
What are facts about Hydrogen Energy?
Hydrogen Energy Facts. Hydrogen is the most basic and most common element on Earth. Represented by the letter "H" on the periodic table, hydrogen is a gas that combines with oxygen to make water (H 2 O), and with carbon to form compounds such as methane and coal. Hydrogen is also a potent source of clean energy.
Is hydrogen a source of energy?
Hydrogen is considered as a secondary source of energy, commonly referred to as an energy carrier. Energy carriers are used to move, store and deliver energy in a form that can be easily used. Electricity is the most well-known example of an energy carrier. Hydrogen as an important energy carrier in the future has a number of advantages.
Is hydrogen actually a resource?
Natural, or white, hydrogen is continuously produced in the earth’s crust, and scientists are now discovering there’s much more of it stored underground than previously thought. It’s a renewable resource that can be captured by simply drilling a well.
What are the sources of hydrogen energy?
Hydrogen: A Clean, Flexible Energy Carrier
- Sources of Energy. Hydrogen can be produced from diverse, domestic resources. ...
- Production Pathways. Most hydrogen can also be produced through steam methane reforming, a high-temperature process in which steam reacts with a hydrocarbon fuel to produce hydrogen.
- Energy Carrier. ...
- Uses for Hydrogen. ...
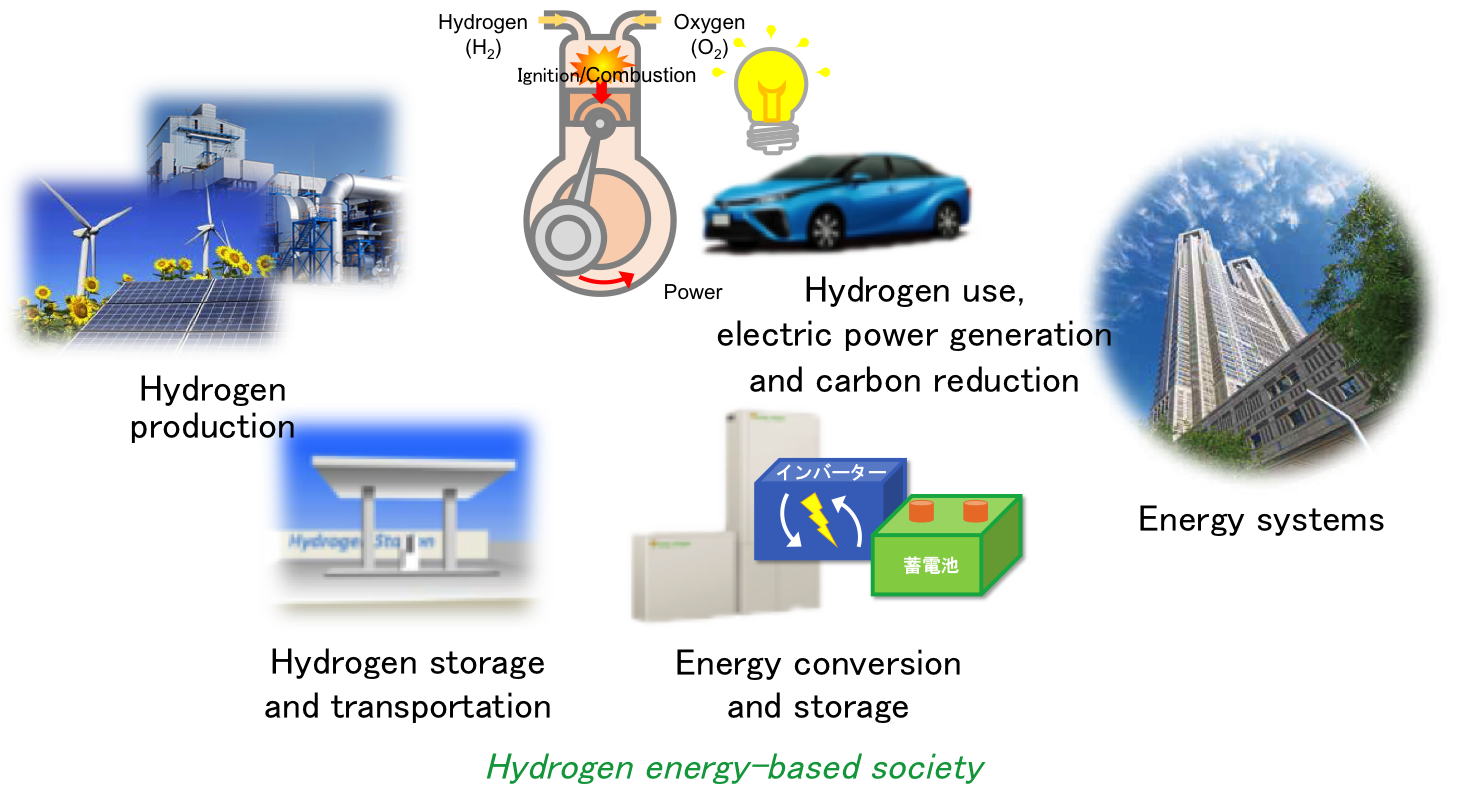
Why is hydrogen an energy carrier not a source?
