
Is there a cure for hypogonadism?
There's not really a cure that can get rid of hypogonadism, but there are treatments that can successfully reduce or eliminate symptoms. Most cases of hypogonadism are treated with hormone replacement therapy. These treatments use medication (available in a variety of forms from patches to pills to injections) to replace the estrogen (in women ...
What are the risks hypogonadism?
Risk factors for hypogonadism (low testosterone) include obesity, large waist, diabetes, heart ...
What is the prognosis of hypogonadism?
What is the prognosis (outlook) for people who have hypogonadism? Primary hypogonadism can be a chronic condition that requires ongoing treatment. If you stop hormone replacement therapy, hormone levels can plummet, causing symptoms to return.
What problems are associated with hypogonadism?
- Worsening of the prostatic hypertrophy
- Increased risk of prostate cancer
- Lower sperm count with large doses
- Swelling of ankles, feet, or body, with or without heart failure
- Gynecomastia
- Sleep apnea
- Blood clots
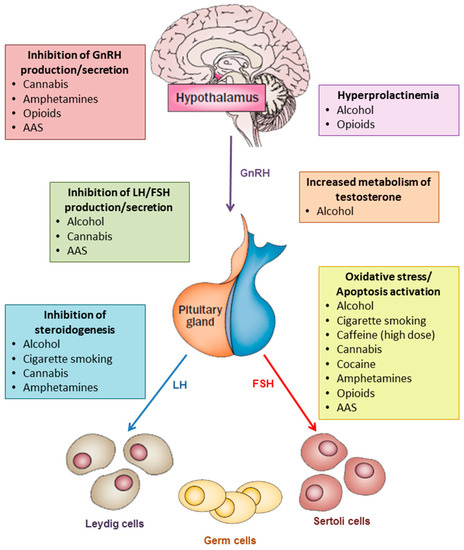
Can hypogonadism be cured?
Unless it's caused by a treatable condition, hypogonadism is a chronic condition that may require lifelong treatment. Your sex hormone level may decrease if you stop treatment. Seeking support through therapy or support groups can help you before, during, and after treatment.
Can hypogonadism reverse itself?
A subset of patients diagnosed with idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism (IHH) later achieves activation of their hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis with normalization of steroidogenesis and/or gametogenesis, a phenomenon termed reversal.
How long does it take to recover from hypogonadism?
Most men feel improvement in symptoms within four to six weeks of taking testosterone replacement therapy, although changes like increases in muscle mass may take from three to six months.
What does hypogonadism cause?
Hypogonadism occurs when sex glands called gonads produce little, if any, sex hormones. It affects teenagers and adults of all genders. The condition causes a low sex drive or libido. Hypogonadism is sometimes called gonad deficiency.
Can male hypogonadism reversed?
It is believed that lifelong hormone therapy is required to maintain sexual function and secondary sexual characteristics in men with idiopathic hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. However, rare cases of spontaneous reversal of this condition later in life have been reported.
Can low testosterone be fixed?
Testosterone replacement therapy is used to help treat people with abnormally low levels of testosterone. Abnormally low levels of testosterone can affect normal body functions.
How can I regain testosterone?
Here are 8 evidence-based ways to increase testosterone levels naturally.Exercise and Lift Weights. ... Eat Protein, Fat and Carbs. ... Minimize Stress and Cortisol Levels. ... Get Some Sun or Take a Vitamin D Supplement. ... Take Vitamin and Mineral Supplements. ... Get Plenty of Restful, High-Quality Sleep.More items...•
How long does it take for testosterone levels to come back?
Almost all of the men had testosterone concentrations return to normal three months after the end of the cycle, and 100% by 12 months, providing they had normal gonadal function at the beginning of the study.
What happens if hypogonadism is left untreated?
In men, complications of untreated hypogonadism include loss of libido, failure to achieve physical strength, the social implications of failing to go through puberty with peers (if hypogonadism occurs before puberty), and osteoporosis.
How many men are affected by hypogonadism?
Hypogonadism affects an estimated 4 to 5 million men in the United States, and although it may occur in men at any age, low testosterone levels are especially common in older males. More than 60% of men over age 65 have free testosterone levels below the normal values of men aged 30 to 35.
Is hypogonadism the same as low testosterone?
Low testosterone (male hypogonadism) is a condition in which the testes (testicles, the male reproductive glands) do not produce enough testosterone (a male sex hormone). In men, testosterone helps maintain and develop: Sexual features. Muscle mass.
Is testicular shrinkage from TRT permanent?
If it's not treated within a few hours, it can cause permanent testicular atrophy. Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT). Some men undergoing TRT experience testicular atrophy.
What causes hypogonadism in men?
Common causes of primary hypogonadism include: Klinefelter syndrome. This condition results from a congenital abnormality of the sex chromosomes, X and Y. A male normally has one X and one Y chromosome. In Klinefelter syndrome, two or more X chromosomes are present in addition to one Y chromosome.
What causes hypogonadism in the pituitary gland?
Also, treatment for a brain tumor, such as surgery or radiation therapy , can affect the pituitary gland and cause hypogonadism. Inflammatory disease.
What is the primary testicular failure?
Primary. This type of hypogonadism — also known as primary testicular failure — originates from a problem in the testicles. Secondary. This type of hypogonadism indicates a problem in the hypothalamus or the pituitary gland — parts of the brain that signal the testicles to produce testosterone.
