(Age and Sex Distribution)
- Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus is a benign skin condition that may occur in a wide age range of individuals; both children and adults may be affected
- Males and females are affected and there is no gender bias observed
- Individuals of all racial and ethnic background may be affected
Full Answer
What is melanocytic nevus and how to treat it?
Melanocytic nevi are benign neoplasms or hamartomas composed of melanocytes, the pigment-producing cells that constitutively colonize the epidermis. Melanocytes are derived from the neural crest and migrate during embryogenesis to selected ectodermal sites (primarily the skin and the CNS), but also to the eyes and the ears.
Will your nevus develop into a skin issue?
These moles are frequently found on the trunk or limbs, although they can appear anywhere on the body. Most congenital nevi usually do not cause health problems, but a small percentage may develop into skin cancer (melanoma) later in life. The risk of melanoma increases with the size of the nevus.
What is a compound nevus with mild atypia?
Nevi with architectural disorder and cytologic atypia of melanocytes (NAD), aka "dysplastic nevi," have varying degrees of histologic abnormalities, which can be considered on a spectrum of grades of atypia. Somewhat controversial and subjective criteria have been developed for grading of NAD into three categories "mild," "moderate," and "severe."
What does compound melanocytic nevus mean?
The term "Compound melanocytic nevus" is basically a mole with nevus cells (melanocytes). This is basically a mole.

What is a Lentiginous compound nevus?
The term lentiginous junctional nevus is used for junctional nevi in which the epidermis has lentigo-like features with elongated and pigmented epidermal rete ridges. In lentiginous nevi, there is typically a proliferation of solitary units and nests.
Is lentiginous nevus cancerous?
Background: Atypical lentiginous nevus (of the elderly) is a peculiar form of dysplastic nevus. Clinically, this condition can resemble malignant melanoma and histologically, it has a lentiginous pattern with variable degrees of atypia and an absence of dermal nests.
Is a compound nevus benign?
Compound Nevi Typically they are light tan to dark brown, dome shaped papules that are 1-10 mm in diameter. Compound Nevi are benign proliferations of melanocytes at the epidermal-dermal junction.
Is nevus malignant or benign?
A benign (not cancer) growth on the skin that is formed by a cluster of melanocytes (cells that make a substance called melanin, which gives color to skin and eyes). A nevus is usually dark and may be raised from the skin. Also called mole.
Is lentiginous melanoma curable?
Treatment for Acral Lentiginous Melanoma Acral lentiginous melanoma is highly curable when diagnosed early. The goals of treatment are to: cure the cancer. preserve the appearance of your skin.
Can compound nevus turn into melanoma?
Can a dysplastic nevus turn into melanoma? Yes, but most dysplastic nevi do not turn into melanoma (1, 3). Most remain stable over time.
Should compound nevus be removed?
None is usually required. If there has been significant recent growth of intradermal naevi then consider excision biopsy to exclude basal cell carcinoma. Where a previously non-pigmented lesion develops pigmentation then excision biopsy should be carried out.
Does compound nevus grow?
A junctional nevus will typically evolve over time into a compound nevus, which is a nevus with both epidermal and dermal melanocytes. Compound nevi become elevated and usually are more pale. Junctional nevi will typically grow to be 3 or 4 mm across, stop growing sideways, and begin to evolve into a compound nevus.
How do you get rid of compound nevus?
Small nevi can be removed by simple surgical excision. The nevus is cut out, and the adjacent skin stitched together leaving a small scar. Removal of a large congenital nevus, however, requires replacement of the affected skin.
Can compound nevus cancerous?
Prognosis / outcome. Compound moles are normal and harmless and usually persist unchanged without developing into skin cancer.
What is atypical lentiginous nevus?
Atypical lentiginous nevus (of the elderly) is a peculiar form of dysplastic nevus. Clinically, this condition can resemble malignant melanoma and histologically, it has a lentiginous pattern with variable degrees of atypia and an absence of dermal nests.
What does a benign nevus look like?
Most people have between 10 and 40. Common nevi are harmless collections of colored cells. They typically appear as small brown, tan, or pink spots. You can be born with moles or develop them later.