Because hydrogen does not exist freely in nature and is only produced from other sources of energy, it is known as an energy carrier. It is a clean-burning fuel, and when combined with oxygen in a fuel cell, hydrogen produces heat and electricity with only water vapor as a by-product.
Can hydrogen be used as an energy source?
However, hydrogen is useful as an energy source/fuel because it has a high energy content per unit of weight, which is why it is used as a rocket fuel and in fuel cells to produce electricity on some spacecraft. Hydrogen is not widely used as a fuel now, but it has the potential for greater use in the future.
What are 3 energy carriers?
Energy carriers include electricity and heat as well as solid, liquid and gaseous fuels.
What are examples of energy carriers?
Such carriers include springs, electrical batteries, capacitors, pressurized air, dammed water, hydrogen, petroleum, coal, wood, and natural gas. An energy carrier does not produce energy; it simply contains energy imbued by another system.
What is the difference between an energy source and an energy carrier?
The distinction between energy carriers and sources is important. Energy carriers can exist in a variety of forms and can be converted from one form to another, while energy sources are the original resource from which an energy carrier is produced.
Why is hydrogen not used as fuel?
But it is not used as domestic fuel, due to several reasons : Hydrogen is not easily available and cost of production is high Unlike other gases, hydrogen is not readily available in the atmosphere. It requires processes like electrolysis of water for its production. This is a very costly process and time consuming.
Is co2 an energy carrier?
The conversion of CO2 into a dense energy carrier using renewable energy (also referred to as solar fuel) is an important element of Shell's so-called 'Long Range Research' program.
Is oil an energy carrier?
Summary. Electricity and liquid petroleum are the two primary energy carriers in the United States, and in the world.
Is ATP an energy carrier?
adenosine triphosphate (ATP), energy-carrying molecule found in the cells of all living things. ATP captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes.
Whats a energy carrier?
Noun. energy carrier (plural energy carriers) A substance or phenomenon that can be used to produce mechanical work or heat or to operate chemical or physical processes (ISO 13600). Solar radiation is an energy carrier that is not an energyware.
What does it mean to be an energy carrier?
An energy carrier is a substance or sometimes a phenomenon that contains energy that can be later converted to other forms such as mechanical work or heat or to operate chemical or physical processes. An energy carrier does not produce energy; it simply contains energy imbued by another system.
Why is hydrogen so important?
Hydrogen can be used to power vehicles, generate electricity, power industry and heat our homes and businesses. It could make a huge difference on our carbon emissions, and will be critical to achieving net zero.
What are the disadvantages of hydrogen energy?
Hydrogen is a much lighter gas than gasoline which makes it difficult to store and transport. To be able to store it we need to compress it into a liquid and store it at a low temperature. The high amounts of pressure needed to store hydrogen makes it a difficult fuel to transport in large quantities.
Can hydrogen replace fossil fuels?
Unlike most fuels, hydrogen does not produce the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2) when burned: instead, it yields water. This means that burning hydrogen fuel does not contribute to climate change. The versatility of hydrogen fuel creates many opportunities to replace fossil fuels in different parts of our economy.
Is hydrogen a good alternative fuel?
Hydrogen can also serve as fuel for internal combustion engines. However, unlike FCEVs, these produce tailpipe emissions and are less efficient. Learn more about fuel cells. The energy in 2.2 pounds (1 kilogram) of hydrogen gas is about the same as the energy in 1 gallon (6.2 pounds, 2.8 kilograms) of gasoline.
Does hydrogen power have a future?
Hydrogen fuel has long been seen as a potentially key component of a carbon-neutral future. At the 2022 MIT Energy Initiative Spring Symposium, industry experts describe efforts to produce it at scale.
Why is hydrogen used as a fuel?
However, hydrogen is useful as an energy source/fuel because it has a high energy content per unit of weight, which is why it is used as a rocket fuel and in fuel cells to produce electricity on some spacecraft . Hydrogen is not widely used as a fuel now, but it has the potential for greater use in the future.
Which fuel has the highest energy content?
Hydrogen has the highest energy content of any common fuel by weight (about three times more than gasoline), but it has the lowest energy content by volume (about four times less than gasoline).
