
Full Answer
Do ionic solids have a high melting point?
Ionic solids also tend to have high melting points, often over 1000 degrees but they vary. Some are low enough to melt in the lab with a Bunsen burner: Lead bromide for example has a melting point of 383 deg C. Why does an ionic compound have a higher boiling point than a covalent compound?
What is the difference between ionic and covalent compounds?
Covalent compounds are held together by covalent bonds. And ionic compounds are help together by ionic bonds. These are two different ways that elements can combine to make substances. So what is the difference between ionic and covalent bonds?
Why do covalent compounds have a high melting point?
Covalent network solids like dimond ,graphite , silicon dioxide have very high melting points (because breaking of large no of covalent bonds requires large amount of energy). Molecular solids due to weak Van der waals force of attraction have low melting point than ionic solids.
Why do molecular and ionic compounds have different melting and boiling points?
The melting and boiling points of molecular compounds are generally quite low compared to those of ionic compounds. This is because the energy required to disrupt the intermolecular forces between molecules is far less than the energy required to break the ionic bonds in a crystalline ionic compound (Figure 6.2. 1) .
What happens when a metal atom is ionic?
What type of bond is covalent?
What is an ionic bond?
What type of bond transfers electrons between metals and nonmetals?
What is the difference between ionic and non-metal compounds?
Is carbon dioxide ionic or covalent?
Is NaCl an ionic compound?
See 2 more
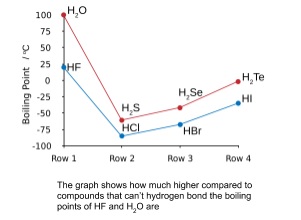
Is ice melting an ionic solid?
Because the intermolecular forces between molecules are typically less strong than in ionic solids, molecular solids typically melt at lower temperatures and are softer than ionic solids. Ice is an example of a molecular solid.
Is ice covalent or ionic?
In the solid state (ice), intermolecular interactions lead to a highly ordered but loose structure in which each oxygen atom is surrounded by four hydrogen atoms; two of these hydrogen atoms are covalently bonded to the oxygen atom, and the two others (at longer distances) are hydrogen bonded to the oxygen atom's ...
Is ice a ionic compound?
3:357:50Ionic Compounds and Bonds: Why does salt melt ice? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThey become negatively charged anions. And these opposite charges attract. And that's what forms ourMoreThey become negatively charged anions. And these opposite charges attract. And that's what forms our ionic bond.
What is the type of ice melting?
The two main types of ice melts are exothermic and endothermic, and the common types of ice melts include ‒ calcium chloride ice melt, sodium chloride ice melt, sodium acetate ice melt, and urea, among others. Most of these include the chemical compounds having chlorine compounds.
Is ice covalent bonding?
Types of bond present in ice are covalent bonds and intermolecular hydrogen bonds.
Is ice An example of covalent solid?
Examples of molecular solids include hydrocarbons, ice, sugar, fullerenes, sulfur and solid carbon dioxide. Was this answer helpful?
What type of bond is in ice?
hydrogen bondsIn ice, the crystalline lattice is dominated by a regular array of hydrogen bonds which space the water molecules farther apart than they are in liquid water.
How do you identify an ionic compound?
As a general rule of thumb, compounds that involve a metal binding with either a non-metal or a semi-metal will display ionic bonding. Compounds that are composed of only non-metals or semi-metals with non-metals will display covalent bonding and will be classified as molecular compounds.
How do ions melt ice?
These ions, in turn, react with water molecules and hydratethat is, form hydrated ions (charged ions joined to water molecules). This process gives off heat, because hydrates are more stable than the individual ions. That energy then melts microscopic parts of the ice surface.
What is the chemical compound of ice melt?
Ice melt, typically, is a blend of sodium chloride, magnesium chloride pellets, and calcium chloride pellets. Calcium chloride is typically regarded as the best performing ice melt for fast melting and long lasting action. It melts to -15°F.
What is it called when ice melts into water?
When solid ice gains heat, it changes state from solid ice to liquid water in a process called melting.
Is ice melting a chemical change?
The melting of ice is a physical change when it occurs naturally. But when you speed up the process by using a reactant, such as salt, it becomes a chemical reaction.
What type of bond is ice?
hydrogen bondsIn ice, the crystalline lattice is dominated by a regular array of hydrogen bonds which space the water molecules farther apart than they are in liquid water.
How do you know if its ionic or covalent?
Classifying compounds as ionic or covalentIf a compound is made from a metal and a non-metal, its bonding will be ionic.If a compound is made from two non-metals, its bonding will be covalent.
