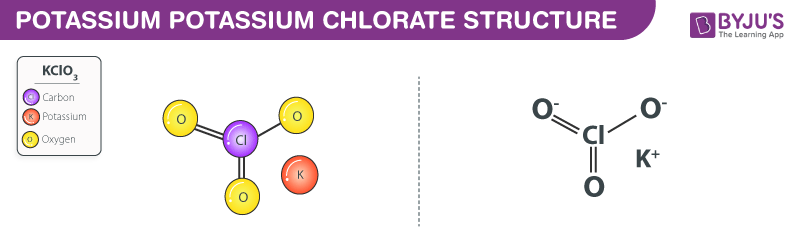
KClO3 is a salt and breaks up completely in an aqueous solution, therefore it is a strong electrolyte. It’s a salt, and any salt with K as its cation is a strong electrolyte. What is the atomicity of KClO3? (d) The formula of Potassium Chlorate
Chlorate
The chlorate anion has the formula ClO⁻₃. In this case, the chlorine atom is in the +5 oxidation state. "Chlorate" can also refer to chemical compounds containing this anion; chlorates are the salts of chloric acid. "Chlorate", when followed by a Roman numeral in parentheses, e.g. chlorate(VII), refers …
What does KClO3 stand for?
Learn more about the chemical behaviour and importance of potassium chlorate (KClO 3) from the expert faculties at BYJU’S – India’s largest education company. Test Your Knowledge On Potassium Chlorate!
What is potassium chlorate?
The aqueous solution of potassium chlorate is a colourless liquid that is denser than water. It could be toxic when ingested. When it comes in contact it can irritate your eyes, skin, mucous membranes.
What is the temperature of KClO3 reaction?
This reaction occurs at a temperature of between 150-300 ° C. For this reaction manganese (IV) oxide can be the catalyst. Learn more about the chemical behaviour and importance of potassium chlorate (KClO 3) from the expert faculties at BYJU’S – India’s largest education company.
What is the thermal decomposition of potassium chlorate to obtain oxygen?
The thermal decomposition of potassium chlorate to obtain oxygen and potassium chloride. This reaction occurs at a temperature of between 150-300 ° C. For this reaction manganese (IV) oxide can be the catalyst.

Is KClO3 soluble or insoluble?
Potassium chlorateNamesSolubility in water3.13 g/100 mL (0 °C) 4.46 g/100 mL (10 °C) 8.15 g/100 mL (25 °C) 13.21 g/100 mL (40 °C) 53.51 g/100 mL (100 °C) 183 g/100 g (190 °C) 2930 g/100 g (330 °C)Solubilitysoluble in glycerol negligible in acetone and liquid ammoniaSolubility in glycerol1 g/100 g (20 °C)47 more rows
Is KCl solid or aqueous?
Potassium chloride (KCl, or potassium salt) is a metal halide salt composed of potassium and chlorine. It is odorless and has a white or colorless vitreous crystal appearance. The solid dissolves readily in water, and its solutions have a salt-like taste....Potassium chloride.NamesRelated compoundsPotassium chlorate Potassium perchlorate56 more rows
Is KClO3 a gas?
b) KClO3 is a liquid at room temperature and 1 atm.
Is Ki soluble in water?
WaterPotassium iodide / Soluble inPotassium iodide is highly soluble in water so SSKI is a concentrated source of KI. At 20 degrees Celsius the solubility of KI is 140-148 grams per 100 grams of water.
Is potassium chloride soluble to water?
WaterGlycerolPotassium chloride/Soluble in
Is potassium chloride a solid?
Potassium chloride is characterized by a colourless, crystalline appearance and an odourless smell. In its solid form, potassium chloride can be easily dissolved in water and the resulting KCl solution is said to have a salty taste.
Is KClO3 a solid liquid or gas?
Potassium chlorate appears as a white crystalline solid. Forms a very flammable mixture with combustible materials.
Is potassium chloride a solid liquid or gas?
Potassium chloride is an inorganic metal halide composed of a potassium ion and a chloride ion with the chemical formula KCl. It is a odorless white crystal or crystalline powder. As a solid, KCl dissolves promptly in water and its solutions have a salt-like taste.
What state of matter is potassium chloride?
solidPotassium chloride naturally occurs as a white or colorless solid that has a powdery, crystalline appearance. Its chemical formula is KCl, consists of one potassium (K) atom and one chlorine (Cl) atom.
Does KI dissociate in water?
0:241:19Equation for KI + H2O (Potassium iodide + Water) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipHere plus liquid water when we put the solid into the liquid it dissolves into its ions itMoreHere plus liquid water when we put the solid into the liquid it dissolves into its ions it dissociates. So we can write k. Plus that's the potassium cation.
Is potassium iodide insoluble or soluble?
Potassium iodide, an ionic compound, dissolves easily in water but does not dissolve in chloroform and hexane.
Is potassium ion soluble in water?
Potassium is non-water soluble, but it does react with water as was explained earlier. Potassium compounds may be water soluble.
Is potassium chloride a solid or gas?
solidPotassium chloride is an inorganic metal halide composed of a potassium ion and a chloride ion with the chemical formula KCl. It is a odorless white crystal or crystalline powder. As a solid, KCl dissolves promptly in water and its solutions have a salt-like taste.