What is the name of the gas that is fusioned with oxygen?
The sun is essentially a giant ball of hydrogen gas undergoing fusion into helium gas. This process causes the sun to produce vast amounts of energy.
What is the most abundant element in the universe?
Hydrogen is also the most abundant element in the universe. Stars such as the sun consist mostly of hydrogen. The sun is essentially a giant ball of hydrogen and helium gases. Hydrogen occurs naturally on earth only in compound form with other elements in liquids, gases, or solids. Hydrogen combined with oxygen is water (H2O).
Is hydrogen an energy carrier?
Hydrogen is an energy carrier. Energy carriers allow the transport of energy in a usable form from one place to another. Hydrogen, like electricity, is an energy carrier that must be produced from another substance.
Where does hydrogen come from?
Hydrogen sources mainly include water, hydrocarbons, and biomass. Hydrogen also exists naturally on its own underground although very rarely ( Source ).
Why is hydrogen used in fuel cells?
Finally, hydrogen is used in fuel cells to produce power and heat for stationary and portable applications . There are many different types of fuel cells that differ according to the used electrolyte and the operating temperature. Fuel cell vehicles also make use of hydrogen to generate the required power for their electric motors. These vehicles include cars, busses, trucks, and trains. Their advantage over battery-powered electric vehicles is lower costs when transporting heavy loads over long distances.
How can hydrogen be stored?
Hydrogen can be stored at high pressures, very low temperatures, or a combination of both . Hydrogen gas has a very low density which makes it ineffective to store it without any compression or cooling. Alternatively, hydrogen can also be stored using organic hydrogen carriers and various other chemicals .
What are the different colors of hydrogen?
Hydrogen is assigned a color based on how it was produced. Grey, blue, and green are the main colors of hydrogen. Several other colors such as brown, black, turquoise, and yellow are related to a specific source or production method.
What are hydrogen vehicles?
Hydrogen can be used in fuel cells onboard electric vehicles to power their electric motors. Fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEV) use hydrogen to generate electricity and produce water vapor. In these vehicles, hydrogen is stored at high pressures in pressurized tanks. These tanks can be filled at hydrogen refueling stations.
Is hydrogen a better energy carrier than batteries?
When comparing electric vehicles, the source of energy can either be hydrogen stored in a fuel tank or lithium-ion batteries. Although hydrogen-powered vehicles require a fuel cell to convert hydrogen into electricity, there are many advantages to using hydrogen.
What are renewable energy sources?
Renewable energy sources are those methods by which energy is produced from clean sources. They mainly include solar, wind, hydropower, biomass, geothermal, and nuclear energy systems.
What is hydrogen energy carrier?
Hydrogen as an Energy Carrier: What It Is and Why It Matters. Last week, the U.S. Department of Energy announced it would make available up to $ 9 million in new funding to accelerate the development of hydrogen and fuel cell technologies for use in vehicles, backup power systems, and hydrogen refueling components.
How is hydrogen made?
Hydrogen can be produced through various methods such as steam reforming, (photo-)electrolysis and thermolysis. Unlike coal, crude oil or natural gas, it is not a primary energy source but an energy carrier, comparable to electricity. It can be converted into usable energy by means of combustion or, most commonly, an electrochemical process in fuel cells. A fuel cell is a device in which chemical energy from a fuel like hydrogen is directly converted into electricity through a chemical reaction with oxygen.
Why is hydrogen important in fuel cell?
Hydrogen can help because its conversion into electricity does not emit greenhouse gases, but only heat and water as by-products , hydrogen is a unique zero-emission energy carrier. In a fuel cell, this process is 2-3 times more efficient than in an internal combustion engine.
How far can hydrogen fuel cells drive?
For commercial application, hydrogen fueled vehicles have a driving range of 350 miles, whereas battery electric vehicles only reach up to 200 miles. Hydrogen fuel cells help overcome the hurdles that battery electric vehicles have: battery replacement and irreversible capacity loss. Furthermore, it introduces the revolutionary concept ...
How many terawatts does a hydrogen car have?
According to environmental scientist Amory Lovins, the U.S. hydrogen fueled ‘Hypercar’ fleet will ultimately total 3-6 terawatts, which is 5-10 times the total generating capacity of the national grid. Hydrogen is a sustainable next-generation energy carrier with the option for unique zero-emission and highly efficient energy conversion.
How does hydrogen help the military?
For the military, it can provide the tactical advantage of reducing the weight burden for a standard 72-hour mission profile of 24 lbs. in batteries to only 9.5 lbs. in fuel cell power systems, a 60% reduction. This reduces physical stress and increases power flexibility of troops. The utilization of hydrogen can also significantly extend the reach of unmanned aerial, undersea and ground vehicles, while reducing noise and heat signatures, and enabling ‘silent watch’ operations.
