Symptoms
Hepatocelluar carcinoma, a type of liver cancer, is deadly. Even in the best-case scenario -- a localized tumor detected before it spreads from the liver -- the five-year survival rate is only 33 percent.
Causes
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver cancer Liver cancer begins in the cells of the liver. The most common form of liver cancer begins in cells called hepatocytes and is called hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer.
Prevention
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer. Hepatocellular carcinoma occurs most often in people with chronic liver diseases, such as cirrhosis caused by hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection.
Complications
What Is Hepatocellular Carcinoma? Hepatocellular carcinoma is a cancer that starts in your liver. It's different from "secondary" liver cancers, which have spread to the liver from other organs. If caught early, it can sometimes be cured with surgery or transplant.
How deadly is hepatocelluar carcinoma?
What is the most common type of hepatocellular cancer?
What is hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)?
What is hepatocellular carcinoma and how is it treated?
How long can you live with hepatocellular carcinoma?
Unfortunately, HCC is typically diagnosed late in its course, with a median survival following diagnosis of approximately 6 to 20 months. In the United States, 2 years survival is less than 50% and 5-year survival is only 10%.
Is hepatocellular carcinoma curable?
Since HCC usually grows slowly in its early stages, it can often be cured if discovered early enough.
Is hepatocellular carcinoma life-threatening?
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common form of liver cancer. It is a serious illness that can be life-threatening. If it diagnosed early, hepatocellular carcinoma can be treated with surgery to remove the cancerous tumor or with a liver transplant.
Is hepatocellular carcinoma a terminal?
Among HCC patients, 15–20% present with end stage or terminal stage HCC. Their median survival is less than 3–4 months.
How aggressive is hepatocellular carcinoma?
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an aggressive malignancy, resulting as the third cause of death by cancer each year. The management of patients with HCC is complex, as both the tumour stage and any underlying liver disease must be considered conjointly.
How does hepatocellular carcinoma cause death?
Background: Most cases of HCC are associated to liver cirrhosis. Tumor extension and liver failure may be competing causes of death in these patients.
What is the best treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma?
Chemotherapy. Systemic chemotherapy remains the mainstay of therapy for patients with advanced HCC who are not candidates for surgical resection, liver transplantation, or localized tumor ablation.
How do you get hepatocellular carcinoma?
Hepatocellular carcinoma occurs most often in people with chronic liver diseases, such as cirrhosis caused by hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection.
How long does it take for HCC to develop?
It takes 10 years to develop chronic hepatitis, 20 years to develop cirrhosis and 30 years to develop HCC which explains why it usually affects patients in the 50–70-year age group [12]. Macroscopically, HCC can be solitary or multifocal, nodular or diffuse.
How painful is hepatocellular carcinoma?
Pain has long been a significant concern for HCC patients and their clinicians; it may manifest as abdominal pain, metastatic bone pain, or in some cases, pain related to LRT. More than 80% of patients who develop HCC have underlying liver disease or cirrhosis,5 creating special challenges for pain management.
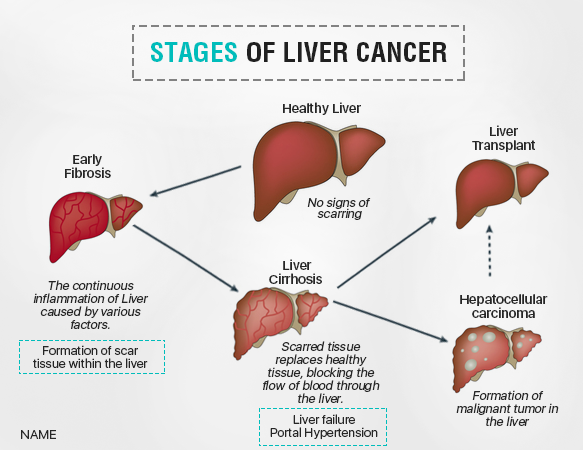
What are the stages of hepatocellular carcinoma?
Based on these variables, patients are classified into three stages (I: not advanced; II: moderately advanced; III: very advanced) with different outcomes [Table 2]. Okuda staging system was accepted and widely used as an improved classification system for HCC.
Who is at risk for hepatocellular carcinoma?
Major risk factors for HCC include chronic alcohol consumption, hepatitis B, hepatitis C and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [3]. Other, less common causes are Wilson's disease, hereditary hemochromatosis, alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency, primary biliary cirrhosis and autoimmune hepatitis [4, 5].
Does hepatocellular carcinoma spread quickly?
Liver cancer can spread quickly depending on the type of cancer. Hemangiosarcoma and angiosarcoma types of liver cancer are fast spreading, whereas hepatocellular carcinoma spreads late in the disease.
