What is the idea behind Maslows hierarchy of needs?
What is Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs?
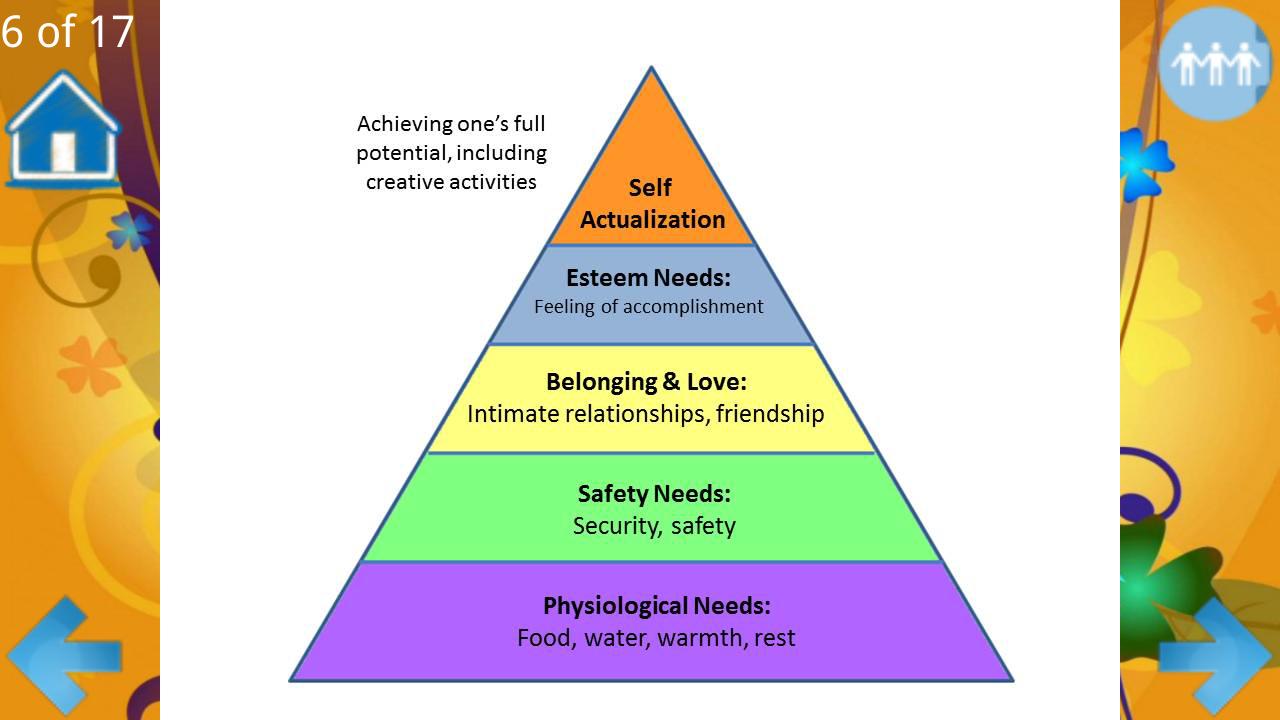
- Physiological Needs are the basic elements the human body needs to survive. ...
- Safety Needs are the items a person needs to feel safe from physical or economic harm.
- Social Needs include the desire to give and receive affection and to be part of a group.
- Esteem Needs have to do with the recognition received from others as well as with self-esteem.
What is the highest need in Maslows hierarchy of needs?
Maslow examined this hierarchy in 5 basic categories. These are physiological needs, the need for security, the need to belong to love, the need for dignity, the need for self-realization. If we open these needs; 1. Physiological needs: Breathing, eating, sleeping, petting. 2 . Security needs: Feeling safe in your family and loved ones. 3.
How accurate is Maslow's hiearchy of needs?
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is wrong. It's wrong in more ways than one, but people keep promoting it as if it is an accurate or helpful model for understanding the human experience and human behaviour. It is not. If you belong to the people who often refer to it, know that you are contributing to suffering and misery.
What is Abraham Marlow theory hierachy of needs?
What is Abraham Maslow hierarchy of needs? Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is a theory of motivation which states that five categories of human needs dictate an individual’s behavior. Those needs are physiological needs, safety needs, love and belonging needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs.
What type of theory is Maslow's hierarchy of needs?
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a theory of motivation which states that five categories of human needs dictate an individual's behavior. Those needs are physiological needs, safety needs, love and belonging needs, esteem needs, and self-actualization needs.
What are the developmental theory?
In general, developmental theories view development as progress from simple to more complex understandings of the self and the world over time. Progress may be continuous in nature, or occurring in stages, but the momentum is most always forward toward greater, more complex understandings.