Is water covalent or ionic?
covalentLikewise, a water molecule is ionic in nature, but the bond is called covalent, with two hydrogen atoms both situating themselves with their positive charge on one side of the oxygen atom, which has a negative charge.
How do you tell if a substance is ionic or covalent?
As a general rule of thumb, compounds that involve a metal binding with either a non-metal or a semi-metal will display ionic bonding. Compounds that are composed of only non-metals or semi-metals with non-metals will display covalent bonding and will be classified as molecular compounds.
What happens when a metal atom is ionic?
Consequently, ionic bonds create two charged ions, the metal always donates its electron , and the non-metal always accepts the electron.
What type of bond is covalent?
What is a covalent bond? There are two types of chemical bonds: covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Covalent bonds occur between two non-metals or a non-metal, and a metalloid.
What is an ionic bond?
So what is an ionic bond? The definition of ionic bond, is a bond between atoms where electrons are (mostly) transferred from one atom to another. We say mostly, because there is always some sharing of electrons between atoms, but in Ionic bonds, the sharing is very unequal. The less equal the sharing of the electrons, the more ionic character the bond has.
What type of bond transfers electrons between metals and nonmetals?
Ionic bonds occur between a metal and a non-metal. Unlike covalent bonds, ionic bonds transfer their valence electrons between atoms. The electronegativity difference between non-metals and metals exceeds 1.7. The metal atom transfers its electrons to the non-metal atom.
What is the difference between ionic and non-metal compounds?
Ionic compounds are usually between a metal and a non-metal. Non-metal with a non-metal compounds are covalent.
Is carbon dioxide ionic or covalent?
Carbon dioxide, gas we breathe out of our lungs, is a compound with covalent bonds. But what is the difference between ionic vs covalent?
Is NaCl an ionic compound?
NaCl, so dium chloride or table salt, is the “classic” example of an ionic compound. Sodium is a metal, and chlorine is a non-metal. It has ionic bonds, has a crystalline structure. In solution, it separates into ions in solution.
How to tell if a substance is ionic or covalent?
So how can you tell if a substance is an ionic compound (rock, salt, mineral) or a covalent compound? That is, how to tell if a substance is ionic vs molecular? The really simple test is: 1 Ionic compounds have a metal element (1 or more) 2 Covalent compounds (molecules) do not have metal elements
Why do teachers teach covalent vs ionic?
That’s why teachers teach about covalent vs ionic in the first place, because it’s a good starting point for learning, even though it’s just a simple categorization into two bins called covalent vs ionic. This idea of putting metals in molecules won a Nobel Prize in 1912.
What are the plus minus attractions of ionic compounds?
The plus-minus attractions for ionic compounds necessarily hold the atoms to touch, like a pile of hopelessly interlocked magnets that you could not pull apart with all your strength.
How are covalent compounds held together?
Covalent compounds are held together by covalent bonds. And ionic compounds are help together by ionic bonds. These are two different ways that elements can combine to make substances.
What is a high melting point for ionic compounds?
Such as lava, which is melted rock, which is ionic compounds. Or molten salt at 1500 degrees Fahrenheit (800 C). These really high melting points for ionic compounds indicate that a lot of energy is required to get them flowing as liquids. Note that all salts are ionic compounds, but not all ionic compounds are salts.
Why are molecules arranged differently in the 3 states of matter?
But the molecules themselves are arranged differently in the 3 states of matter. The reason why molecules can be a gas is because they are neutral and don’t have any plus or minus charge. Thus the molecules can separate, unlike the ionic compounds which are locked together by the plus-minus attractions.
What does ionic mean in solid form?
Now take a look at the diagram for an ionic compound, in solid form. First thing, ionic means charged, like plus and minus that attract each other . Note how the atoms alternate green (negatively charged chlorine) and purple (positively charged sodium) in all three directions.
What are covalent solids?
Covalent Network Solid. Covalent network solids include crystals of diamond, silicon, some other nonmetals, and some covalent compounds such as silicon dioxide (sand) and silicon carbide (carborundum, the abrasive on sandpaper). Many minerals have networks of covalent bonds.
What are ionic solids?
Ionic solids, such as sodium chloride and nickel oxide, are composed of positive and negative ions that are held together by electrostatic attractions, which can be quite strong ( Figure 3 ). Many ionic crystals also have high melting points. This is due to the very strong attractions between the ions—in ionic compounds, the attractions between full charges are (much) larger than those between the partial charges in polar molecular compounds. This will be looked at in more detail in a later discussion of lattice energies. Although they are hard, they also tend to be brittle, and they shatter rather than bend. Ionic solids do not conduct electricity; however, they do conduct when molten or dissolved because their ions are free to move. Many simple compounds formed by the reaction of a metallic element with a nonmetallic element are ionic.