What is the most common cause of hepatocellular carcinoma?
Hepatocellular carcinoma occurs most often in people with chronic liver diseases, such as cirrhosis caused by hepatitis B or hepatitis C infection.
Where does hepatocellular carcinoma spread to?
HCC commonly metastasises to lungs, lymph nodes, adrenal gland and bones, including the skull. The overall prognosis of patients with metastatic HCC is poor.
How quickly does HCC progress?
It takes 10 years to develop chronic hepatitis, 20 years to develop cirrhosis and 30 years to develop HCC which explains why it usually affects patients in the 50–70-year age group [12].
What is hepatocellular carcinoma?
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is cancer in your liver. Although it is a life-threatening illness, catching it early can mean successful treatment with surgery or a liver transplant. Other treatments focus on easing your symptoms and helping you to live longer. People at risk for hepatocellular carcinoma should have regular checks for signs of cancer.
What age is more likely to develop hepatocellular carcinoma?
Men ages 60 and older are more likely to develop hepatocellular carcinoma than women and younger men.
What is the most common form of liver cancer?
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common form of liver cancer. It is a serious illness that can be life-threatening. If it diagnosed early, hepatocellular carcinoma can be treated with surgery to remove the cancerous tumor or with a liver transplant. Other treatments can shrink the tumor or slow its growth and relieve your symptoms. Hepatocellular carcinoma is linked to cirrhosis of the liver and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD ). People who have cirrhosis or NAFLD should be regularly checked for signs of hepatocellular carcinoma.
How long does it take for hepatocellular carcinoma to grow?
In the beginning, hepatocellular carcinoma grows very slowly. It can take years before you notice any symptoms. Hepatocellular carcinoma growth speeds up as it progresses.
How to cure a tumor in the liver?
Surgery to remove your tumor or a liver transplant are the best options for a cure. If surgery is not an option, there are other treatments to ease your symptoms, slow the tumor’s growth and help you to live longer.
When were you born with hepatitis C?
You were born from 1945 through 1965. Most people in the United State who have hepatitis C were born in these years.
Can you get hepatocellular cancer if you smoke?
If you have or have had any of these illnesses, talk to your healthcare provider about being screened for hepatocellular cancer. If you smoke, have obesity or drink a lot of alcohol, your provider can help you improve your health and decrease your risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
What is the treatment for liver cancer at Johns Hopkins?
Treatment options include surgical resection (removal) and liver transplantation.
What happens if you have a biopsy of your liver?
If the results from other procedures are unclear, your doctor may order a biopsy. During a biopsy, liver tissue is removed and is sent to a pathology lab to determine whether the tissue is cancerous.
Can liver cancer be detected?
Liver cancer is frequently detected during a screening for an underlying disease. Patients often complain of symptoms related to a liver disease, and upon investigation, the cancer is discovered.
Does liver cancer respond to radiation?
Although chemotherapy and radiation therapy are common treatment choices for cancer, liver cancer does not respond to those therapies. Learn more about liver cancer treatment at Johns Hopkins.
Can a liver biopsy be done without a biopsy?
A liver biopsy offers a definitive diagnosis but may not be necessary. If your AFP level is significantly elevated and your doctor sees a tumor on an imaging scan, then a diagnosis can be made without a biopsy. If the results from other procedures are unclear, your doctor may order a biopsy.
What is hepatocellular carcinoma?
Hepatocellular carcinoma is a cancer that starts in your liver. It's different from "secondary" liver cancers, which have spread to the liver from other organs.
What is the substance that causes hepatocellular carcinoma?
Aflatoxin. This harmful substance, which is made by certain types of mold on peanuts, corn, and other nuts and grains, can cause hepatocellular carcinoma. The U.S. has safety measures that limit aflatoxin in the food supply.
What is the cause of liver damage?
This serious disease happens when liver cells are damaged and replaced with scar tissue. Many things can cause it: hepatitis B or C infection, alcohol drinking, certain drugs, and too much iron stored in the liver.
How to remove liver tissue?
This can be done several ways. In one method, your doctor removes some liver tissue with a needle that they place through your skin and into your liver. They numb the area first so you won't feel pain.
How to do a biopsy of the liver?
Your doctor may also do a biopsy by making a small cut in your belly and putting a needle into the liver to pull out a sample of tissue. You'll get anesthesia first, so you won't be awake while this is going on.
How many alcoholic drinks a day can cause cancer?
Heavy drinking. Having more than two alcoholic drinks a day for many years raises your risk of hepatocellular cancer. The more you drink, the higher your risk.
What is the best way to find a tumor in the liver?
