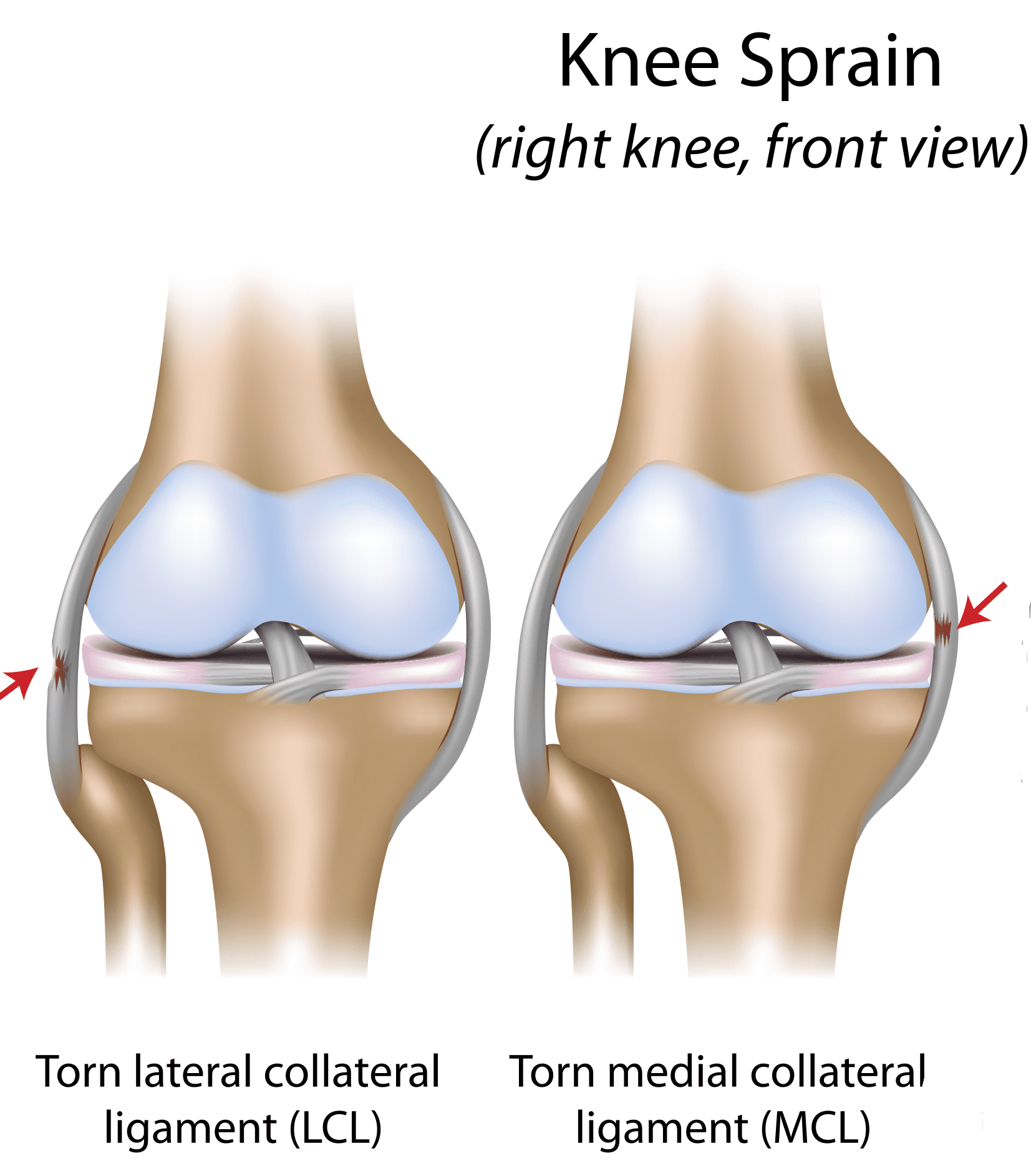
What is the difference between the LCL and MCL?
Similar to the LCL, your medical collateral ligament sits on the side of your knee, but it is positioned on the inside of your knee. Due to its placement in the knee, the MCL is more likely to be injured or torn than the other knee ligaments.
Is the MCL more dangerous than the other knee ligaments?
Due to its placement in the knee, the MCL is more likely to be injured or torn than the other knee ligaments. That being said, it also generally has a quicker recovery timeline.
