Hence, the atomic weight of an element is approximately equal to its mass number. The atomic weight of an element in its nearest integer is equal to its mass number. Example: Atomic weight of oxygen-16 is 15.99949 and its mass number is 16. The atomic weight of hydrogen-1 is 1.007825 and its mass number is 1.
What is the formula for calculating atomic mass?
Atomic mass = Number of protons + number of neutrons + number of electrons In other words, when proton, electrons, and neutrons of one atom are added together then this is named as average mass of the atom.
What is average atomic mass and how is it calculated?
What is average atomic mass and how is it calculated? The average atomic mass for an element is calculated by summing the masses of the element’s isotopes, each multiplied by its natural abundance on Earth. When doing any mass calculations involving elements or compounds, always use average atomic mass, which can be found on the periodic table.
How to calculate the atomic weight?
Locate atomic mass on the periodic table.
- Note that the relative atomic masses listed on the periodic table are average values for the associated element. ...
- Relative atomic masses, as listed on the periodic table, are used to calculate molar masses for atoms and molecules. ...
- For example, the atomic mass of iron is 55.847 amu, which means one mole of iron atoms would weigh 55.847 grams.
What is atomic mass and how is it determined?
The atomic mass of the atom is the mass of the protons plus the mass of the neutrons, 6 + 7, or 13. 3) Weighted Average for All Atoms of an Element The atomic mass of an element is a weighted average of all the element's isotopes based on their natural abundance. It is simple to calculate the atomic mass of an element with these steps.

Who discovered the atomic number?
The number of protons (positive charges) in the nucleus of an atom is given by its atomic number. This term was first introduced by Henry Gwyn-Jeff...
How do you find atomic mass from the atomic number and the number of neutrons?
Add the mass of protons and neutrons to calculate the atomic mass of a single atom of an element. The number of protons and the number of neutrons...
Why the atomic number is denoted by Z?
The atomic number symbol, Z, stands for “Zahl,” meaning German number. The symbol Z denoted an element’s place in the periodic table before 1915.
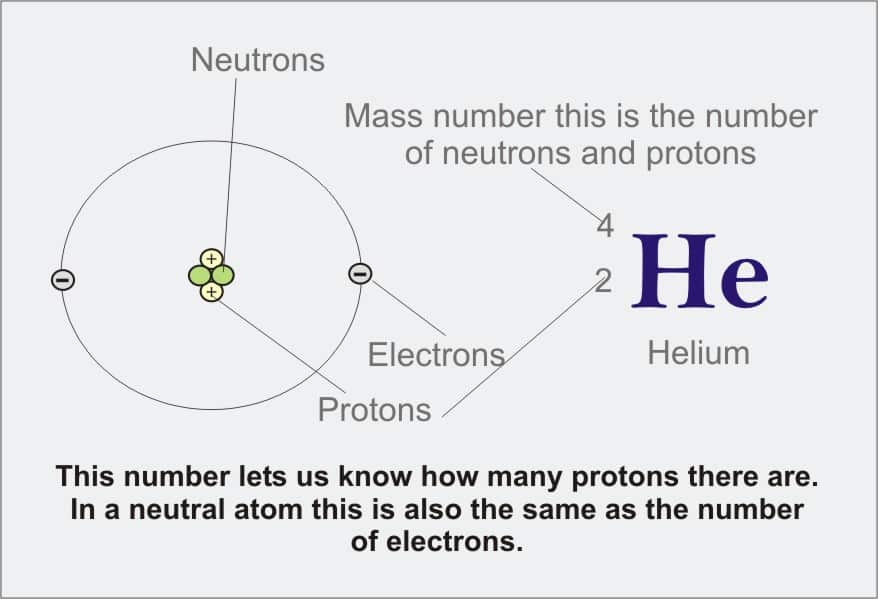
What is the mass number?
The complete amount in the protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. For example, nitrogen has seven protons in its nucleus and seven neutron...
What is an atomic number and mass number?
The number of protons and neutrons combines to give us the mass number of an atom. It is represented using the letter ‘A.’ The atomic number of an...
What is the difference between atomic mass and mass number?
There is a difference between the meanings of the chemistry terms atomic mass and mass number. One is the average weight of an element and the other is the total number of nucleons in the atom's nucleus.
When is the atomic number and mass number the same?
The only time the atomic number and mass number are the same is when you are dealing with the protium isotope of hydrogen, which consists of a single proton. When considering elements in general, remember the atomic number never changes, but because there may be multiple isotopes, the mass number may change.
How to tell the mass of an atom?
Key Takeaways: Atomic Mass Versus Mass Number 1 The mass number is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in an atom. It is a whole number. 2 The atomic mass is the average number of protons and neutrons for all natural isotopes of an element. It is a decimal number. 3 Atomic mass value sometimes change over time in publications as scientists revise the natural isotope abundance of elements.