Your doctor may ask you to get an ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to look for tumors in your liver. An ultrasound creates images of your liver with sound waves. A CT scan is a powerful X-ray that makes detailed pictures inside your body. An MRI uses strong magnets and radio waves to make an image of your liver.
What causes hepatocellular carcinoma?
Hepatocellular carcinoma, like any other cancer, develops when epigenetic alterations and mutations affecting the cellular machinery cause the cell to replicate at a higher rate and/or result in the cell avoiding apoptosis.
What are the four architectural and cytological types of hepatocellular carcinoma?
Microscopically, the four architectural and cytological types (patterns) of hepatocellular carcinoma are: fibrolamellar, pseudoglandular ( adenoid ), pleomorphic (giant cell), and clear cell. In well-differentiated forms, tumor cells resemble hepatocytes, form trabeculae, cords, and nests, and may contain bile pigment in the cytoplasm. In poorly differentiated forms, malignant epithelial cells are discohesive, pleomorphic, anaplastic, and giant. The tumor has a scant stroma and central necrosis because of the poor vascularization. A fifth form – lymphoepithelioma like hepatocellular carcinoma – has also been described.
What is the most common type of liver cancer?
Hepatocellular carcinoma ( HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer in adults and is currently the most common cause of death in people with cirrhosis. HCC is the third leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. It occurs in the setting of chronic liver inflammation, and is most closely linked to chronic viral hepatitis infection ...
Where is HCC most common?
HCC is one of the most common tumors worldwide. The epidemiology of HCC exhibits two main patterns, one in North America and Western Europe and another in non-Western countries, such as those in sub-Saharan Africa, Central and Southeast Asia, and the Amazon basin. Males are affected more than females usually, and it is most common between the ages of 30 and 50, Hepatocellular carcinoma causes 662,000 deaths worldwide per year about half of them in China.
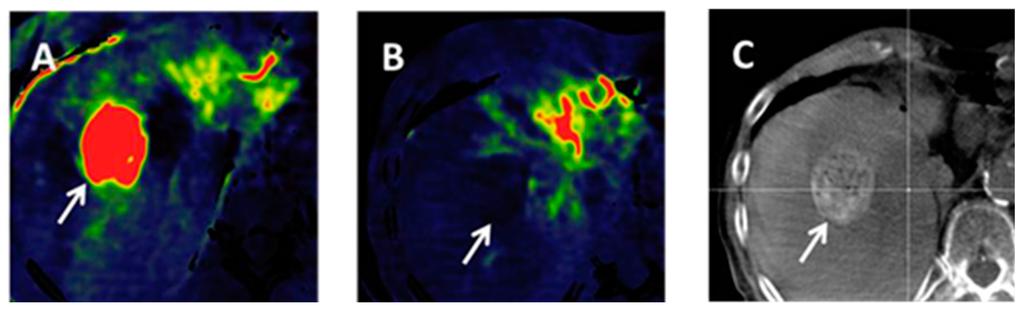
How to detect HCC?
alpha-fetoprotein and des-gamma carboxyprothrombin levels), evaluation requires imaging of the liver by CT or MRI scans. Optimally, these scans are performed with intravenous contrast in multiple phases of hepatic perfusion to improve detection and accurate classification of any liver lesions by the interpreting radiologist. Due to the characteristic blood flow pattern of HCC tumors, a specific perfusion pattern of any detected liver lesion may conclusively detect an HCC tumor. Alternatively, the scan may detect an indeterminate lesion and further evaluation may be performed by obtaining a physical sample of the lesion.
What are the most common causes of HCC?
It occurs in the setting of chronic liver inflammation, and is most closely linked to chronic viral hepatitis infection ( hepatitis B or C) or exposure to toxins such as alcohol, aflatoxin, or pyrrolizidine alkaloids. Certain diseases, such as hemochromatosis and alpha 1-antitrypsin deficiency, markedly increase the risk of developing HCC. Metabolic syndrome and NASH are also increasingly recognized as risk factors for HCC.
Does proton therapy help with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma?
Proton therapy for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma was associated with improved survival relative to photon-based radiation therapy which may be driven by decreased incidence of post-treatment liver decompensation and a number of randomized controlled trials are currently ongoing.
What is the most common liver cancer?
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary liver malignancy and is a leading cause of cancer-related death worldwide. In the United States, HCC is the ninth leading cause of cancer deaths. Despite advances in prevention techniques, screening, and new technologies in both diagnosis and treatment, incidence ...
What is the genotype of HCV?
Genotypes I, II, and III are predominant in the Western countries and the Far East, while type IV is predominant in the Middle East.
What is the ratio of HCC?