How do you know if you tore your MCL or LCL?
Blows to the inside of the knee that push the knee outwards may injure the lateral collateral ligament. Symptoms Pain at the sides of your knee. If there is an MCL injury, the pain is on the inside of the knee; an LCL injury may cause pain on the outside of the knee. Swelling over the site of the injury.
Where is the MCL located in the knee?
NB The MCL is also known as the tibial collateral ligament (see image) Provides valgus stability to the knee joint . Is a strong broad band [2] found on the inner aspect of the knee joint and is the largest structure situated on the medial side. [3] The most common ligament injury of the knee. [4]
Is the LCL stronger than the MCL?
However, direct comparison across studies is difficult, as the range in reported strength and stiffness of the LCL is approximately 2-fold greater than that reported for the MCL. Thus, depending on the study, the LCL may be as much as 40% stronger or 40% weaker than the MCL.
Which is worse MCL or LCL tear?
While not always the case, an ACL tear is in most cases going to be the more severe injury. It is considered worse than tearing the MCL because ACL tears are in general more complex to treat and require a longer recovery time after surgery.
Why is MCL more injured than LCL?
Grade 3 Sprains. The MCL is injured more often than the LCL. Due to the more complex anatomy of the outside of the knee, if you injure your LCL, you usually injure other structures in the joint, as well.
What is the strongest ligament of the knee?
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is the strongest ligament in the knee. It extends from the top-rear surface of the tibia (bone between the knee and ankle) to the bottom-front surface of the femur (bone that extends from the pelvis to the knee).
What is the most painful knee injury?
Complete tears are more painful and the patellar tendon completely separates from the kneecap. You won't be able to straighten your knee to walk, and you'll likely need surgery and a few months to recover.
Can you still walk with a torn LCL?
Will LCL tears affect how I walk? For a while, you'll have to use crutches or a knee brace. Your healthcare provider will tell you how long you need to wait before putting weight on your knee. You'll be back to walking normally after your LCL tear heals.
Can LCL heal itself?
A: No specific exercise can help a LCL heal. The ligament will heal on its own, and the main thing to do is to prevent re-injury to the ligament during its healing.
Can I run with a sprained MCL?
Continuing to run will not only prolong your pain but could cause secondary injuries through a change in your gait. Although it may be sore to pressure, your doctor may not be able to demonstrate any local swelling. Depending on how severe the sprain is, there may be an effusion.
Does LCL tear require surgery?
When the LCL is completely torn or not healing with nonsurgical therapy, you may need surgery to reconstruct the ligament. While some LCL injuries can be treated with anti-inflammatory medications as well as conservative treatments such as rest, ice, compression, and elevation, most people will need surgery.
How do I know if I tore my LCL?
The symptoms of a tear in the lateral collateral ligament can include: Knee swelling. Locking or catching of your knee with movement. Pain or tenderness along the outside of your knee.
Is an MCL sprain a tear?
An MCL sprain or medial collateral knee ligament sprain is a tear of the ligament on the inside of the knee. It usually occurs suddenly from twisting or direct impact.
How do you know if you tear your MCL?
If your MCL (medial collateral ligament) is torn, you may experience the following signs and symptoms: Hearing a popping sound at the time of the injury. Experiencing pain in your knee. Having tenderness along the inner side of your knee.
Whats worse LCL or ACL?
The quick answer is that the ACL (Anterior Cruciate Ligament) is most likely to be considered the worst ligament in the knee to tear.
What is the difference between MCL and LCL?
The MCL is the ligament located on the inside of your knee joint. It links your thighbone (femur) and shinbone (tibia). The LCL is the ligament located on the outside of your knee linking the thighbone and calf bone (fibula).
Can you tear LCL and MCL?
The MCL is on the inner side of the knee, while the LCL is on the outer side of the knee. Injury to these ligaments is known as a sprain or tear. Background: Injury to either ligament can be caused by sudden twisting or blows to the knee.
How long does LCL take to heal?
A minor, or grade 1, LCL tear can take from a few days to a week and a half to heal sufficiently for you to return to normal activities, including sports. A grade 2 tear can take from two to four weeks.
Where is the LCL located?
Your LCL is on the outside of your knee, running from the outside of the bottom of the thighbone to the top of your fibula.
How many ligaments are there in the knee?