Was Maslow a developmental psychologist?
Few readily identify Maslow as a developmental psychologist. Both he and the humanistic movement are almost always excluded from developmental textbooks (DeRobertis, 2008), and an EBSCO search in February 2017 yielded a dearth of relevant articles.
Which of the following is not a developmental theory?
From the above, we can conclude that the Theory of conditioned reflex is not a Theory of development.
What are the five major developmental theories?
Erikson's Psychosocial Developmental Theory.Bowlby's Attachment Theory.Freud's Psychosexual Developmental Theory.Bandura's Social Learning Theory.Piaget's Cognitive Developmental Theory.Which Theory of Child Development is Right?
How does Maslow's theory related to human growth and development?
According to Maslow, people will only focus on growth needs after their deficiency needs have been met. An implication of this view is that fewer people manage to satisfy their growth needs than to satisfy their deficiency needs.
Who are the child development theories?
Today we will review the basic theories of Erik Erikson, Sigmund Freud, Arnold Gesell, Lawrence Kohlberg, Abraham Maslow, and Jean Piaget. ERIKSON (ERIK) Erik Erikson developed eight specific stages of personality from birth to old age. He believes that the personality develops continuously throughout the life cycle.
How is Maslow's hierarchy of needs related to early childhood development?
Maslow's hierarchy of needs uses a pyramid to define the different levels of people's needs. 2,3 The most essential needs, which form the base of the pyramid below, must be met before you can support children's higher-level needs like learning, self-esteem, and personal growth.
What is Maslow's hierarchy of needs?
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is a theory of psychology explaining human motivation. Intrinsic Motivation Intrinsic motivation refers to the stimulation that drives adopting or changing behavior for personal satisfaction or fulfillment. Such motivation drives an individual to perform an activity for internal reasons that are personally satisfying, ...
How many levels of Maslow's hierarchy of needs are there?
There are five main levels to Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. These levels begin from the most basic needs to the most advanced needs. Maslow originally believed that a person needed to completely satisfy one level to begin pursuing further levels. A more modern perspective is that these levels overlap.
What happens to motivation when you reach higher levels?
However, though their main focus is on higher levels, they will still continue to pursue lower levels of the hierarchy but with less intensity. Learn how psychology relates to financial analysis.
What is esteem need?
Esteem needs are related to a person’s need to gain recognition, status, and feel respected. Once someone has fulfilled their love and belonging needs, they seek to fulfill their esteem needs. Maslow broke up esteem needs into two categories: the need for respect from others and the need for respect from oneself.
Why is motivation important?
Motivation comes from the need for law, order, and protection from unpredictable and dangerous conditions. There are many examples of safety needs in modern society. To find stability and security, a person must consider their physical safety.
What is the need of a human?
This level of the hierarchy outlines the need for friendship, intimacy, family, and love. Humans have the need to give and receive love; to feel like they belong in a group. When deprived of these needs, individuals may experience loneliness or depression.
When was Maslow's hierarchy of needs first introduced?
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs was first introduced in Abraham Maslow’s 1943 paper, “ A Theory of Human Motivation “. Maslow later refined this theory in 1954 with his book, “ Motivation and Personality “. Since then, this theory has remained a popular subject in sociology, management training. , and psychology classes.
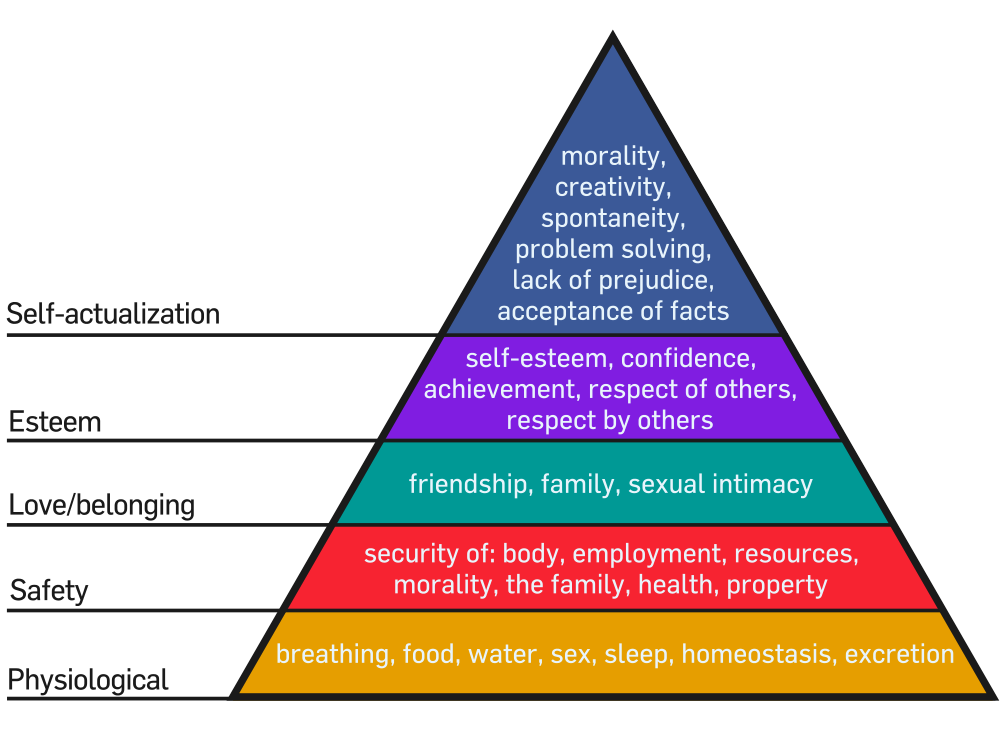
What is Maslow's hierarchy of needs?
