBVcan spread are: 1. Sexual contact.You may get hepatitis B if you have unprotected sex with someone who is infected. The virus can pass to you if the person's blood, s…
Risk Factors
- Hepatitis B spreads through contact with blood, semen or other body fluids from an infected person. Your risk of hepatitis B infection increases if you: 1. Have unprotected sex with multiple sex partners or with someone who's infected with HBV 2. Share needles during IV drug use 3. Are a man who has sex with other men 4. Live with someone who has a chronic HBVinfection 5. Are …
Complications
- Having a chronic HBVinfection can lead to serious complications, such as: 1. Scarring of the liver (cirrhosis).The inflammation associated with a hepatitis B infection can lead to extensive liver scarring (cirrhosis), which may impair the liver's ability to function. 2. Liver cancer.People with chronic hepatitis B infection have an increased risk of liver cancer. 3. Liver failure.Acute liver fail…
Prevention
- The hepatitis B vaccine is typically given as three or four injections over six months. You can't get hepatitis B from the vaccine. The hepatitis B vaccine is recommended for: 1. Newborns 2. Children and adolescents not vaccinated at birth 3. Those who work or live in a center for people who are developmentally disabled 4. People who live with someone who has hepatitis B 5. Healt…