What are the entities of a solid phase?
The entities of a solid phase may be arranged in a regular, repeating pattern (crystalline solids) or randomly (amorphous). Metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. Substances that consist of large molecules, or a mixture of molecules whose movements are more restricted, often form amorphous solids.
How are metallic solids formed?
Metallic solids such as crystals of copper, aluminum, and iron are formed by metal atoms Figure 4. The structure of metallic crystals is often described as a uniform distribution of atomic nuclei within a “sea” of delocalized electrons. The atoms within such a metallic solid are held together by a unique force known as metallic bonding that gives rise to many useful and varied bulk properties. All exhibit high thermal and electrical conductivity, metallic luster, and malleability. Many are very hard and quite strong. Because of their malleability (the ability to deform under pressure or hammering), they do not shatter and, therefore, make useful construction materials. The melting points of the metals vary widely. Mercury is a liquid at room temperature, and the alkali metals melt below 200 °C. Several post-transition metals also have low melting points, whereas the transition metals melt at temperatures above 1000 °C. These differences reflect differences in strengths of metallic bonding among the metals.
Why does a crystalline solid melt?
A crystalline solid, like those listed in Table 7, has a precise melting temperature because each atom or molecule of the same type is held in place with the same forces or energy. Thus, the attractions between the units that make up the crystal all have the same strength and all require the same amount of energy to be broken. The gradual softening of an amorphous material differs dramatically from the distinct melting of a crystalline solid. This results from the structural nonequivalence of the molecules in the amorphous solid. Some forces are weaker than others, and when an amorphous material is heated, the weakest intermolecular attractions break first. As the temperature is increased further, the stronger attractions are broken. Thus amorphous materials soften over a range of temperatures.
What happens when liquids freeze?
When most liquids are cooled, they eventually freeze and form crystalline solids, solids in which the atoms, ions, or molecules are arranged in a definite repeating pattern. It is also possible for a liquid to freeze before its molecules become arranged in an orderly pattern.
What temperature does mercury melt?
Mercury is a liquid at room temperature, and the alkali metals melt below 200 °C. Several post-transition metals also have low melting points, whereas the transition metals melt at temperatures above 1000 °C. These differences reflect differences in strengths of metallic bonding among the metals. Figure 4.
How are ionic and covalent solids attracted to each other?
Ionic solids have particles attracted to each other via differential electric charge. For instance NaCl is not made of molecules of NaCl, but rather numerous Na+ and Cl- ions. Each one closely attracted to its neighboring ions of opposite charge in a crystalline lattice. In a way, each crystal is one molecule. Covalent solids, on the other hand, as long as they are pretty small, have individual molecules wherein the atoms are strongly attracted to each other, but not so much between molecules.
Which solid has a higher melting point?
Ionic solids have stable crystal lattice structures so they have higher melting point than molecular solids.
How do ionic bonds break?
After the transfer of electrons, the atoms (or molecules) can be separated. This means that the bond is broken. We had to give an amount of energy called bond energy to the molecule to break the bond. In case of ionic bonds, the sole way of interactions between the two atoms is electrostatic force. There is no need to transfer electrons. The same force will be between these atoms and molecules of water. Note, that the atoms at the edge of a crystal are quite weakly bonded as there are less atoms with opposite charge. These ions are easily washed away and, gradually, all ions will be separated. Moreover all these ions will be stabilised by water molecules by electrostatic interactions. This means that it is very stable state for them to be separated and solvated. Not the case for residual parts after cleavage of covalent bond. These parts tend to be very reactive.
Why are brittle ionic solids brittle?
They are brittle because of low mobility of defects called dislocations present in ionic solids.
What is the melting point of a compound?
The melting point is when there is enough energy (heat) in the system , that the electromagnetic forces (intermolecular forces)between the molecules of the compound start to weaken and diminish, this allows the molecules to move further apart from each other which is what we perceive as the change of the state of matter in a substance. So as you can tell, the stronger the intermolecular forces are, the more energy (heat)is needed to change its state of matter, ionic compounds have the strongest intermolecular forces with ion-ion interactions, and then it is polar covalent compounds bonds with dipo
How many electrons are transferred to one atom?
Transfer one electron to one of the atoms forming the bond and one electron to the second bonded atom. This is called homolysis, because the electrons are evenly separated to atoms. The result is two radicals.
Why are ionic liquids considered liquids?
Some of which can be even lower than water’s freezing point despite having stronger bonds! Despite their stronger bonds they remain liquid because of the large entropy difference between the solid and liquid phase.