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is a motivational theory in psychology comprising a five-tier model of human needs, often depicted as hierarchical levels within a pyramid. From the bottom of the hierarchy upwards, the needs are: physiological (food and clothing), safety (job security), love and belonging needs (friendship), esteem, and self-actualization.
What is Maslow's theory of human needs?
Maslow posited that human needs are arranged in a hierarchy: "It is quite true that man lives by bread alone — when there is no bread.
What did Maslow focus on?
Instead of focusing on psychopathology and what goes wrong with people , Maslow (1943) formulated a more positive account of human behavior which focused on what goes right. He was interested in human potential, and how we fulfill that potential.
What is transcendence need?
Transcendence needs - A person is motivated by values which transcend beyond the personal self (e.g., mystical experiences and certain experiences with nature, aesthetic experiences, sexual experiences, service to others, the pursuit of science, religious faith, etc.).
What are the safety needs?
Safety needs - protection from elements, security, order, law, stability, freedom from fear. 3. Love and belongingness needs - friendship, intimacy, trust, and acceptance, receiving and giving affection and love. Affiliating, being part of a group (family, friends, work). 4.
What are the levels of the 5 stage model?
This five-stage model can be divided into deficiency needs and growth needs. The first four levels are often referred to as deficiency needs ( D-needs ), and the top level is known as growth or being needs ( B-needs ).
What is the growth of self-actualization?
The growth of self-actualization (Maslow, 1962) refers to the need for personal growth and discovery that is present throughout a person’s life. For Maslow, a person is always 'becoming' and never remains static in these terms. In self-actualization, a person comes to find a meaning to life that is important to them.
What is Maslow's hierarchy of needs?
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is an idea in psychology proposed by Abraham Maslow in his 1943 paper "A theory of Human Motivation" in the journal Psychological Review. Maslow subsequently extended the idea to include his observations of humans' innate curiosity. His theories parallel many other theories of human developmental psychology, some of which focus on describing the stages of growth in humans. He then created a classification system which reflected the universal needs of society as its base and then proceeding to more acquired emotions. His theories, including the hierarchy, may have been influenced by teachings and philosophy of the Blackfeet tribe, where he spent several weeks prior to writing his influential paper.
What is the higher order of Maslow's hierarchy of needs?
The higher-order (self-esteem and self-actualization) and lower-order (physiological, safety, and love) needs classification of Maslow's hierarchy of needs is not universal and may vary across cultures due to individual differences and availability of resources in the region or geopolitical entity/country.
What a man can be, he must be?
"What a man can be, he must be." This quotation forms the basis of the perceived need for self-actualization . This level of need refers to the realization of one's full potential. Maslow describes this as the desire to accomplish everything that one can, to become the most that one can be. People may have a strong, particular desire to become an ideal parent, succeed athletically, or create paintings, pictures, or inventions. To understand this level of need, a person must not only succeed in the previous needs but master them. Self-actualization can be described as a value-based system when discussing its role in motivation. Self-actualization is understood as the goal or explicit motive, and the previous stages in Maslow's hierarchy fall in line to become the step-by-step process by which self-actualization is achievable; an explicit motive is the objective of a reward-based system that is used to intrinsically drive completion of certain values or goals. Individuals who are motivated to pursue this goal seek and understand how their needs, relationships, and sense of self are expressed through their behavior. Self-actualization needs include:
What is the need for esteem?
