
How do you calculate monetary base?
What Is the Monetary Base Formula? The formula for monetary base is MB (monetary base) equals current bank reserves added to liquid currency, or MB = R + C. Liquid currency is the amount of money at hand, and bank reserves are money in the banks.
What is the monetary base formula?
They use monetary policies and open market operations to maintain the intended level of MB. What is the monetary base formula? The formula for MB is: MB = C + R Where C is the total value of the currency in circulation and R is the reserve balances. What is the difference between the monetary base and the money supply?
What is the definition of monetary base?
The monetary base refers to the amount of cash circulating in the economy. The monetary base is composed of two parts: currency in circulation and bank reserves. Not to be confused with the money supply, the monetary base does not include non-cash assets, such as demand deposits, time deposits, or checks.
What does the monetary base include?
What is the Monetary Base?
- Understanding the Monetary Base. The monetary base is usually measured by the central bank, which controls the circulation of currency in the economy.
- Monetary Base vs. Money Supply. ...
- Importance of the Monetary Base. Central banks can increase or decrease the monetary base through various forms of monetary policy. ...
- Practical Example. ...
- Additional Resources. ...
Which is considered as monetary base?
The monetary base: the sum of currency in circulation and reserve balances (deposits held by banks and other depository institutions in their accounts at the Federal Reserve).
What is M0 in macroeconomics?
M0: The total of all physical currency including coinage. M0 = Federal Reserve Notes + US Notes + Coins. It is not relevant whether the currency is held inside or outside of the private banking system as reserves.
Is cash M1 or M0?
M1 is the money supply that encompasses physical currency and coin, demand deposits, traveler's checks, and other checkable deposits.
Is M3 considered as monetary base?
M3 is a collection of the money supply that includes M2 money as well as large time deposits, institutional money market funds, short-term repurchase agreements, and larger liquid funds. M3 is closely associated with larger financial institutions and corporations than with small businesses and individuals.
What is M0 and M1?
The smallest and most liquid measure, M0, is strictly currency in circulation and money being kept by banks in reserves; hence, M0 is often referred to as the "monetary base." M1 is defined as all of M0 plus the remaining demand deposits not in reserves as well as traveler's checks; it is often referred to as "narrow ...
How do you calculate monetary base?
The monetary base is either held by the public as currency or held by the banks as reserves: B =C+R. For example, a one-dollar withdrawal from the bank causes C to rise by one and R to fall by one, so the sum is unchanged.
What is M0 M1 M2 M3 M4?
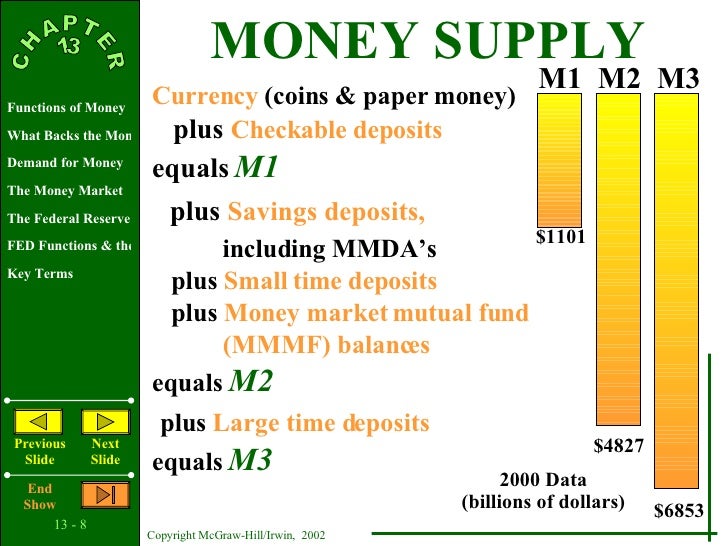
M0 = Currency notes + coins + bank reserves. M1 = M0 + demand deposits. M2 = M1 + marketable securities + other less liquid bank deposits. M3 = M2 + money market funds. M4 = M3 + least liquid assets.
