The AD–AS model can be related to the Phillips curve model of wage or price inflation and unemployment. The AD curve represents the locus of equilibrium in the IS–LM model, also invented and developed by Keynes. The two models produce the same results with a constant price level. What is the ad as framework?
Full Answer
What happens to the LM curve in the IS-LM model?
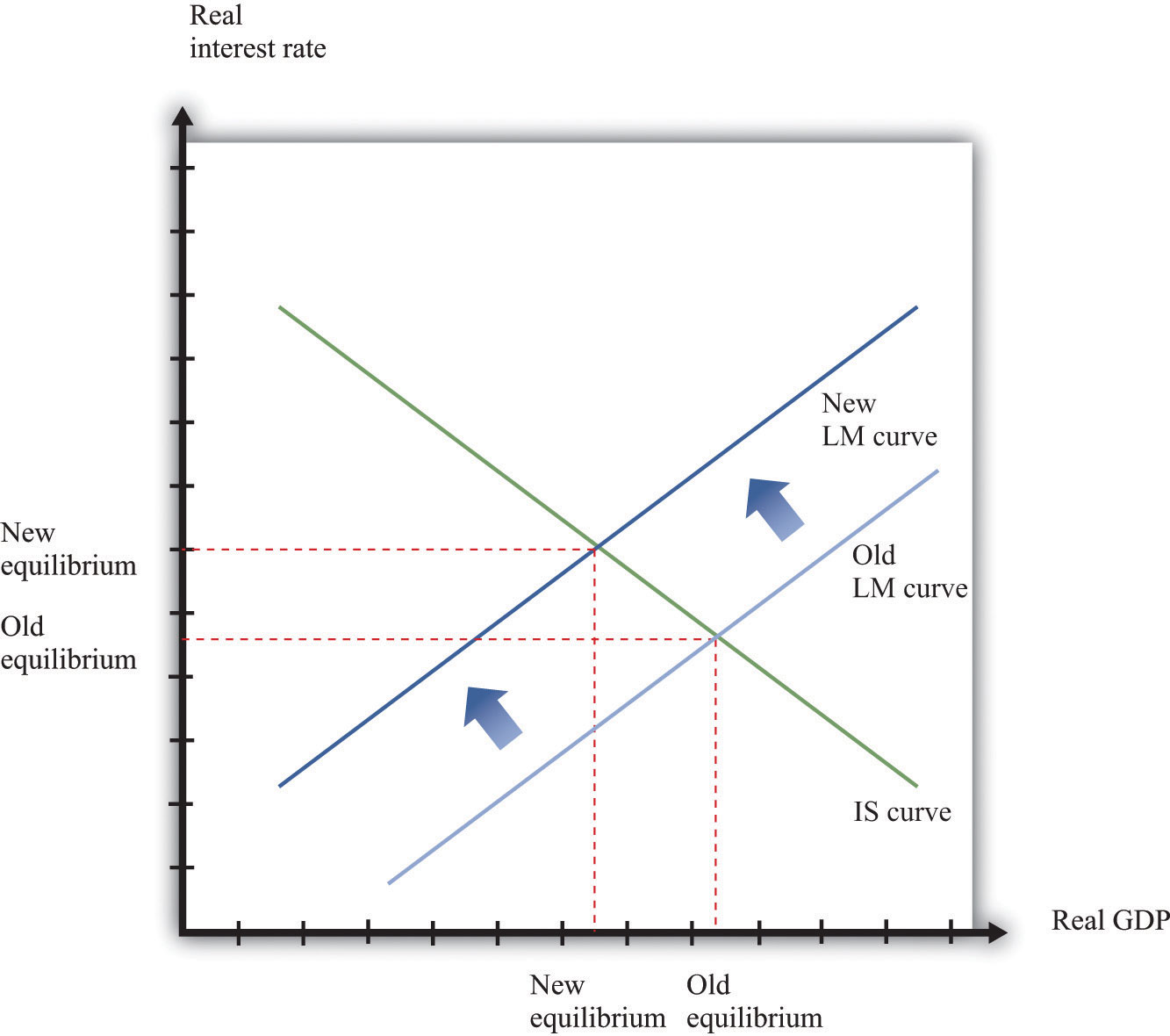
•The LM curve shifts out. An Increase in the Money Supply Equilibrium in the IS-LM Model (Again, ignore the labelling). Aggregate Supply • We have derived a model of the aggregate demand for goods and services. • But we need to also think about the supply side of the economy.
What is the difference between IS-LM and AD-as models?
The IS-LM and AD-AS models are plots of the points where supply equals demand in the markets for goods and for money; the plots purport an intersection at a price for money (IS-LM model) or a price for goods (AD-AS model) at which activities in both markets are in equilibrium.
What is the AD–as model?
The AD–AS or aggregate demand–aggregate supply model is a macroeconomic model that explains price level and output through the relationship of aggregate demand and aggregate supply.
What role do prices play in the IS-LM model?
•This is just the IS-LM model but with a more explicit focus on the role played by prices. •We have just shown that a higher price level means an inward shift in the LM curve. •Money and prices have symmetric effects in the model. A doubling of prices has the same impact as a halving of the money supply.
IS-LM a framework in economics?
The IS-LM model describes how aggregate markets for real goods and financial markets interact to balance the rate of interest and total output in the macroeconomy. IS-LM stands for "investment savings-liquidity preference-money supply."
What is AD-as framework?