Esteem needs. Most people have a need for a stable esteem, meaning which is soundly based on real capacity or achievement. Maslow noted two versions of esteem needs. The "lower" version of esteem is the need for respect from others, and may include a need for status, recognition, fame, prestige, and attention.
What is transcendence in Maslow's philosophy?
He equated this with the desire to reach the infinite. "Transcendence refers to the very highest and most inclusive or holistic levels of human consciousness, behaving and relating, as ends rather than means, to oneself, to significant others, to human beings in general, to other species, to nature, and to the cosmos " .
What term is used to describe the pattern through which human motivations generally move?
Maslow used the terms "physiological", "safety", "belonging and love", "social needs" or "esteem", and " self-actualization " to describe the pattern through which human motivations generally move. This means that in order for motivation to arise at the next stage, each stage must be satisfied within the individual themselves.
What is the search for one's own intrinsic values?
After all, the latter, according to Maslow, constitutes "an inner, more biological, more instinctoid core of human nature," thus "the search for one's own intrinsic, authentic values" checks the human freedom of choice: "A musician must make music," so freedom is limited to merely the choice of instrument.
What is the theory of human needs?
There are many theories about healthy development and how to care for young children. One of of these particular development models is Maslow's theory of human needs. Originally based upon five key hierarchical stages created by the psychologist Abraham Maslow, these stages help parents and teachers understand how to best take care of young children and their specific needs.
What are the basic needs of a child?
On the base level, biological and physiological needs must first be met before the children can advance to any other level. Some of these needs include basic rights such as food, drink, warmth, shelter, and sleep.
What is the second stage of a child's life?
Safety is the second stage and deals with the need for stability, security, protection, and freedom from fear. Once a child's initial needs are met, they may be more aware of their additional needs in this stage. This awareness manifests itself in areas such as separation anxiety or uncertainty about new activities.
What is Maslow's principle?
The Principle: Abraham Maslow (1908-1970) theorized that a specific series of needs must be met before any child could learn. Current brain research confirms his theory. Below is a brief explanation of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs: Physiological needs: nutrition, sleep, exercise, health; Safety needs: both physical and emotional;
What are the physiological needs of a child?
Physiological needs: nutrition, sleep, exercise, health; Safety needs: both physical and emotional; Love and belonging needs: affection shown to the child, trust of those around him, someone who listens, daily order, a right to privacy, unconditional love;
What is the need for self esteem?
Self-esteem needs: someone affirms the child’s worth, child is given the opportunity to achieve, to make choices, to be successful ; Self-actualization needs: child is developing abilities and strengths, problem-solving skills strengthening. A child who is hungry cannot learn.
Can a child learn if they are hungry?
A child who is hungry cannot learn. A child who is stressed cannot learn. A child who is in an environment absent of unconditional love cannot learn. In fact, the brain of a child who feels emotionally or physically threatened produces chemicals that actually inhibit learning.
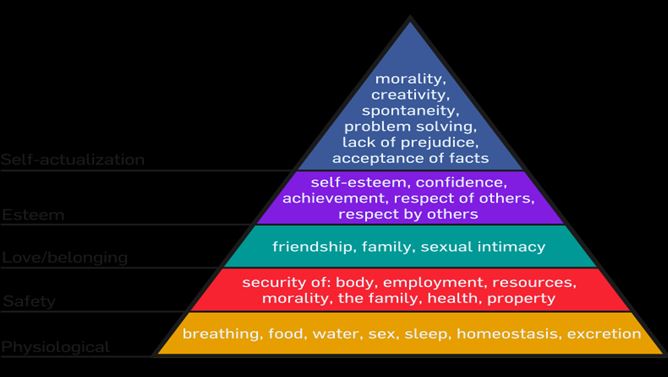
History
Levels of Hierarchy
- There are five main levels to Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. These levels begin from the most basic needs to the most advanced needs. Maslow originally believed that a person needed to completely satisfy one level to begin pursuing further levels. A more modern perspective is that these levels overlap. As a person reaches higher levels, their motivation is directed more toward…
Growth vs. Deficiency Needs
- Maslow separated his hierarchy into two different overarching types of needs: growth needs and deficiency needs. The main difference between growth and deficiency needs is the change in motivation as needs are met. Motivation increases are growth needs are met. Conversely, motivation decreases as deficiency needs are met. As mentioned previously, self-actualization i…
Examples of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
- In general, a person’s motivation lies in the level of the hierarchy that they are currently pursuing. Here are some situations that are examples of this. For example, if a person is lost in the woods, they are likely looking to fulfill their physiological needs. They may be hungry, thirsty, lacking shelter, or cold. This individual would probably not be concerned with their financial security or t…
Additional Resources
- Fulfill your self-actualization needs and become a world-class financial analyst! Corporate Finance Institute has a range of courses and resources that can help you grow and become the best you can be! Check them out below: 1. Financial Modeling & Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® Certification Program 2. Free Financial Analyst Training Courses 3. Investing: A Beginner’s Guide 4. Stock Inv…
Deficiency Needs vs. Growth Needs
The Original Hierarchy of Needs Five-Stage Model Includes
- Maslow (1943, 1954) stated that people are motivated to achieve certain needs and that some needs take precedence over others. Our most basic need is for physical survival, and this will be the first thing that motivates our behavior. Once that level is fulfilled the next level up is what motivates us, and so on. 1. Physiological needs- these are b...
