
Medication
Impetigo can be caused by Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphylococcus aureus. This page focuses on infections caused by S. pyogenes, which are also called group A Streptococcus or group A strep. Impetigo can be bullous or non-bullous.
What type of bacteria causes impetigo?
Impetigo - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf Impetigo is a common infection of the superficial layers of the epidermis that is highly contagious and most commonly caused by gram-positive bacteria. It most commonly presents as erythematous plaques with a yellow crust and may be itchy or painful. The lesions are highly contagious and spread easily.
What is impetigo?
Impetigo is a superficial bacterial skin infection that is highly contagious. Impetigo can be caused by Streptococcus pyogenes and Staphylococcus aureus.
Is impetigo contagious?
Gram-positive bacteria are a very large and diverse group of microorganisms. Understanding their taxonomy and knowing their unique features is important for diagnostics and treatment of infectious diseases. Actinobacteria is the taxonomic name of the class of high G+C gram-positive bacteria.
What is the taxonomy of Gram positive bacteria?

Is impetigo Gram-positive cocci?
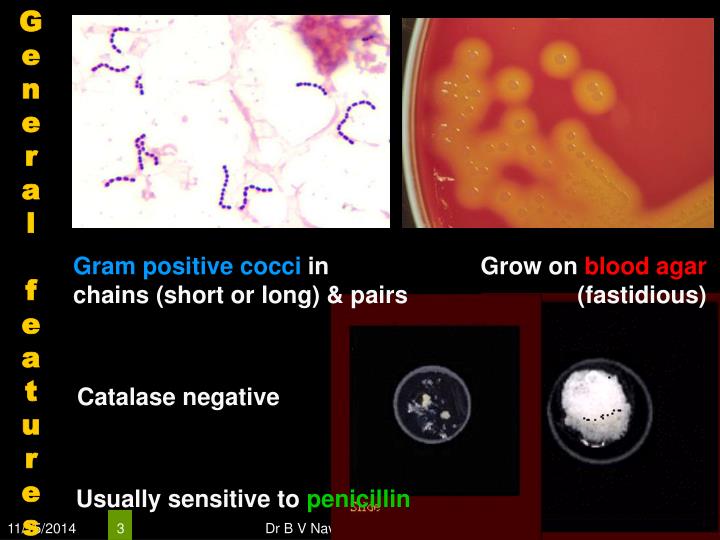
aureus, S. pyogenes, or both cause non-bullous impetigo, which is also called “impetigo contagiosa.” S. pyogenes are gram-positive cocci that grow in chains (see Figure 1).
Is impetigo gram negative?
It is active against Gram-positive cocci such as staphylococci and streptococci. Most Gram-negative microorganisms and yeasts are resistant to it.
What bacteria is responsible for impetigo?
Impetigo is a skin infection caused by one or both of the following bacteria: group A Streptococcus and Staphylococcus aureus.
Is a gram-positive Streptococcus in Group A that causes impetigo?
sanguinis). Streptococcus pyogenes is a gram-positive group A cocci that can cause pyogenic infections (pharyngitis, cellulitis, impetigo, erysipelas), toxigenic infections (scarlet fever, necrotizing fasciitis), and immunologic infections (glomerulonephritis and rheumatic fever).
What type of antibiotics treat impetigo?
Impetigo is treated with prescription mupirocin antibiotic ointment or cream applied directly to the sores two to three times a day for five to 10 days. Before applying the medicine, soak the area in warm water or apply a wet cloth compress for a few minutes.
Which antibiotics is best for impetigo?
Oral antibiotics (e.g., antistaphylococcal penicillins, amoxicillin/clavulanate [Augmentin], cephalosporins, macrolides) are effective for the treatment of impetigo; erythromycin is less effective.
What is the difference between MRSA and impetigo?
Some impetigo is caused by a type of bacteria called MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus). This type of bacteria is hard to kill. This type of impetigo can be hard to treat.
Is impetigo a type of staph?
Impetigo is a skin infection caused by bacteria. It is usually caused by staphylococcal (staph) bacteria, but it can also be caused by streptococcal (strep) bacteria. It is most common in children between the ages of two and six.
What cells are affected by impetigo?
Bullous impetigo Exfoliative toxins target intracellular adhesion molecules (desmoglein – 1) present in the epidermal granular layer. Results in dissociation of epidermal cells which causes blister formation. Can occur on areas of intact skin.
Is staph gram-positive or negative?
Staphylococcus aureus is a gram-positive bacteria that cause a wide variety of clinical diseases. Infections caused by this pathogen are common both in community-acquired and hospital-acquired settings.
Which bacteria is gram negative?
Commonly isolated Gram-negative organisms include Pseudomonas, Klebsiella, Proteus, Salmonella, Providencia, Escherichia, Morganella, Aeromonas, and Citrobacter.