Is potassium soluble in water?
Potassium is in most foods. It's easily absorbed by the body. Potassium salts dissolve in water (water soluble). It's found in solution as a positively charged particle (cation).
What is KCl solution?
KCl, or Potassium Chloride, is a storage and hydration solution for pH pens and probes. Our Bluelab pH Probe KCl Storage Solution is a storage solution designed specifically for use with Bluelab pH Pens or pH Probes.
What are the properties of KCl?
Physical properties: KCl is an odorless, white crystalline solid, with a density of 1.98 g/mL, a melting point of 770 °C, and a boiling point of 1420 °C. Chemical properties: KCl is highly soluble in water and a variety of polar solvents, and insoluble in many organic solvents.
What is Potassium Chlorate?
Potassium Chlorate is an inorganic compound with chemical formula KClO 3.
What temperature does potassium chlorate react with?
The thermal decomposition of potassium chlorate to obtain oxygen and potassium chloride. This reaction occurs at a temperature of between 150-300 ° C. For this reaction manganese (IV) oxide can be the catalyst.
Is potassium chlorate a crystalline substance?
It appears as a white crystalline substance in its pure form. It is the most widely used chlorate industry. The aqueous solution of potassium chlorate is a colourless liquid that is denser than water. It could be toxic when ingested. When it comes in contact it can irritate your eyes, skin, mucous membranes.
Is potassium chlorate thermal decomposition excessive?
Potassium chlorate thermal decomposition is not excessive, it’s just a redox reaction. Disproportionation refers to the same product that functions both as an oxidizing agent and as a reduction agent, resulting in compounds that contain the same product in different oxidation states.
What is KClO3 in rat kidney?
Sodium chlorate (NaClO3) and potassium chlorate (KClO3) ... were tested for potential promoting effect in two-stage rat renal carcinogenesis. Three groups of 15 male F344 rats each were given N-ethyl-N-hydroxyethylnitrosamine ( EHEN) at the level of 0.05% for the first 2 weeks during the initiation phase. Thereafter, the rats were treated orally for 25 weeks with NaClO3 (1%), KClO3 (1%), or distilled water (DW). Three other groups (controls) were treated similarly, except that DW was given in the initiation phase. All animals survived for the duration of the experiment. Renal neoplastic lesions were classified histologically as dysplastic foci (DF) and renal cell tumors (RCT). The number of these lesions per unit area, in six sections from each kidney, was determined microscopically. There were no statistically significant differences in the incidences and in the mean number of DF and RCT of the kidney between compound- and DW-treated rats initiated with EHEN. It is concluded that NaClO3 and KClO3 show no promoting effect in rat renal carcinogenesis under the conditions of this study.
How is KCl added to sodium chlorate?
Solid KCl is added to the sodium chlorate cell liquor in stoichiometric amounts. The mixture is then transferred to a crystallizer and the potassium chlorate slurry is removed ... The mother liquor is recycled to the cells, where the salt is converted to chlorate and the process is repeated.
What is potassium chlorate used for?
/VET/ In veterinary medicine, potassium chlorate is used as an oxidizing agent, antiseptic, and astringent ... . A 2 to 4% aqueous solution can be used as a weak astringent antiseptic in stomatitis and vaginitis; however, its effectiveness is questionable.
How much potassium chlorate is lethal?
The lethal dose in adults is estimated to be...5 to 30 g for potassium chlorate.
Is sodium thiosulfate a chlorate ion?
Intravenous sodium thiosulfate may inactivate the chlorate ion and has been reported to be successful in a necdotal reports. However, this treatment has not been clinically tested. Administration as a lavage fluid may potentially produce some hydrogen sulfide, and so it is contraindicated. /Chlorates/.
Is potassium chlorate a liquid?
Potassium chlorate, aqueous solution appears as a colorless liquid. Denser than water. Contact may irritate skin, eyes and mucous membranes. May be toxic by ingestion. Used to make other chemicals. Ignites organic materials upon contact .
Is chlorate an oxidant?
Metal chlorates are oxidants in the presence of strong acid; liberates explosive chlorine dioxide gas; liberates chlorine dioxide and carbon dioxide by heating a moist metal chlorate and a dibasic organic acid; mixtures of perchlorates with sulfur or phosphorus are explosives [Bretherick 1979 p. 100]; mixtures of the chlorate with ammonium salts, powdered metals, silicon, sulfur, or sulfides are readily ignited and potentially explosive [Bretherick 1979 p. 806]. A combination of finely divided aluminum with finely divided bromates (also chlorates and iodates) of barium, calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, or zinc can explode by heat, percussion, or friction [Mellor 2:310. 1946-47]. An explosion occurred during heating of a mixture of potassium chlorate and magnesium [Chem. Eng. News 14:451. 1936]. Gaseous ammonia, mixed with air reacts so vigorously with potassium chlorate that the reaction could become dangerous [Mellor 8:217. 1946-47]. A mixture of potassium chlorate and sodium amide explodes [Mellor 8:258. 1946-47]. If a drop of a solution of sulfur dioxide in ether or alcohol is added to powdered potassium chlorate, the mass explodes [Mellor 2:311. 1946-47]. Potassium chlorate and sulfuric acid react to cause fire and possible explosions [Mellor 2:315. 1946-47].