Is Lutheran a clinically significant blood group?
Is Lutheran a clinically significant? Nine blood group systems (ABO, Rhesus, Kell, Kidd, Duffy, MNS, P, Lewis, and Lutheran) are considered to be clinically significant as these are known to cause hemolytic transfusion reactions (HTR) and hemolytic disease of fetus and newborn (HDFN) [1–4]. Click to see full answer.
What are the main beliefs of Lutheranism?
Lutherans believe that whoever has faith in Jesus alone will receive salvation from the grace of God and will enter eternity in heaven instead of eternity in hell after death or at the second coming of Jesus. The key doctrine, or material principle, of Lutheranism is the doctrine of justification.
What is the prevalence of Lutheran B?
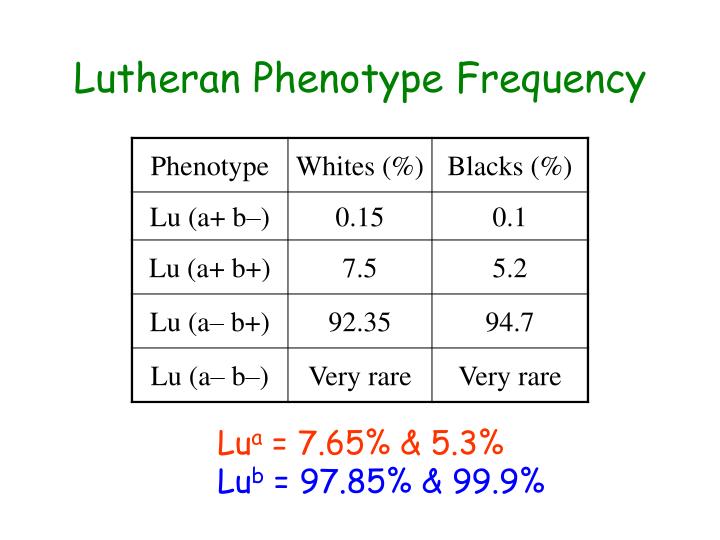
The Lutheran b blood antigen is a high prevalence antigen occurring in 99.8% of Caucasians. Consequently, antibody formation against Lutheran b is very rare.
What is the difference between a Christian and a Lutheran?
They teach that while other Christian churches teach partially orthodox doctrine and have true Christians as members, the doctrines of those churches contain significant errors. More conservative Lutherans strive to maintain historical distinctiveness while emphasizing doctrinal purity alongside Gospel-motivated outreach.
Is Lutheran antibody significant?
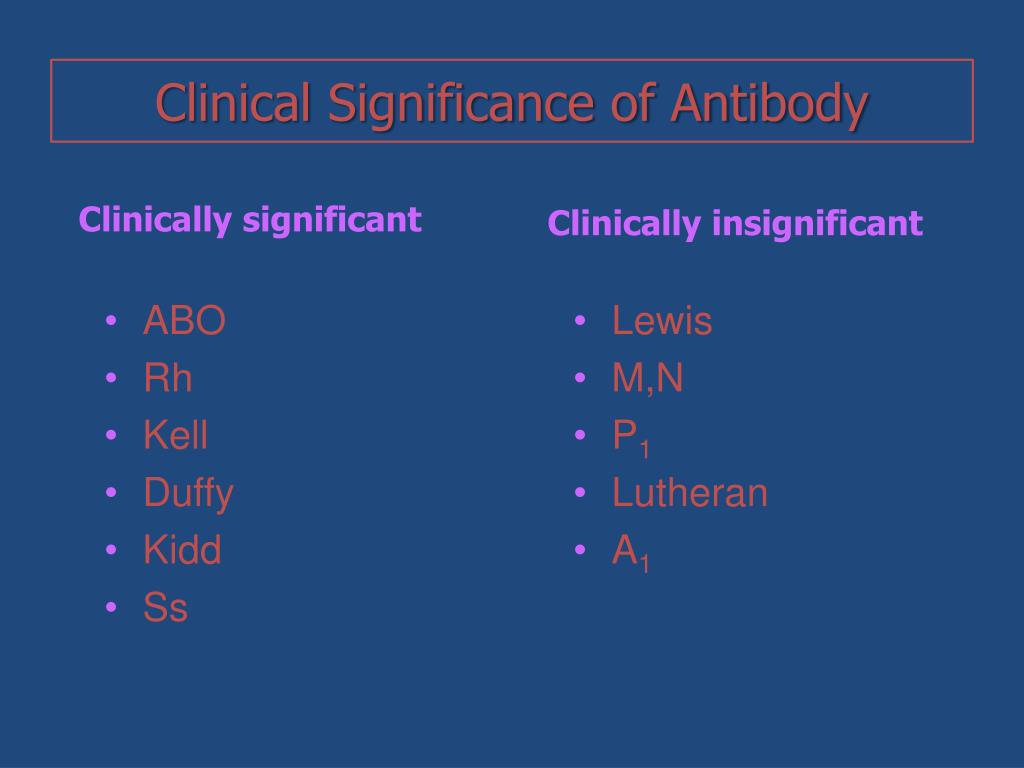
In the context of transfusion, anti-Lua is rarely clinically significant for most patients. It does not contribute to acute hemolytic transfusion reactions and is very rarely associated with mild, delayed hemolytic transfusion reactions and mild hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn (HDFN).
What is the Lutheran blood group?
Abstract. The Lutheran blood group system consists of 19 antigens: four pairs of antithetical antigens--Lu(a)/Lu(b), Lu6/Lu9, Lu8/Lu14, and Au(a)/Au(b)--and 11 antigens of very high frequency. These antigens are located on four of the five immunoglobulin-like domains of both isoforms of the Lutheran glycoprotein.
What are clinically significant antibodies?
A clinically significant antibody can be defined as one capable of causing accelerated destruction of a significant proportion of transfused cells, or one capable of crossing the placenta and causing haemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn.
What is Lutheran antibody?