What is mass number?
The mass number is a count of the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom's nucleus.
Why does the atomic mass change over time?
Atomic mass value sometimes change over time in publications as scientists revise the natural isotope abundance of elements.
Why is the atomic number the key to the periodic table?
The atomic number is the value found associated with an element on the periodic table because it is the key to the element's identity.
How many neutrons does 1 H have?
1 H has 1 proton; its mass number is 1. 2 H has 1 proton and 1 neutron; its mass number is 2. 3 H has 1 proton and 2 neutrons; its mass number is 3. 99.98% of all hydrogen is 1 H. 1 It is combined with 2 H and 3 H to form the total value of atomic mass of hydrogen, which is 1.00784 g/mol.
What is the mass of an atom?
Atomic mass (m a) is the mass of an atom. A single atom has a set number of protons and neutrons, so the mass is unequivocal (won't change) and is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the atom. Electrons contribute so little mass that they aren't counted.
What is the difference between mass and weight?
Mass is a measure of the quantity of a substance, while weight is a measure of how a mass acts in a gravitational field. On Earth, where we are exposed to a fairly constant acceleration due to gravity, we don't pay much attention to the difference between the terms.
Why does atomic weight change?
The atomic weight can change because it depends on our understanding of how much of each isotope of an element exists. Both atomic mass and atomic weight rely on the atomic mass unit ...
When was the atomic weight of the moon first used?
Now, if you take that 1 kg mass to the Moon, it's weight will be less. So, when the term atomic weight was coined back in 1808, isotopes were unknown and Earth gravity was the norm.
Is atomic mass the same as atomic weight?
Atomic weight and atomic mass are two important concepts in chemistry and physics. Many people use the terms interchangeably, but they don't actually mean the same thing. Take a look at the difference between atomic weight and atomic mass and understand why most people are confused or don't care about the distinction. (If you're taking a chemistry class, it could show up on a test, so pay attention!)
Can Atomic Mass and Atomic Weight Ever Be the Same?
If you find an element that exists as only one is otope, then the atomic mass and the atomic weight will be the same. Atomic mass and atomic weight may equal each other whenever you are working with a single isotope of an element, too. In this case, you use the atomic mass in calculations rather than the atomic weight of the element from the periodic table.
What is the atomic mass of an element called?
If the atomic mass of an element is expressed in grams, it is called the gram-atomic mass of that element.
How to find the atomic weight of an element?
To find the atomic weight of an element, the average weight of 1 atom of that element is compared to 1/12 of the weight of one atom of carbon-12. It should be noted that it is comparable to the isotopic mass of 12 mass numbers of carbon (Carbon-12) atom and not natural carbon atom (mixture of Carbon-12 and carbon-13).
What is the atomic mass of 1H1?
An atom of 1H1 is 1.007825 times heavier than 1/12 of an atom of carbon-12, hence the atomic weight of 1H1 is 1.007825. Similarly, atomic weight of 1H2 is 2.0140 and atomic weight of 1H3 is 3.01605. In other words the isotopic masses of 1H1 1H2 and 1H3 are 1.007825 2.0140 and 3.01605 respectively. In the above definition, the use ...
How much mass does a protons have?
The actual masses of protons and neutrons are about 1 amu. The mass of the electron is negligible compared to the mass of these particles.
What is the atomic weight of an element in its nearest integer?
The atomic weight of an element in its nearest integer is equal to its mass number.
How many elements have been discovered?
So far 112 elements have been discovered. Isotopes of all elements are known. Different isotopes of a single element have different mass and their atomic weights.
Is the actual mass of an atom of any element equal to its atomic weight?
On this basis, the actual mass in the amu of an atom of any element is equal to its atomic weight. Similarly, the actual mass in the amu of 1 molecule of any element or additive is equal to its molecular weight.
What is the mass of an atom?
An atom has an atomic number of 9 and a mass number of 19.
How is the mass number of an element determined?
The mass number of an element is determined by the number of protons and neutrons combined. The modern periodic table is arranged in such a way that all the elements have an increasing atomic number, and subsequently, increasing mass number.
What is Atomic Number?
The total number of protons in the nucleus of an atom gives us the atomic number of that atom.
How many electrons are in an atom with 12?
So an atom with the atomic number 12 has an electronic structure 2, 8, 2, with two electrons in the inner energy level, then eight in the next energy level and two in the outer highest energy level. The simplest way to understand these arrangements is to look at lots of examples of them.
What is the difference between isotopes and neutrons?
Isotopes are atoms with the same atomic number but distinct neutron numbers, and hence distinct mass numbers. The average isotopic mass of an isotopic mixture for an element in a defined environment on Earth determines ...
What is the valency of an atom?
Well, as you know, an atom consists of electrons, protons and neutrons. The number of electrons in the outermost shell gives us the valency of the atom. Similarly, the number of protons and neutrons are associated with the atomic number and mass number of the atom.