Your knee is made up of four distinct ligaments, with one on the front, back and each side. Damage to the knee can result in a partial or complete tear of one or more of these ligaments. Below, we take a closer look at each of the four ligaments in the knee, and what an injury to these areas means for your knee and whole body.
What is the final ligament in the knee?
Posterior Cruciate Ligament ( PCL) The final ligament in your knee is known as the posterior cruciate ligament, or PCL. It is located toward the back of your knee and can be injured when your knee joint improperly bends or hyperextends.
Can you heal a MCL injury without surgery?
That being said, it also generally has a quicker recovery timeline. MCL injuries can typically heal without surgery so long as the person sticks to a dedicated rehabilitation plan, which will include anti-inflammatories, rest, strength training and physical therapy.
Can you get a LCL tear from a knee injury?
If you only suffer an LCL tear, you can usually get by with conservative care options like rest, ice, anti-inflammatory medications and physical therapy.
What is the MCL in the knee?
Another of the four main knee ligaments is the medial collateral ligament (MCL). This runs from the bottom of the femur, down the inside of the knee and over the joint to the top of the tibia. Like the ACL, it limits mobility of the knee joint and prevents it opening up too far when pressure is applied to the outside of the knee. Partial or complete tearing of the MCL ligament fibers is known as an MCL sprain. Although it can be injured in isolation, often the ACL is damaged at the same time. The most common cause of an MCL sprain is traumatic force applied to the outer side of the knee, and is an injury often sustained during the playing of contact sports. You can find a brace specifically designed for MCL injuries on this page.
What causes a sprain of the MCL?
The most common cause of an MCL sprain is traumatic force applied to the outer side of the knee, and is an injury often sustained during the playing of contact sports. You can find a brace specifically designed for MCL injuries on this page. A third main knee ligament is the lateral collateral ligament (LCL).
What are the four main ligaments of the knee?
ACL, MCL, LCL, and PCL All Present. One of the four main ligaments of the knee is the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). Together with the posterior cruciate ligament (PCL), it forms an 'X' shape inside the knee joint. The ACL runs from the bottom of the femur at the back of the knee, diagonally through the joint and attaches to the top ...
Which ligament is the least likely to be injured?
It holds the outer surfaces of the joint closely together and limits the sideways movement of the knee. Damage to the ligament fibers of the LCL is known as an LCL tear. Of the four main stabilizing knee ligaments, the LCL is the least likely to be injured.
Where is the ACL located?
The ACL runs from the bottom of the femur at the back of the knee, diagonally through the joint and attaches to the top of the tibia at the front of the knee. It provides stability to the joint by limiting the rotation and forward movement of the tibia underneath the femur. It is very strong but not very flexible.
Can a twisting motion tear the LCL?
Less commonly, a sudden, twisting motion can also tear the ligament. Athletes playing football, soccer or engaging in wrestling are more susceptible to LCL injuries. For an overview of all the braces available here at MMAR Medical for these types of knee injuries, click here.
Is the ACL flexible?
It is very strong but not very flexible. The ligament fibers can be torn by a sudden change of direction, a sudden transference of weight from one leg to the other, as when landing from a jump, a sudden stop, or by straightening the leg beyond the knee's normal range of motion. An injury of this kind is called an ACL tear.
Which is more injured, the MCL or the LCL?
The MCL is injured more often than the LCL. Due to the more complex anatomy of the outside of the knee, if you injure your LCL, you usually injure other structures in the joint, as well. Complete tears of the MCL (left) and LCL (right).
How to tell if you have a MCL injury?
Symptoms. Pain at the sides of your knee. If there is an MCL injury, the pain is on the inside of the knee; an LCL injury may cause pain on the outside of the knee. Swelling over the site of the injury. Instability — the feeling that your knee is giving way.
What is the collateral ligament?
Collateral Ligaments. These are found on the sides of your knee. The medial or "inside" collateral ligament (MCL) connects the femur to the tibia. The lateral or "outside" collateral ligament (LCL) connects the femur to the smaller bone in the lower leg (fibula). The collateral ligaments control the sideways motion of your knee ...
How to protect knee ligaments?
Bracing. Your knee must be protected from the same sideways force that caused the injury. You may need to change your daily activities to avoid risky movements. Your doctor may recommend a brace to protect the injured ligament from stress. To further protect your knee, you may be given crutches to keep you from putting weight on your leg.