What glands control testosterone?
Pituitary gland and hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus are located within the brain and control hormone production. Male hypogonadism means the testicles don't produce enough of the male sex hormone testosterone. There are two basic types of hypogonadism:
What causes low testosterone levels?
HIV/AIDS. HIV/AIDS can cause low levels of testosterone by affecting the hypothalamus, the pituitary and the testes.
What is it called when the body doesn't produce enough testosterone?
Male hypogonadism is a condition in which the body doesn't produce enough of the hormone that plays a key role in masculine growth and development during puberty (testosterone) or enough sperm or both.
Why are testicles not functioning properly?
Secondary hypogonadism. In secondary hypogonadism, the testicles are normal but don't function properly due to a problem with the pituitary or hypothalamus. A number of conditions can cause secondary hypogonadism, including: Kallmann's syndrome.
How does hypogonadism affect women?
Onset in women after puberty causes cessation of menstruation, lowered libido, loss of body hair, and hot flashes. In men it causes impaired muscle and body hair development, gynecomastia, decreased height, erectile dysfunction, and sexual difficulties. If hypogonadism is caused by a disorder of the central nervous system (e.g., a brain tumor ), then this is known as central hypogonadism. Signs and symptoms of central hypogonadism may involve headaches, impaired vision, double vision, milky discharge from the breast, and symptoms caused by other hormone problems.
What is hypogonadism resulting from lack of hormone response?
An example of a hypogonadism resulting from the lack of hormone response is androgen insensitivity syndrome, where there are inadequate receptors to bind the testosterone, resulting in varying clinical phenotypes of sexual characteristics despite XY chromosomes.
What is the term for a defect in the gonads?
Hypogonadism resulting from defects of the gonads is referred to as hypergonadotropic hypogonadism or primary hypogonadism. Examples include Klinefelter syndrome and Turner syndrome. Mumps is known to cause testicular failure, and in recent years has been immunized against in the US.
Why does LH and FSH rise during menopause?
This is because hypogonadism is an abnormality, whereas menopause is a normal change in hormone levels. In any case, the LH and FSH levels will rise in cases of primary hypogonadism or menopause, while they will be low in women with secondary or tertiary hypogonadism.
Why do women test for LH?
Women. Testing serum LH and FSH levels are often used to assess hypogonadism in women, particularly when menopause is believed to be happening. These levels change during a woman's normal menstrual cycle, so the history of having ceased menstruation coupled with high levels aids the diagnosis of being menopausal.
What is the cause of hypogonadism in men?
In men it causes impaired muscle and body hair development, gynecomastia, decreased height, erectile dysfunction, and sexual difficulties . If hypogonadism is caused by a disorder of the central nervous system (e.g., a brain tumor ), then this is known as central hypogonadism.
What is the term for a deficiency in sex hormones?
Defective egg or sperm development results in infertility. The term hypogonadism usually means permanent rather than transient or reversible defects, and usually implies deficiency ...
How does hypogonadism affect women?
In women with hypogonadism, the ovaries produce low levels of female sex hormones. This affects the functioning of the ovaries and the reproductive system. Symptoms include delayed puberty and a lack of menstruation or irregular menstruation.
What are the causes of secondary hypogonadism?
Situations that can cause secondary hypogonadism include: malnutrition. systemic illness. stress.
What is the name of the disease that causes the male testes to not produce sperm?
Diagnosis. Male hypogonadism , also known as testosterone deficiency, is a failure of the testes to produce the male sex hormone testosterone, sperm, or both. It can be due to a testicular disorder or the result of a disease process involving the hypothalamus and pituitary gland.
What is the term for the decline in testosterone levels?
morbid obesity. Andropause is sometimes used to describe decreased testosterone due to the normal aging process. Testosterone levels in males increase until the age of 17 years. Then, starting at approximately 40 years of age, testosterone levels begin to decline at 1.2-2 percent per year.
What tests are needed to confirm hypogonadism?
If an individual is at risk of or may have hypogonadism, a doctor will take a thorough medical history taken and carry out a physical examination, including blood tests. Two key blood tests must be carried out to confirm the presence of hypogonadism: serum total. free testosterone.
Why do my testicles not respond to hormones?
In primary hypogonadism, the testicles do not respond to hormone stimulation. This can be due to a congenital disorder such as Klinefelter’s syndrome, or acquired as a result of radiation treatment, chemotherapy, mumps, tumors or trauma to the testes.
Is TRT contraindicated for men?
This will include regular blood tests and periodic digital rectal exams. TRT is contraindicated in men with erythrocytosis, a condition involving a high volume percentage of red blood cells in the blood.
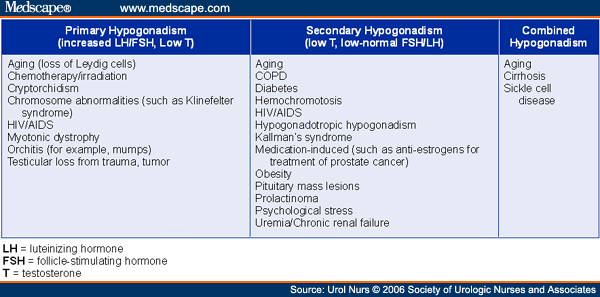
Overview
Classification
Signs and symptoms
Diagnosis
Screening
Treatment
See also
External links