What is monetary base and money supply?
The monetary base in its broadest perspective captures the entirety of currency available for immediate use in an economy, this includes banknotes and coins and commercial bank deposits held in central bank's reserves. The money supply captures all the assets, both liquid and less liquid assets owned by a country.
What is in M1 and M2?
Money is measured with several definitions: M1 includes currency and money in checking accounts (demand deposits). Traveler's checks are also a component of M1, but are declining in use. M2 includes all of M1, plus savings deposits, time deposits like certificates of deposit, and money market funds.
What is M0 and M3?
In short, there are two types of money. Central bank money (M0)- obligations of a central bank, including currency and central bank depository accounts. Commercial bank money (M1-M3) – obligations of commercial banks, including current accounts and savings accounts.
What is M1 M2 and M3 money?
M1, M2 and M3 are measurements of the United States money supply, known as the money aggregates. M1 includes money in circulation plus checkable deposits in banks. M2 includes M1 plus savings deposits (less than $100,000) and money market mutual funds. M3 includes M2 plus large time deposits in banks.
How big is the monetary base?
US Monetary Base is at a current level of 5.582T, up from 5.537T last month and down from 6.329T one year ago.
What is M0 M1 M2 M3?
M0 = Currency notes + coins + bank reserves. M1 = M0 + demand deposits. M2 = M1 + marketable securities + other less liquid bank deposits. M3 = M2 + money market funds. M4 = M3 + least liquid assets.
What is M1 and M2 in macroeconomics?
M1 money supply includes those monies that are very liquid such as cash, checkable (demand) deposits, and traveler's checks M2 money supply is less liquid in nature and includes M1 plus savings and time deposits, certificates of deposits, and money market funds.
What is M1 M2 M3 in economics?
M3 is broad money. M3 = M1 + Time deposits with the banking system. M2 = M1 + Savings deposits of post office savings banks. M1 = Currency with public + Demand deposits with the Banking system (savings account, current account).
What is m5 money?
symbol for. (Economics) the amount of money in circulation given by M4 plus building-society deposits. Also called: PSL2.
What is the monetary base?
Summary. The monetary base refers to the amount of cash circulating in the economy. The monetary base is composed of two parts: currency in circulation and bank reserves. Not to be confused with the money supply, the monetary base does not include non-cash assets, such as demand deposits, time deposits, or checks.
What is the difference between monetary base and money supply?
Monetary Base vs. Money Supply. In comparison to the money supply, the monetary base only includes currency in circulation and cash reserves at a bank. In contrast, the money supply is a broad term that encompasses the entire supply of money in a country. Money supply includes fewer liquid assets, such as demand deposits ...
How much money does Anko own?
In total, Anko’s monetary base would be $500 million.
What is the Federal Reserve?
Federal Reserve (The Fed) The Federal Reserve is the central bank of the United States and is the financial authority behind the world’s largest free market economy. . The two components above account for an economy’s most liquid assets – cash and cash deposits. Overall, the monetary base provides a measure of how much cash currency is circulating ...
What is the tool that central banks use to modify interest rates?
Therefore, adjusting the monetary base is another tool that central banks use to modify interest rates. By using monetary policy to maintain the monetary base, central banks can also ensure that a steady supply of cash is always available for use.
How do central banks increase their monetary base?
For many central banks, the monetary base is increased through the purchase of government bonds, also known as open market operations. By purchasing bonds from commercial banks.
What is the purpose of monetary policy?
Monetary Policy Monetary policy is an economic policy that manages the size and growth rate of the money supply in an economy. It is a powerful tool to. Inflation Inflation is an economic concept that refers to increases in the price level of goods over a set period of time.
What is M0 in banking?