Where are the cruciate ligaments located?
These are found inside your knee joint. They cross each other to form an "X" with the anterior cruciate ligament in front and the posterior cruciate ligament in back. The cruciate ligaments control the back and forth motion of your knee.
Can a knee ligament be injured?
Because the knee joint relies just on these ligaments and surrounding muscles for stability, it is easily injured. Any direct contact to the knee or hard muscle contraction — such as changing direction rapidly while running — can injure a knee ligament.
Can you have surgery on your MCL?
Injuries to the MCL rarely require surgery. If you have injured just your LCL, treatment is similar to an MCL sprain. But if your LCL injury involves other structures in your knee, your treatment will address those, as well.
What is the MCL?
Description. The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is a flat band of connective tissue that runs from the medial epicondyle of the femur to the medial condyle of the tibia and is one of four major ligaments that supports the knee. MCL injuries often occur in sports, being the most common ligamentous injury of the knee, ...
What is the most common injury to the MCL?
The MCL is one of the most commonly injured ligaments of the knee. Valgus stress is the most common mechanism of injury. Injuries can be contact (a direct blow to the outer aspect of the lower thigh or upper leg) or non-contact (common in skiing). Contact injuries are usually more severe.
What is the role of the DMCL in knee rotation?
The dMCL helps stabilize internal rotation of the knee from full extension through 90-degree flexion (assists the knee in rotational stability primarily in extension moving through into early flexion).. Despite the relationship of the dMCL with the medial meniscus, there is no influence of the MCL on the stability of the medial meniscus.
What is the most common ligamentous injury in the knee?
MCL injuries often occur in sports, being the most common ligamentous injury of the knee, and 60% of skiing knee injuries involve the MCL) . NB The MCL is also known as the tibial collateral ligament (see image) Provides valgus stability to the knee joint .
How many degrees of flexion is required for MCL testing?
Perform with the knee in approximately 30 degrees flexion rather than extension, ensuring isolated testing of the MCL (flexion helps to relax surrounding structures including the posterior capsule).
What is the VST of MCL?
The VST assesses laxity of the MCL compared to the contralateral knee as a control. An increase in laxity and joint space usually distinguishes damage to the medical collateral ligament.
Which ligament is a primary static stabiliser of the knee and assists in passively stabilising the joint?
The medial collateral ligament is recognised as being a primary static stabiliser of the knee and assists in passively stabilising the joint.
Causes of an MCL sprain
An MCL sprain often happens when the knee joint is pushed beyond its normal range of motion. It's most common during a blow to the knee from the outside, pushing the knee inward. It may also happen if the knee is forced into a twist. These movements stretch and tear the MCL. Other parts of the knee may be damaged along with the MCL.
Treatment for an MCL sprain
Treatment will depend on the severity of the sprain and whether there is damage to other parts of the knee. Options often include:
Why is my pes anserinus misdiagnosed as MCL?
It oftens misdiagnosed as MCL or medial-meniscus strain. This is because of the close location of the pes anserinus tendon to the MCL and medial meniscus.
Which muscle is the longest in the human body?
1 Ed note. The Sartorius is the longest muscle in the human body
Why is the MCL running on the inside of the body?
Running on the inside of the body, the MCL is designed to prevent or protect the knee from lateral or sideways movement. This is something that can be hazardous for a joint of this kind. When a force like this interferes with the knee (such as pivoting), the MCL, as well as other ligaments, become under strain.
What is the best compression knee sleeve for MCL?
Obviously there are plenty of choices, but the PentagonFit Plus Size Compression Knee Sleeve is the best choice to provide the support, comfort and stability you need to continue to be active while you deal with whatever MCL issues you’re having.
Which knee brace is the most flexible?
Level 1 knee braces are the most flexible kind. However, they don’t offer as much support as other levels. Although level 2 knee braces offer more protection, they aren’t as flexible as level 1. Having said this, it’s rare that braces of level 1 or 2 support restrict movement to a high degree.
Is Lycra a hydrogel?
Lycra is a durable fabric used for sporting gear, so there’s that. But, these cocoons are also double-stitched and have leakproof hydrogels.
Does Mycocoon work on knees?
Designed for any knee injury, Mycocoon uses weighted compression to heal the body while also using hydrogel that can be both heated or frozen to provide pain relief on the go.