Abstract. The Lutheran b blood antigen is a high prevalence antigen occurring in 99.8% of Caucasians. Consequently, antibody formation against Lutheran b is very rare. While this antibody can cause hemolytic reactions in adults, there is limited clinical information on its effects on the fetus and newborn.
What's the rarest blood type?
AB negativeWhat's the rarest blood type? AB negative is the rarest of the eight main blood types - just 1% of our donors have it. Despite being rare, demand for AB negative blood is low and we don't struggle to find donors with AB negative blood.
How rare is Lutheran B negative?
The rare blood group phenotype lacking Lutheran antigens, Lu(a-b-), is known to have two genetic backgrounds. Tests on 250000 blood donors show the frequency of Lu(a-b-) to be approximately 1 in 3000.
What antibodies are not clinically significant?
Though anti-M is a frequently encountered antibody of the MNSs blood group system, anti-N is relatively rare. They are not considered to be clinically significant and are very occasionally associated with HTR or HDN.
What is meant by clinical significance?
In medical terms, clinical significance (also known as practical significance) is assigned to a result where a course of treatment has had genuine and quantifiable effects. Broadly speaking, statistical significance is assigned to a result when an event is found to be unlikely to have occurred by chance.
Which red cell antibody is clinically significant?
Most significant antibodies are IgG antibodies rather than IgM. IgG antibodies typically react at or near body temperature (37 C) and are more likely to damage incompatible transfused red blood cells than antibodies that react best at lower temperatures.
What is so special about Rh negative blood?
This protein is also often called the D antigen. When it comes to blood transfusion, anyone who is Rh positive can receive blood from someone who is Rh negative, but those with negative blood types cannot receive from anyone with a positive blood type.
Is anti lub clinically significant?
Anti-Leb is an IgM antibody directed against the Leb antigen in the Lewis blood group system. Anti-Leb is not considered clinically significant and antigen negative blood is not necessary. Units provided are crossmatch compatible through the AHG phase of testing. Pregnancy can cause transient Lewis antibodies to form.
Who discovered Lutheran?
Martin Luther founded Lutheranism, a Protestant religious denomination, during the 1500s.