M0 is the sum of Currency in Circulation, Bankers’ Deposits with RBI, and ‘ Other’ Deposits with RBI
What is M3=M2+?
M3=M2+ Term Deposits of residents with a contractual maturity of over one year with the Banking System + Call/Term borrowings from ‘Non-depository’ financial corporations by the Banking System.
What is meant by Monetary Aggregate?
Monetary aggregates are the measures of the money supply in a country.
What are other deposits in RBI?
Note: ‘Other’ deposits with RBI comprise mainly: (i) deposits of quasi-government and other financial institutions including primary dealers, (ii) balances in the accounts of foreign Central banks and Governments, (iii) accounts of international agencies such as the International Monetary Fund, etc.
What is the significance of M1?
Significance of M1: M1 includes currency with the public and non-interest bearing deposits with the banking sector including that of RBI.
What aggregates does RBI use to calculate the money supply?
To understand the money supply in the economy RBI uses monetary aggregates like M0, M1, M2, M3 etc.
What is the new aggregate in RBI?
To distinguish new aggregates from old aggregates, RBI sometimes mentions new aggregates as NM0, NM1, NM2, and NM3.
What does M0 mean in banking?
Direct link to Tejas's post “M0 is not the monetary base (sometimes abbreviated...”. more. M0 is not the monetary base (sometimes abbreviated MB). They measure two separate things, even if they are related. M0 refers to the most liquid form of money: cash. That includes central bank notes and coins.
What is the difference between MB and M0?
That includes central bank notes and coins. MB refers to the base money supply from which banks can extend the money supply. In addition to M0, that also includes central bank deposits, which can't be used to pay anyone other than banks.
What are the two measures of money that are part of the money supply?
In this video, learn about the two measures of money that are part of the money supply: M1 and M2. Topics include what is included in M1 and M2 and the monetary base (which is sometimes called M0). Created by Sal Khan.
What are the two most important measures of money?
First, M1 & M2 have always been the two most important measures of money. In fact, a lot of Economic textbooks don't even bother with the broader definitions of money (beyond merely acknowledging that broader measures exist, at least).
What is M0 in banking?
M0 = Currency in Circulation + Bankers’ Deposits with RBI + Other deposits with RBI. It is the monetary base of economy. Narrow Money (M1):
What is M4 in savings?
M4 = M3 + All deposits with post office savings banks
What is the total stock of money in circulation among the public at a particular point of time called?
The total stock of money in circulation among the public at a particular point of time is called money supply . The measures of money supply in India are classified into four categories M1, M2, M3 and M4 along with M0. This classification was introduced in April 1977 by Reserve Bank of India. Let’s discuss these one by one:

Understanding The Monetary Base
Monetary Base vs. Money Supply
- In comparison to the money supply, the monetary base only includes currency in circulation and cash reserves at a bank. In contrast, the money supply is a broad term that encompasses the entire supply of money in a country. Money supply includes fewer liquid assets, such as demand deposits (money in a checking account), time deposits (CD, GIC), or ...
Importance of The Monetary Base
- Central banks can increase or decrease the monetary base through various forms of monetary policy. For many central banks, the monetary base is increased through the purchase of government bonds, also known as open market operations. By purchasing bonds from commercial banks, the central bank can replace the illiquid bonds with a cash deposit in the ban…
Practical Example
- Let’s suppose that the fictional country of Anko owns $250 million in banknotes and coins circulating for public use. The commercial banks also got $100 million in cash held in their vaults and $150 million in cash reserves held in Anko’s central bank. In total, Anko’s monetary base would be $500 million. Now suppose the Central Bank of Anko decides to increase the monetar…
Additional Resources
- CFI is the official provider of the Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA)™certification program, designed to transform anyone into a world-class financial analyst. To keep learning and developing your knowledge of financial analysis, we highly recommend the additional resources below: 1. Cash Reserves 2. Monetary Policy 3. Inflation 4. Quantity Theory of Money