HCC occurs more often in males, with a ratio of 2:1–4:1; however, this may not be due to sex alone.42Males are more likely to be infected with viral hepatitis, consume greater quantities of alcohol, smoke cigarettes, and have a higher body mass index than women.
What are the most important risk factors for the development of HCC?
Chronic liver disease and cirrhosis remain the most important risk factors for the development of HCC of which viral hepatitis and excessive alcohol intake are the leading risk factors worldwide.
What percentage of the world's population is infected with hepatitis B?
Five percent of the world’s population is infected with hepatitis B.6. Several epidemiological studies have demonstrated significant hepatocarcinogenicity with chronic HBV infection.7Hepatitis B carriers have a 10%–25% lifetime risk of developing HCC.
Does testosterone cause HCC?
It is known that high testosterone levels have been linked to HCC in hepatitis B carriers and to advanced hepatic fibrosis in males with chronic hepatitis C infection.43,44Elevated testosterone or intake of anabolic steroids has been associated with an increased incidence of HCC and liver adenomas.
Is aflatoxin a hepatocarcinogen?
Aflatoxin produced by Aspergillusspecies (molds) found on grains, corn, peanuts, or soybeans stored in warm humid conditions is a potent hepatocarcinogen. The risk of HCC with aflatoxin is dependent on the dose and duration of exposure. Aflatoxin exposure is more prevalent in rural United States.
How long does hepatocelluar carcinoma last?
Even in the best-case scenario -- a localized tumor detected before it spreads from the liver -- the five-year survival rate is only 33 percent.
What causes hepatocellular carcinoma?
Hepatocellular carcinoma is believed to be caused by genetic changes (mutations), however, the exact cause for these mutations is unknown.
What is the most common form of liver cancer?
Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common form of liver cancer in adults. Liver cancer occurs when cells in the liver grow out of control.
How long do you live with liver cancer?
Life expectancy for liver cancer such as hepatocellular carcinoma is often expressed in 5-year survival rates, that is, how many people will be alive 5 years after diagnosis. Liver cancer 5-year survival rates: Localized (no sign cancer has spread outside the liver): 33%.
What is the name of the treatment for a tumor in the liver?
Cryoablation (cryotherapy) Ethanol ( alcohol) ablation (also called percutaneous ethanol injection, or PEI) Embolization therapy: injects substances directly into an artery in the liver to block or reduce the blood flow to a tumor in the liver. Trans-arterial embolization (TAE)
Which group has the highest liver cancer rate?
Gender: much more common in men than in women. Race/ethnicity: In the U.S., Asian Americans and Pacific Islanders have the highest rates of liver cancer, followed by Hispanics/Latinos, American Indians/Alaska Natives, African Americans, and whites.
What percentage of cancer is spread to distant parts of the body?
Distant (cancer has spread to distant parts of the body such as the lungs or bones): 2%.
What type of cancer is found in the liver?
Several types of cancer can form in the liver. The most common type of liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma, which begins in the main type of liver cell (hepatocyte). Other types of liver cancer, such as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatoblastoma, are much less common. Cancer that spreads to the liver is more common than cancer ...
How to prevent hepatitis C?
Take measures to prevent hepatitis C. No vaccine for hepatitis C exists, but you can reduce your risk of infection. Know the health status of any sexual partner. Don't engage in unprotected sex unless you're certain your partner isn't infected with HBV, HCV or any other sexually transmitted infection.
What are the risk factors for liver cancer?
Factors that increase the risk of primary liver cancer include: Chronic infection with HBV or HCV. Chronic infection with the hepatitis B virus (HBV) or hepatitis C virus (HCV) increases your risk of liver cancer.
What happens when liver cells change?
Liver cancer happens when liver cells develop changes (mutations) in their DNA. A cell's DNA is the material that provides instructions for every chemical process in your body. DNA mutations cause changes in these instructions. One result is that cells may begin to grow out of control and eventually form a tumor — a mass of cancerous cells.
How do you know if you have liver cancer?
When signs and symptoms do appear, they may include: Losing weight without trying. Loss of appetite. Upper abdominal pain. Nausea and vomiting.
What causes scar tissue in the liver?
Cirrhosis. This progressive and irreversible condition causes scar tissue to form in your liver and increases your chances of developing liver cancer. Certain inherited liver diseases. Liver diseases that can increase the risk of liver cancer include hemochromatosis and Wilson's disease. Diabetes.
Where does liver cancer begin?
Liver cancer. Liver cancer begins in the cells of the liver. The most common form of liver cancer begins in cells called hepatocytes and is called hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver cancer is cancer that begins in the cells of your liver. Your liver is a football-sized organ that sits in the upper right portion of your abdomen, ...