What is the doctrine of Lutheranism?
The key doctrine, or material principle, of Lutheranism is the doctrine of justification. Lutherans believe that humans are saved from their sins by God's grace alone ( Sola Gratia ), through faith alone ( Sola Fide ), on the basis of Scripture alone ( Sola Scriptura ).
Why do Lutherans believe the Bible is not a part of the Bible?
Although many Lutherans today hold less specific views of inspiration, historically, Lutherans affirm that the Bible does not merely contain the Word of God, but every word of it is, because of plenary, verbal inspiration, the direct, immediate word of God . The Apology of the Augsburg Confession identifies Holy Scripture with the Word of God and calls the Holy Spirit the author of the Bible. Because of this, Lutherans confess in the Formula of Concord, "we receive and embrace with our whole heart the prophetic and apostolic Scriptures of the Old and New Testaments as the pure, clear fountain of Israel." The apocryphal books were not written by the prophets nor by inspiration; they contain errors and were never included in the Judean Canon that Jesus used; therefore they are not a part of Holy Scripture. The prophetic and apostolic Scriptures are authentic as written by the prophets and apostles. A correct translation of their writings is God's Word because it has the same meaning as the original Hebrew and Greek. A mistranslation is not God's word, and no human authority can invest it with divine authority.
What was the state religion of Northern Europe during the Reformation?
During the Reformation, Lutheranism became the state religion of numerous states of Northern Europe, especially in northern Germany and the Nordic countries. Lutheran clergy became civil servants and the Lutheran churches became part of the state.
What is the largest branch of Protestantism?
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism that identifies with the teachings of Jesus Christ and was founded by Martin Luther, a 16th-century German reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the church launched the Protestant Reformation. The reaction of the government and church authorities to the international spread of his writings, beginning with the 95 Theses, divided Western Christianity. During the Reformation, Lutheranism became the state religion of numerous states of Northern Europe, especially in northern Germany and the Nordic countries. Lutheran clergy became civil servants and the Lutheran churches became part of the state.
What did Martin Luther dislike?
Martin Luther always disliked the term Lutheran, preferring the term Evangelical, which was derived from εὐαγγέλιον euangelion, a Greek word meaning "good news", i.e. " Gospel ". The followers of John Calvin, Huldrych Zwingli, and other theologians linked to the Reformed tradition also used that term.
Where did Lutheranism spread?
Lutheranism spread through all of Scandinavia during the 16th century, as the monarch of Denmark–Norway (also ruling Iceland and the Faroe Islands) and the monarch of Sweden (also ruling Finland) adopted Lutheranism. Through Baltic-German and Swedish rule, Lutheranism also spread into Estonia and Latvia .
Who was the Lutheran theologian?
Eck and other Roman Catholics followed the traditional practice of naming a heresy after its leader, thus labeling all who identified with the theology of Martin Luther as Lutherans.
mhinrichs
I work at a reference lab and we recommend crossmatch compatible units for Anti-Lu (a) since it has not been implicated in transfusion reactions AND there is no antisera available to type units.
Malcolm Needs
Just wondering what other places do...... we have a patient with a previously reacting Lua. It is no longer detectable, but now she has built a Kpa. We are screening units for the Kpa and doing coombs crossmatches but there is a question whether we still need to screen these units for the Lua antigen as well.