The Expanded Hierarchy of Needs
- It is important to note that Maslow's (1943, 1954) five-stage model has been expanded to include cognitive and aesthetic needs (Maslow, 1970a) and later transcendence needs (Maslow, 1970b). Changes to the original five-stage model are highlighted and include a seven-stage model and an eight-stage model; both developed during the 1960s and 1970s.
Self-Actualization
- Instead of focusing on psychopathologyand what goes wrong with people, Maslow (1943) formulated a more positive account of human behavior which focused on what goes right. He was interested in human potential, and how we fulfill that potential. Psychologist Abraham Maslow (1943, 1954) stated that human motivation is based on people seeking fulfillment and change th…
Characteristics of Self-Actualized People
- Although we are all, theoretically, capable of self-actualizing, most of us will not do so, or only to a limited degree. Maslow (1970) estimated that only two percent of people would reach the state of self-actualization. He was especially interested in the characteristics of people whom he considered to have achieved their potential as individuals. By studying 18 people he considered …
Educational Applications
- Maslow's (1962) hierarchy of needs theory has made a major contribution to teaching and classroom management in schools. Rather than reducing behavior to a response in the environment, Maslow (1970a) adopts a holistic approach to education and learning. Maslow looks at the complete physical, emotional, social, and intellectual qualities of an individual and how th…
Critical Evaluation
- The most significant limitation of Maslow's theory concerns his methodology. Maslow formulated the characteristics of self-actualized individuals from undertaking a qualitative method called biographical analysis. He looked at the biographies and writings of 18 people he identified as being self-actualized. From these sources, he developed a list of qualities that seemed characte…
Overview
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is an idea in psychology proposed by American Abraham Maslow in his 1943 paper "A Theory of Human Motivation" in the journal Psychological Review. Maslow subsequently extended the idea to include his observations of humans' innate curiosity. His theories parallel many other theories of human developmental psychology, some of which focus on d…
Stages
Maslow's hierarchy of needs is often portrayed in the shape of a pyramid, with the largest, most fundamental needs at the bottom, and the need for self-actualization and transcendence at the top. In other words, the idea is that individuals' most basic needs must be met before they become motivated to achieve higher-level needs. However, it has been pointed out that, although th…
History
Maslow's hierarchy of needs was created as Maslow "studied and observed monkeys [...] noticing their unusual pattern of behavior that addressed priorities based on individual needs."
Some indigenous academics have speculated that his theories, including the hierarchy, may have been influenced by teachings and philosophy of the Blackfeet tribe, where he spent several weeks doing fieldwork in 1938; however, while this idea has gained attention on social media, there is n…
Criticism
Maslow's hierarchy of needs has widespread influence outside academia, perhaps because it explains things "that most humans immediately recognize in themselves and others." Still, academically, Maslow's idea is heavily contested. Although recent research appears to validate the existence of universal human needs, as well as shared ordering of the way in which people seek and satisfy needs, the exact hierarchy proposed by Maslow is called into question.
See also
• ERG theory, further expands and explains Maslow's theory
• First World problem reflects on trivial concerns in the context of more pressing needs
• Manfred Max-Neef's Fundamental human needs, Manfred Max-Neef's model
Further reading
• Heylighen, Francis (1992). "A cognitive-systemic reconstruction of Maslow's theory of self-actualization" (PDF). Behavioral Science. 37 (1): 39–58. doi:10.1002/bs.3830370105.
• Koltko-Rivera, Mark E. (2006). "Rediscovering the Later Version of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs: Self-Transcendence and Opportunities for Theory, Research, and Unification" (PDF). Review of General Psychology. American Psychological Association. 10 (4): 302–317. doi:10.1037/1089-2680.10.4…
External links
• "A Theory of Human Motivation", original 1943 article by Maslow.