How do you know if gram-positive or Gram negative?
A Gram stain is colored purple. When the stain combines with bacteria in a sample, the bacteria will either stay purple or turn pink or red. If the bacteria stays purple, they are Gram-positive. If the bacteria turns pink or red, they are Gram-negative.
Etiology
Previously, impetiginous lesions were primarily of streptococcal origin. Currently, most cases of impetigo in the United States involve Staphylococcus aureus or a combination of S. aureus and streptococci (5). Bullous impetigo is most always caused by coagulase -positive S.
Treatment
Untreated impetigo may take several weeks to resolve, with spreading and development of new lesions during the resolution period. Scarring rarely occurs.
What is the classification of Gram positive bacteria?
Gram-positive bacteria are classified into high G+C gram-positive and low G+C gram-positive bacteria, based on the prevalence of guanine and cytosine nucleotides in their genome. Actinobacteria is the taxonomic name of the class of high G+C gram-positive bacteria.
Which order of bacteria is a gram positive?
The order Lactobacillales comprises low G+C gram-positive bacteria that include both bacilli and cocci in the genera Lactobacillus, Leuconostoc, Enterococcus, and Streptococcus. Bacteria of the latter three genera typically are spherical or ovoid and often form chains.
What is the name of the bacteria that causes boils?
Strains of S. aureus cause a wide variety of infections in humans, including skin infections that produce boils, carbuncles, cellulitis, or impetigo. Certain strains of S. aureus produce a substance called enterotoxin, which can cause severe enteritis, often called staph food poisoning.
What is the name of the bacteria that has a high G+C?
Actinobacteria: High G+C Gram-Positive Bacteria. The name Actinobacteria comes from the Greek words for rays and small rod, but Actinobacteria are very diverse. Their microscopic appearance can range from thin filamentous branching rods to coccobacilli.
What is the class of bacteria that produces endospores?
One large and diverse class of low G+C gram-positive bacteria is Clostridia. The best studied genus of this class is Clostridium. These rod-shaped bacteria are generally obligate anaerobes that produce endospores and can be found in anaerobic habitats like soil and aquatic sediments rich in organic nutrients.
Which class of bacteria has the most guanine and cytosine nucleotides?
The class Actinobacteria comprises the high G+C gram-positive bacteria, which have more than 50% guanine and cytosine nucleotides in their DNA. The class Bacilli comprises low G+C gram-positive bacteria, which have less than 50% of guanine and cytosine nucleotides in their DNA.
What bacteria are in the nosocomial environment?
Anaerobic aerotolerant bacteria, abundant in the human gut, may cause urinary tract and other infections in the nosocomial environment. Lactobacillus. Gram-positive bacillus. Facultative anaerobes; ferment sugars into lactic acid; part of the vaginal microbiota; used as probiotics.
Etiology
Clinical Features
Transmission
Incubation Period
Specialist to consult
Risk Factors
- Impetigo can be bullous or non-bullous. Toxin-producing S. aureus cause bullous impetigo. S. aureus, S. pyogenes, or both cause non-bullous impetigo, which is also called “impetigo contagiosa.” S. pyogenes are gram-positive cocci that grow in chains (see Figure 1). They exhibit β-hemolysis (complete hemolysis) when grown on blood agar plates. They ...
Diagnosis and Testing
- Streptococcal impetigo, or non-bullous impetigo, begins as papules. The papules evolve to pustules and then break down to form thick, adherent crusty lesions (Figure 2). The crusts are typically golden or “honey-colored.” These lesions usually appear on exposed areas of the body, most commonly the face and extremities. Multiple lesions typically develop. In cases of non-bull…
Treatment
- Streptococcal impetigo is most commonly spread through direct contact with other people with impetigo. People with impetigo are much more likely to transmit the bacteria than asymptomatic carriers. Crowding, such as found in schools and daycare centers, increases the risk of disease spread from person to person. Lesions can be spread (by fingers and clothing) to other parts of …
Prognosis and Complications
- The incubation period of impetigo, from colonization of the skin to development of the characteristic lesions, is about 10 days.1 It is important to note not everyone who becomes colonized will go on to develop impetigo.
Prevention
- Impetigo can occur in people of all ages, but it is most common among children 2 through 5 years of age. Scabies infections and activities that result in cutaneous cuts or abrasions (e.g., sports such as wrestling and football) increase the risk of impetigo. It is also more common in tropical or subtropical locations and in the summer in temperate climates but can occur anywhere.1
Epidemiology
- Impetigo is usually diagnosed by physical examination, but physical examination cannot reliably differentiate between streptococcal and staphylococcal non-bullous impetigo.1Gram stain or culture of the exudate or pus from an impetigo lesion can identify the bacterial cause. However, laboratory testing is not necessary nor routinely performed in clinical practice.