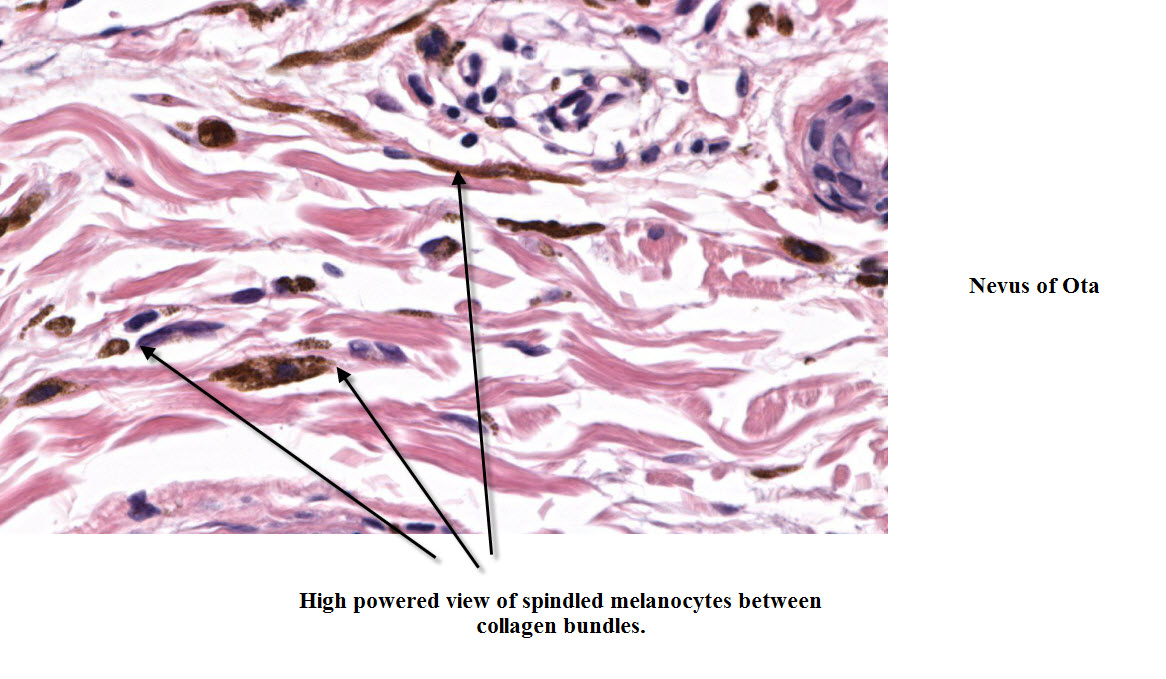
What Is Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus? (Definition/Background Information)
1. A nevus (plural nevi) is a mole on the skin that can occur on any part of the body. A melanocytic nevus is benign tumor of melanocytic (pigment-...
Who Gets Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus? (Age and Sex Distribution)
1. Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus is a benign skin condition that may occur in a wide age range of individuals; both children and adults may be affe...
What Are The Risk Factors For Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus? (Predisposing Factors)
Currently, the following risk factors have been identified for Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus: 1. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome 2. Prolonged sun exposure,...
What Are The Causes of Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus? (Etiology)
1. The cause of development of Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus is unknown. Some researchers believe that it may be due to exposure to sunlight 2. Gen...
What Are The Signs and Symptoms of Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus?
The signs and symptoms of Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus include: 1. It generally occurs as multiple, small, well-defined skin spots 2. The spots ar...
How Is Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus Diagnosed?
A diagnosis of Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus may involve the following: 1. A thorough medical history and physical examination 2. Dermoscopy: It is...
What Are The Possible Complications of Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus?
1. Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus is a common and benign skin condition. It does not cause any significant complication 2. However, some individuals...
How Is Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus Treated?
The treatment of Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus may involve the following: 1. In a majority of cases, removal of the tumor is not necessary, unless...
How Can Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus Be Prevented?
Currently, there are no known methods to prevent Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus occurrence. However, some of the risk factors may be recognized and...
What Is The Prognosis of Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
1. The prognosis for Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus is excellent with appropriate treatment, since it is a benign tumor 2. No malignant transformati...
What causes lentiginous nevus?
The cause of Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus is generally unknown; although the risk factors include sun damage, ultraviolet light exposure , and Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. In a majority of cases, no treatment in necessary, unless it causes worrisome symptoms or cosmetic concerns in the individual. A simple surgical excision of ...
What is a nevus?
A nevus (plural nevi) is a mole on the skin that can occur on any part of the body. A melanocytic nevus is benign tumor of melanocytic (pigment-based) cells that occur on the skin. Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus is described as an early phase in the formation of melanocytic nevus. It is a benign, pigmented skin tumor that chiefly forms on ...
What are the risk factors for lentiginous melanocytic nevus?
Currently, the following risk factors have been identified for Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus: Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Prolonged sun exposure, exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. Use of tanning beds, tanning parlors. Exposure to intense sun for long periods during the course of work or due to regular participation in outdoor sports activities.
Why does nevus develop?
The cause of development of Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus is unknown. Some researchers believe that it may be due to exposure to sunlight. Genetic mutations have been detected in some cases, which are currently being characterized.
Where is nevus found?
The lesions are usually painless and non-itchy. It may appear anywhere on the body, except on the palms and soles. Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus is mostly observed in the chest, back, arms and legs.