What are covalent solids?
Covalent Network Solids. Covalent network solids include crystals of diamond, silicon, some other nonmetals, and some covalent compounds such as silicon dioxide (sand) and silicon carbide (carborundum, the abrasive on sandpaper). Many minerals have networks of covalent bonds.
Why does a crystalline solid melt?
A crystalline solid, like those listed in Table 1, has a precise melting temperature because each atom or molecule of the same type is held in place with the same forces or energy. Thus, the attractions between the units that make up the crystal all have the same strength and all require the same amount of energy to be broken. The gradual softening of an amorphous material differs dramatically from the distinct melting of a crystalline solid. This results from the structural nonequivalence of the molecules in the amorphous solid. Some forces are weaker than others, and when an amorphous material is heated, the weakest intermolecular attractions break first. As the temperature is increased further, the stronger attractions are broken. Thus amorphous materials soften over a range of temperatures.
What are the entities of a solid phase?
The entities of a solid phase may be arranged in a regular, repeating pattern (crystalline solids) or randomly (amorphous). Metals and ionic compounds typically form ordered, crystalline solids. Substances that consist of large molecules, or a mixture of molecules whose movements are more restricted, often form amorphous solids.
What happens when liquids freeze?
When most liquids are cooled, they eventually freeze and form crystalline solids, solids in which the atoms, ions, or molecules are arranged in a definite repeating pattern. It is also possible for a liquid to freeze before its molecules become arranged in an orderly pattern. The resulting materials are called amorphous solids or noncrystalline solids (or, sometimes, glasses). The particles of such solids lack an ordered internal structure and are randomly arranged ( Figure 1 ).
How are metallic solids formed?
Metallic solids such as crystals of copper, aluminum, and iron are formed by metal atoms ( Figure 3 ). The structure of metallic crystals is often described as a uniform distribution of atomic nuclei within a “sea” of delocalized electrons. The atoms within such a metallic solid are held together by a unique force known as metallic bonding that gives rise to many useful and varied bulk properties. All exhibit high thermal and electrical conductivity, metallic luster, and malleability. Many are very hard and quite strong. Because of their malleability (the ability to deform under pressure or hammering), they do not shatter and, therefore, make useful construction materials. The melting points of the metals vary widely. Mercury is a liquid at room temperature, and the alkali metals melt below 200 °C. Several post-transition metals also have low melting points, whereas the transition metals melt at temperatures above 1000 °C. These differences reflect differences in strengths of metallic bonding among the metals.
Why are mercury and alkali metals so hard?
Many are very hard and quite strong. Because of their malleability (the ability to deform under pressure or hammering), they do not shatter and, therefore, make useful construction materials. The melting points of the metals vary widely. Mercury is a liquid at room temperature, and the alkali metals melt below 200 °C.
What temperature does mercury melt?
Mercury is a liquid at room temperature, and the alkali metals melt below 200 °C. Several post-transition metals also have low melting points, whereas the transition metals melt at temperatures above 1000 °C. These differences reflect differences in strengths of metallic bonding among the metals. Figure 3.
What happens when a metal atom is ionic?
Consequently, ionic bonds create two charged ions, the metal always donates its electron , and the non-metal always accepts the electron.
What type of bond is covalent?
What is a covalent bond? There are two types of chemical bonds: covalent bonds and ionic bonds. Covalent bonds occur between two non-metals or a non-metal, and a metalloid.
What is an ionic bond?
So what is an ionic bond? The definition of ionic bond, is a bond between atoms where electrons are (mostly) transferred from one atom to another. We say mostly, because there is always some sharing of electrons between atoms, but in Ionic bonds, the sharing is very unequal. The less equal the sharing of the electrons, the more ionic character the bond has.
What type of bond transfers electrons between metals and nonmetals?
Ionic bonds occur between a metal and a non-metal. Unlike covalent bonds, ionic bonds transfer their valence electrons between atoms. The electronegativity difference between non-metals and metals exceeds 1.7. The metal atom transfers its electrons to the non-metal atom.
What is the difference between ionic and non-metal compounds?
Ionic compounds are usually between a metal and a non-metal. Non-metal with a non-metal compounds are covalent.
Is carbon dioxide ionic or covalent?
Carbon dioxide, gas we breathe out of our lungs, is a compound with covalent bonds. But what is the difference between ionic vs covalent?
Is NaCl an ionic compound?
NaCl, so dium chloride or table salt, is the “classic” example of an ionic compound. Sodium is a metal, and chlorine is a non-metal. It has ionic bonds, has a crystalline structure. In solution, it separates into ions in solution.