The AD/AS framework shows pressures for inflation to rise or fall when the movement from one equilibrium to another causes the price level to rise or to fall. The balance of trade does not appear directly in the AD/AS diagram, but it appears indirectly in several ways.
IS-LM Fe framework?
As the name suggests, the IS-LM-FE model has three components. It looks at the conditions under which the economy reaches general equilibrium, a state of simultaneous equilibrium in the three key component markets of the economy: the labor market, the goods market, and the asset market.
How does LM shift as AD?
It slopes downward because, as the price level increases, the LM curve shifts left as real money balances fall. AD shifts in the same direction as the IS or LM curves, so anything that shifts those curves shifts AD in precisely the same direction and for the same reasons.
Is-LM model and ad as model in Keynesian theory?
The AD curve represents the locus of equilibrium in the IS–LM model, also invented and developed by Keynes. The two models produce the same results with a constant price level.
Why is the ad as model useful?
Summary. The aggregate demand/aggregate supply, or AD/AS, model is one of the fundamental tools in economics because it provides an overall framework for bringing economic factors together in one diagram.
IS-LM vs AS AD?
The AD-AS and the IS-LM models are equivalent. The IS-LM model relates the real interest rate to output. The AD-AS model relates the price level to output. The aggregate demand curve shows the relation between the aggregate quantity of goods demanded (Cd+Id+G) and the price level, P.
IS-LM classical model?
Even though the IS-LM model was developed to express Keynesian ideas, one can express the classical model via IS-LM. In the classical model, the key is that price adjustment brings about equilibrium. Aggregate demand equals aggregate supply, and the economy is at full employment.
IS-LM a model note?
The IS-LM model appears as a graph that shows the intersection of goods and the money market. The IS stands for Investment and Savings. The LM stands for Liquidity and Money. On the vertical axis of the graph, 'r' represents the interest rate on government bonds.
IS-LM to aggregate demand?
The IS-LM model studies the short run with fixed prices. This model combines to form the aggregate demand curve, which is negatively sloped; hence when prices are high, demand is lower. Therefore, each point on the aggregate demand curve is an outcome of this model.
Is the IS curve the AD curve?
More specifically, the AD curve shifts in the same direction as the IS curve, so it shifts right (left) with autonomous increases (decreases) in C, I, G, and NX and decreases (increases) in T. The AD curve also shifts in the same direction as the LM curve.
IS-LM model derive the aggregate demand curve?
To start with we derive the aggregate demand curve from the IS-LM model and explain the position and the slope of the aggregate demand curve. Suppose we hold the nominal money supply constant. Now if the price level (P) rises, the supply of real money balances (M/P) falls.
What shifts the AS AD curve?
The aggregate demand curve, or AD curve, shifts to the right as the components of aggregate demand—consumption spending, investment spending, government spending, and spending on exports minus imports—rise. The AD curve will shift back to the left as these components fall.
How does an expansionary impact the LM curve and why?
Expansionary monetary policy shifts the LM curve down (figure 2). The money supply increases, and the interest rate falls. The economy moves down along the IS curve: the fall in the interest rate raises investment demand, which has a multiplier effect on consumption. Fiscal policy is exogenous.
What affects the slope of the LM curve?
The slope of the LM curve depends upon the income elasticity and the interest elasticity of the demand for money.
IS curve and aggregate demand?
Describing the real sector of the economy, the IS curve represents the condition that aggregate demand equals national product. Whereas in the Keynesian cross model aggregate demand depended only on national income, now it depends as well on the interest rate. The interest rate is the cost of capital to the firm.
How does manipulation affect the IS-LM model?
Any manipulation of the interest rate at the heart of the IS-LM model is double-edged, whereas, as Henry Ford knew, shifts in income distribution are prior and more effective. The manipulation may cause effects which conflict, and at different rates. Higher long term rates which are intended to encourage savings so as to finance greater desirable investment will, at the same time, discourage investment by increasing the costs of investment. Conversely, lower interest rates, intended to discourage saving, encourage full consumption of the bounty of capital, and prevent excess investment, will at the same time encourage borrowing to finance unsound projects, thus sowing the seeds of defaults and bankruptcies. Plus, flooding the redistributive function to achieve lower interest rates (excessive quantitative easing) will cause an increase the values of secondary, previously-issued stocks and bonds amounting to a bifurcation of purchasing power in the operative circuits vs. within the redistributive circuit.
What is Lonergan's theory of macrodynamic equilibrium?
Lonergan discovered a theory which is more fundamental than the traditional wisdom based upon human psychology and imaginary endogenous reactions to external forces. His Functional Macroeconomic Dynamics is a set of relationships between n objects, a set of intelligible relations linking what is implicitly defined by the relations themselves, a set of relational forms wherein the definitive form of any element is known through its dynamic relations to all other elements. His field theory is a single explanatory unity; it is purely relational, completely general, and universally applicable to every configuration in any instance.
What does the second Lonergan diagram represent?
The second and third Lonergan diagrams represent how a normative pure cycle of expansion might play out over time. The horizontal axes of each represent time. The diagrams represent normative, thus equilibrated, differentials of evolutions rather than the textbooks’ comparative snapshots of shocks and shifts.
Is FMD purely relational?
Its basic terms are few and easily handled; they are precisely defined by the functional relations in which they stand with one another; they are of scientific and explanatory significance; and their magnitudes are determinate . F MD is purely relational . It is a dynamical analysis of a dynamic process .