irshadaad
any antibody found in course of transfusion history of a pt wheather it is visible next time or not the safest is to give blood negative for the one....as the antigens positive for the same anti body will prove to be a booster dose ...........which will create a delayed transfusion reaction in the pt
Malcolm Needs
any antibody found in course of transfusion history of a pt wheather it is visible next time or not the safest is to give blood negative for the one....as the antigens positive for the same anti body will prove to be a booster dose ...........which will create a delayed transfusion reaction in the pt
irshadaad
Mainwaring and pickles 1948 attempted to assess the immmunizing capacity of Lua antigen using Lu (a+) blood for transfusion to eight Lu (a-) pts, after a single transfusion two out of eight deveoped anti-l
Nomenclature
Lu(a-b-) Phenotypes
- In 1961, Crawford et al described a sample of blood that was apparently Lu(a-b-). This proved to be unusual in two ways. Firstly, this apparently Lu(a-b-) individual was Crawford herself; secondly, the red cells were not actually Lu(a-b-), but expressed very low levels of Lutheran BGS antigens (by adsorption and elution), but were inhibited from expressing normal levels of these antigens by a …
Carrier Molecules
- There are two slightly different carrier molecules, both of which are described as being part of the immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF). Each is made up of three constant regions and two variable regions. The first, the Lutheran glycoprotein is of apparent molecular weight of 85kDa, while the second, the basal-cell adhesion molecule (B-CAM) is slightly shorter, with an apparent molecula…
Function
- As might be expected, Lutheran antigens have adhesion properties, and help to mediate intracellular signalling. Elevated levels of both types of Lutheran carrier molecules are found on red cells from sickle cell patients. As sickle red cells adhere to α-5-chain containing laminin preparations, it is possible that adherence of sickle red cells to laminin may be relevant to the va…
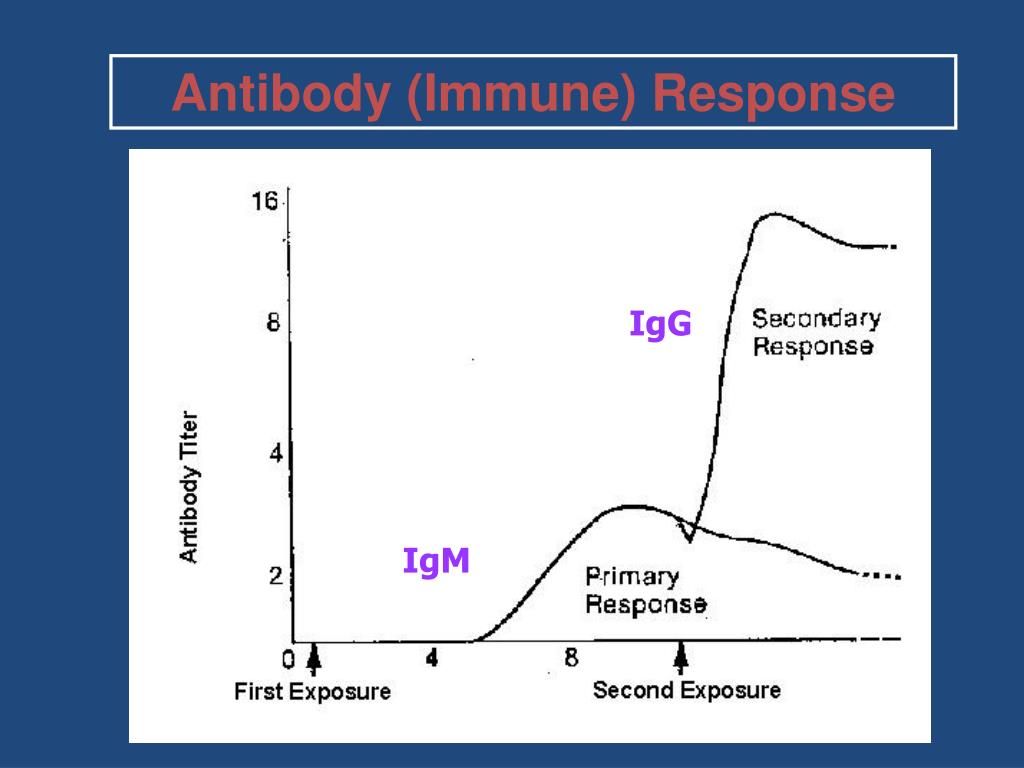
Antibodies and Their Clinical Significance
- Anti-Lua and anti-Lub tend to be IgM and/or IgG (with anti-Luabeing most often IgM). All of the other specificities tend to be found only as IgG (with the possible exception of anti-Lu21, which may contain an element of IgM). With rare exceptions, and where data is available, Lutheran antibodies cause neither a haemolytic transfusion reaction (HTR)...