Can a lentiginous nevus be removed?
The treatment of Lentiginous Melanocytic Nevus may involve the following: In a majority of cases, removal of the tumor is not necessary, unless it causes bothersome signs and symptoms such as cosmetic issues. The treatment of choice is a complete surgical excision, which can result in a cure.
Can nevus spilus be misdiagnosed?
Note: Lenti ginous Melanocytic Nevus may be misdiagnosed as nevus spilus in some cases, since they are histologically similar to each other.
What is compound nevi?
Compound Nevi are a sub-class of Common Acquired Melanocytic Nevi. Typically they are light tan to dark brown, dome shaped papules that are 1-10 mm in diameter. Compound Nevi are benign proliferations of melanocytes at the epidermal-dermal junction. Common finding in all people, however increased numbers of nevi increase risk for developing ...
Where do compound nevi appear?
In childhood, compound nevi may appear anywhere on the body especially sun exposed areas such as the legs, neck, head, and trunk. In adulthood, they are more likely to appear on the palms, soles, and the genital region. Compound nevi that appear in late adulthood are at increased risk for being malignant.
Is compound nevi a papillomatous?
They are generally smooth, but may appear as hyperkarotic (thickened stratum corneum) plaques or may be papillomatous (wart like appearance). Compound Nevi typically appear in childhood and adolescents and begin to regress in adulthood. There are three types of common acquired melanocytic nevi, Junctional nevi, Compound Nevi, and Intradermal Nevi.
Do melanocytic nevi need to be treated?
Melanocytic Nevi are, by definition, benign and most moles remain benign throughout a person’s lifetime. Therefore, most moles will never need to be treated.
What are benign nevi?
The lesions are benign nevi that are often removed incidentally during pregnancy, often at the time of delivery. They are typically benign clinically, but certain histologic features may arouse a suspicion of melanoma on pathological examination. They are typically symmetrical papular lesions as viewed clinically, most often smaller than a centimeter in diameter, usually uniformly pigmented with discrete well-circumscribed borders. The histologically atypical changes are rare in vulvar nevi; in a comparative histologic study of vulvar nevi compared to controls, all but a few lesions were indistinguishable from control nevi of nonvulvar skin. In this study, biopsies of 85 pigmented vulvar lesions were studied. The nevi were compared to a control series of 200 nevi from the torsos of women 20–60 years old. Three vulvar nevi in women between the ages of 20 and 30 years were considered to be unusual, but not dysplastic. The lesions exhibited notable enlargement of junctional melanocytic nests with variability in the size, shape, and position of the nests. Similar changes were not observed in the control group. There was no evidence of an increased incidence of vulvar dysplastic nevi when compared with the control series. 52
Where are nevus cells found?
In lesions of the face and scalp, it is quite common to observe nevus cells in the lower third of the reticular dermis, a finding that seems to be less common in nevi from other locations and that is considered to be suggestive of a small congenital nevus.
What is nevi on skin?
Nevi on the skin of particular body sites and also in physiological states such as old or young age, or pregnancy may show patterns of junctional and/or dermal proliferation that may deviate from ordinary acquired nevi and cause confusion with atypical and dysplastic nevi, and with melanoma.
What are the characteristics of a dysplastic nevi?
Dysplastic nevi present atypical features both clinically and histologically, and thus are important as simulants of melanoma. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 Clinically, they are characterized by four major properties ( Figure 1 ): Their size tends to be greater than that of common nevi but less than that of melanomas; in the most common definition, dysplastic nevi are 5 mm in diameter or greater. Also by definition, dysplastic nevi contain a junctional component, which clinically is macular or flat, sometimes with a ‘pebbly’ surface. The border of this junctional component tends to be ill defined or ‘fuzzy’, compared to that of a papular compound nevus or even of a superficial spreading melanoma, which tends to have a sharp discrete border. Finally, dysplastic nevi exhibit pigmentary variegation. Shades of tan and brown tend to predominate, in addition to reddish colors. Darker blue—black colors are more usually seen in melanomas and should elicit biopsy. These features have been recently illustrated in an atlas. 8 Dysplastic nevi overlap clinically with the widely used ABCDE criteria for melanoma, 9, 10 in which the letters stand for Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variegation, Diameter >6 mm, and Enlargement or Evolution. However the changes in dysplastic nevi are present in lesser degree. In serial photographic follow-up, dysplastic nevi are stable or may even regress. Thus, they do not display the (E) phenomenon of ‘Enlargement’, or increase in size, nor do they exhibit other sinister changes such as increase in elevation, development of a nodule, bleeding, or ulceration. In a recent study, observers tended to use a ‘gestalt’ of findings, rather than these individual findings taken separately. The so-called ‘ugly duckling’ sign of a lesion that looks different from other nevi on the patient's skin is often the motivation for recognition of a melanoma, whether it be by patients, their relatives or friends, or by physicians. 11
What is a melanocytic nevi?