What is the number of protons in an atom?
The number of protons (positive charges) in the nucleus of an atom is given by its atomic number. This term was first introduced by Henry Gwyn-Jefferies Moseley.
What is the mass number of an atom?
The mass number (symbol A, from the German word Atomgewicht [atomic weight]), 1 also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons (together known as nucleons) in an atomic nucleus.
What is the unit of mass?
The atomic mass (ma or m) is the mass of an atom. Although the SI unit of mass is kilogram (symbol: kg), the atomic mass is often expressed in the non-SI unit dalton (symbol: Da, or u) where 1 dalton is defined as 1⁄12 of the mass of a single carbon-12 atom, at rest
How much smaller is the mass defect per nucleon?
While the mass of a proton and the mass of neutron are both approx. 940 M e V / c 2, the upper graph shows that the mass defect per nucleon is approx. 100 times smaller. Hence, in eq. (1) the mass defect constitutes a 1% effect. This is why the two quantities
Why is the atomic number not equal to the atomic number?
The number calculated from the atomic mass number and the atomic number will not be equal due to the binding energy curve and due to the differences between the proton and neutron mass.
How is energy related to mass?
According to Einstein's formula, E = m c 2, energy is related to mass. Therefore, whenever we have some form of interaction inside the nuclei, the associated energy must be provided by the mass. A simple model is the so called droplet model of the nucleus, which yields a good description of the mass defect. Note, that the mass effect is also the energy which nuclear fusion and nuclear fission rely on. (Image copied from Wiki)
Is mass number the same as atomic mass?
I understand that mass number and atomic mass are different by definition.Mass number is the total number of nucleons and isotopic atomic mass is the average atomic weight of all the known isotopes of the element which should be approximately equal to the weight of the nucleons (ignoring binding energy and negligible mass of electrons).
Does carbon 12 have a number of protons?
The carbon-12 in the definition, has a number of protons and neutrons, and the atomic mass in these dalton units will not be the correct mass, depending on how many protons and how many neutrons there are.
What is the mass number of an atom?
An atom’s mass number, also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons present in an atomic nucleus. Protons and neutrons are collectively known as nucleons. An electron is almost negligible in weight. Thus, the atomic mass of an atom is almost the same as its mass number.
How to determine the mass number of an element?
Knowing the number of neutrons and the atomic number or the number of protons or electrons of an atom, we can determine the mass number of an element.
What happens to the atomic number when an atom is decayed?
In the alpha decay of an atom, the nucleus suffers the loss of two neutrons and two protons in the form of an alpha particle. Thus, the atomic number and the number of neutrons each decrease by 2. For example, uranium- 235 usually disintegrates by alpha decay (Atomic number: 92 → 90 ), and the mass number decreases by 4 (Mass number = 235 → 231 ); this results in an atom of thorium − 231 and an alpha particle.
What is the atomic number of an element?
The atomic number of an element represents the number of protons within the atom’s nucleus which is also equal to the number of electrons in the neutral, non-ionized form of the atom. The atomic number gives a unique identity to each element but not to the isotope. This is because an atom of a given element may have a wide range of neutron numbers. The number of protons and neutrons (nucleons) in the nucleus of an atom together contribute to its mass number. However, each isotope of a given element has a different mass number.
Why do isotopes have different atomic numbers?
This happens due to the difference in their mass numbers, resulting in different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei. As the isotopes of a given element have the same atomic number, they exhibit almost the same chemical properties. However, they differ in their physical properties due to different atomic masses.
What happens to the mass number in gamma rays?
In gamma-ray emission, all the protons and neutrons remain unchanged in the nucleus; the mass number is also unchanged .
How to find neutrons?
To determine the number of neutrons, the atomic number is subtracted from the mass number.
What is the mass of an atom?
An atom has an atomic number of 11 and a mass number of 23.
How to find the number of neutrons in an element?
If the number of protons and the mass number of an element is given, then we can also find the number of neutrons simply by subtracting its atomic number from its mass number as shown below;
How many neutrons does an atom of oxygen have?
For instance, an atom of Oxygen has 8 protons and 8 neutrons in the nucleus of its atom. Thus, its mass number is 8+8= 16.
How many neutrons are in an alpha decay?
The heavier atoms frequently practice alpha decay where they terminate 2 protons and 2 neutrons from their radioactive nucleus respectively, the mass number of elements is then altered consequently.
What is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons?
The sum of number of protons and neutrons is termed as the mass number of an atom.
Is the number of protons always equal to the number of electrons present in a neutral atom?
As the number of protons is always equal to number of electrons present in a neutral atom.
Is the mass number of an atom superscript?
The mass number of the atom goes in superscript of the symbol and the atomic number is written below as a subscript as shown below.