What are the barriers to hydrogen?
Major barriers to the cost-effective market entry of hydrogen technology include the high R&D and infrastructural change expenditure. The U.S. Department of Energy set-up a Hydrogen and Fuel Cells Program which works together with industry, academia, and national laboratories, as well as federal and international agencies to overcome such barriers. These joint-efforts are exemplary in achieving a higher public awareness of imminent energy issues and will bring us a step closer to transitioning our energy economies in a sustainable and clean way.
Why is hydrogen considered an energy carrier?
Because hydrogen does not exist freely in nature and is only produced from other sources of energy, it is known as an energy carrier. It is a clean-burning fuel, and when combined with oxygen in a fuel cell, hydrogen produces heat and electricity with only water vapor as a by-product.
What is hydrogen energy?
Hydrogen is a secondary source of energy. It stores and transports energy produced from other resources (fossil fuels, water, and biomass). If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. Full screen is unavailable.
How is hydrogen produced?
Most hydrogen production today is by steam reforming natural gas. But natural gas is already a good fuel and one that is rapidly becoming scarcer and more expensive. It is also a fossil fuel, so the carbon dioxide released in the reformation process adds to the greenhouse effect.
Is hydrogen fuel cell technology still in development?
And fuel cell technology is still in early development, needing improvements in efficiency and durability.
What is hydrogen used for?
Nearly all of this hydrogen is used as a feedstock for production of ammonia, methanol and other chemical products, as well as in petroleum refining. The use of hydrogen as an energy carrier refers to applications where hydrogen is used because of its energy content, i.e., as a fuel.
What are the applications of hydrogen?
The main applications considered are: 1 Hydrogen as fuel for mobility 2 Hydrogen for heating in buildings 3 Hydrogen for industrial processes 4 Hydrogen for valorization of excess electricity from variable renewable power
What is the scale of uptake of hydrogen?
The scale of uptake of hydrogen for these applications will depend on several enabling and limiting factors. This includes learning rates for technology, particularly electrolyzers and fuel-cells, existing regional natural gas consumption, and development of hydrogen distribution infrastructure (e.g., hydrogen pipelines and hydrogen fuelling stations) that can provide users adequate access and supply flexibility.
What is the energy transition?
The energy transition and associated decarbonization targets are stimulating the industry to consider novel ways of delivering energy to consumers, and introduce new energy value chains that have yet to reach scale. We need to understand how these value chains will evolve and impact our customers.
What is the web application for energy value chains?
A web-application for assessment of energy value chains has also been developed. This web-application, called ExplEnergy, allows users to configure various energy value chains and estimate the associated cost and greenhouse gas emissions.
Which countries use hydrogen for heating?
Only a handful of countries will see the use of hydrogen for heating in buildings as an attractive decarbonization option, with the US, Canada, the UK, Australia, South Korea and the Netherlands being the countries that are most likely to adopt this option at a significant scale.
Will hydrogen be used in the future?
Hydrogen will not be deployed at a substantial scale for industry heating in 2030 since other decarbonization alternatives are more mature and often less complex. But use of hydrogen as a fuel may be part of a portfolio of decarbonization measures in some industries in 2050.
What is hydrogen fuel?
Hydrogen is a clean fuel that, when consumed in a fuel cell, produces only water. Hydrogen can be produced from a variety of domestic resources, such as natural gas, nuclear power, biomass, and renewable power like solar and wind.
How is hydrogen fuel made?
Today, hydrogen fuel can be produced through several methods. The most common methods today are natural gas reforming (a thermal process), and electrolysis. Other methods include solar-driven and biological processes.
What is the process of hydrogen?
Thermal processes for hydrogen production typically involve steam reforming, a high-temperature process in which steam reacts with a hydrocarbon fuel to produce hydrogen. Many hydrocarbon fuels can be reformed to produce hydrogen, including natural gas, diesel, renewable liquid fuels, gasified coal, or gasified biomass. Today, about 95% of all hydrogen is produced from steam reforming of natural gas.
How do biological processes produce hydrogen?
Biological processes use microbes such as bacteria and microalgae and can produce hydrogen through biological reactions. In microbial biomass conversion, the microbes break down organic matter like biomass or wastewater to produce hydrogen, while in photobiological processes the microbes use sunlight as the energy source.
What are the processes that are solar driven?
There are a few solar-driven processes, including photobiological, photoelectrochemical, and solar thermochemical. Photobiological processes use the natural photosynthetic activity of bacteria and green algae to produce hydrogen.