Melanocytic nevi are benign tumors of melanocytes. Except for occasional cosmetic significance, for the most part, nevi are important only in relation to melanoma. As such, they may have significance as either simulants of melanoma, as markers of individuals at increased risk for melanoma, or as potential precursors for melanoma. Dysplastic nevi are the most important simulants, risk markers, and potential precursors of melanoma. Congenital melanocytic nevi have similar but more limited significance, and the largest of these also have cosmetic significance. Common acquired nevi are also potential simulants, as well as being weak risk markers and potential precursors of melanoma. The degree of atypia exhibited by congenital and common acquired nevi is much less than that in dysplastic nevi, both clinically and histologically. Therefore, with rare exceptions such as the need to distinguish a benign nevus from a nevoid melanoma or a nevoid metastatic melanoma, common acquired nevi do not usually present diagnostic problems as melanoma simulants. Nevi of special sites have been identified as lesions that may simulate dysplastic nevi on the one hand, or melanomas on the other hand. This review will consider the significance of dysplastic nevi and of special site nevi.
What is nevi of special sites?
Nevi of special sites have been identified as nevi that may show atypical features suggestive of a dysplastic nevus or of a melanoma. However, they are not risk markers and they are not malignancies. Nevi of genital skin, acral skin, and flexural skin are among the most important ‘nevi of special sites’.
Why are nevi important?
Nevi are also important as risk markers, identifying individuals at greater risk of developing melanoma in the future. Dysplastic nevi and, to a lesser extent, common acquired and congenital nevi are among the most important melanoma risk markers. Nevi of special sites have been identified as nevi that may show atypical features suggestive ...
Where is Nevi found?
Clinical features. Nevi common on head, neck and trunk in Caucasians, on acral sites in Asians and Afro-Caribbeans. Mostly occur in skin, but also mucosal membranes covered by squamous epithelium. May be neoplastic since many are clonal.
What is a biopsy of nevi?
Biopsy any clinically atypical melanocytic lesions in adults, such as nevi causing chronic mechanical irritation, itching, bleeding, ulceration or oozing of serum, nevi with rapid growth, deepening pigmentation, pigmentation beyond outline of lesion, flat areas of depigmentation or erythema
What color is the melanin in the stratum corneum?
Color: due to Tyndall effect (scattering of light as it hits melanin granules, Wikipedia ); melanin in stratum corneum appears black, melanin in reticular dermis appears slate-gray or blue. Nevi may regress due to lymphocytic infiltration (see halo nevus )
What is a nevus?
A nevus (plural nevi) is a mole on the skin that can occur on any part of the body. An Acral Nevus (AN) is a benign condition that occurs as a pigmented skin lesion on the palms or soles. The lesion is usually a poorly-defined flat mole, less than 1 cm in size. A majority of them arise during childhood and young adulthood.
What are the four patterns of benign acral nevus?
In benign Acral Nevus, the following four dermoscopic patterns can be seen: Parallel furrow pattern : Here, the melanocytic pigmentation is visible on the parallel sulci of the skin marking. Lattice-like pattern: Here, the melanocytic pigmentation follow and crisscross the skin markings.
How old is Acral Nevus?
Acral Nevus is a benign skin tumor that can occur at any age, but is generally noticed between 10-30 years of age. Both children and adults may be observed with this skin tumor. Both males and females are affected and there is no gender bias observed. All racial and ethnic groups are at risk.
Which pattern of pigmentation is evenly and regularly distributed within the pigmented skin lesion?
Globular pattern: Here, the melanocytic pigmentation is evenly and regularly distributed within the pigmented skin lesion in the form of globules (circular) Homogenous pattern: Here, the melanocytic pigmentation is evenly and regularly distributed within the pigmented skin lesion in diffuse light brown or blue color.
Where is the pigmentation on a nevus?
In a benign Acral Nevus, the pigmentation is along the furrows of the skin markings. In early acral melanoma, the pigmentation is present on the ridges of the skin surface markings. It is important to note that such a dermoscopic examination is mainly performed by a trained healthcare professional.
What is the color of a skin lesion?
The presence of a benign, pigmented skin lesion; the color of the lesion is usually light or dark brown. The pigmented areas may be more prominent on the ridges of the skin than on the grooves of the skin (on the palms and soles). This can be detected with lighted magnification of 5X or 10X.
Is a nevus a melanoma?
There are frequently no complications that arise from an Ac ral Nevus. Nevertheless, in some individuals, it may give rise to cosmetic concerns. It may raise a suspicion of a melanoma (a type of skin cancer) in some cases, which may result in undue stress and anxiety.