
What does medial rotation mean?
Thus, a medial rotation is the movement of a limb or muscle group toward the center of the body. Medial rotation is a type of movement that is considered in job design and in ergonomic evaluations in order to ensure that repetitive stress of rotation on a body part, or muscle group, does not pose a significant injury risk.
How to fix tibial external rotation?
- Lie down on your stomach with both legs extended. Place your palms flat on the floor under your chin.
- Keep your left leg extended.
- Gently lift your right knee off the floor.
- Repeat 20 to 30 times, and then switch legs.
How to improve shoulder internal rotation?
- to best improve internal rotation focus oscillations at
- shoulder IR
- shoulder abduction
- elbow extension
- advanced progression - load into radial nerve stretch, then perform IASTM, STM or joint mobs into posterior glide/inferior glide
What is the definition of internal rotation?
Internal rotation is defined relative to a fixed body position known as anatomical position. In anatomical position, the body is upright with feet together, arms at the sides, and forearms supinated or palm-forward.
Is internal rotation the same as medial?
In anatomy, internal rotation (also known as medial rotation) is an anatomical term referring to rotation towards the center of the body.
What is referred to as internal rotation?
Internal rotation is rotating a joint towards the midline and external rotation is rotating a joint away from the midline.
What is medial internal rotation?
Internal or medial rotation of the arm represents the movement of the humerus when an arm flexed to 90° at the elbow is internally rotated around the longitudinal plane of the humerus such that the hand moves towards the midline of the body.
Is medial rotation the same as external rotation?
Internal rotation (sometimes called medial rotation) and external rotation (sometimes called lateral rotation) differ from pronation and supination by the location of the rotation; unlike pronation and supination, there is no movement in the lower arm.
What does medial rotation look like?
0:442:19Rotation Anatomy Body Movement Term | Arm, Thigh, Head ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipPosition is going to be medial rotation of the head the vertebral column can also rotate laterallyMorePosition is going to be medial rotation of the head the vertebral column can also rotate laterally to either the left or the right. And returning the trunk toward the anatomical.
What is medial rotation of the hip?
Medial rotation of the thigh or hip brings the knee and foot medially. Muscles: gluteus medius and minimus, and the adductors (longus, brevis, magnus).
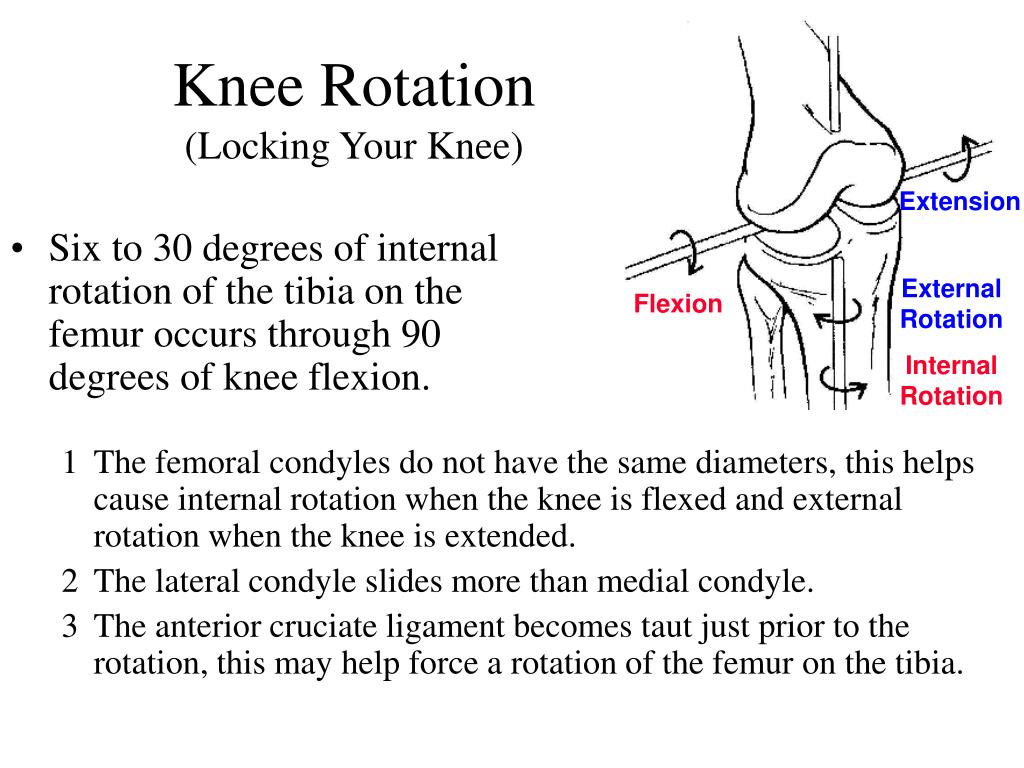
What is medial rotation of the knee?
Introduction. Medial and lateral rotation at the knee joint is the inward or outward rotation of the tibia in relation to the femur. This motion also can contribute to the abduction or adduction of the foot.
What is the difference between medial rotation and pronation?
With the forearm, supination refers to turning the palm up; pronation refers to turning the palm down. Medial rotation turns toward the center of the body as in internal rotation; lateral rotation turns away from the body externally. Inversion turns the foot in; eversion turns the foot out.
What muscles do internal rotation of knee?
Tibial rotation can occur during passive knee flexion and extension. During daily activities, many muscles are used in tibial internal rotation, such as the popliteal muscle, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, sartorius, and gracilis, and in external rotation, such as the biceps femoris and vastus lateralis [10],[11].
Is lateral rotation internal or external rotation?
In anatomy, internal rotation (also known as medial rotation) is rotation towards the centre of the body. External rotation (or lateral rotation) is rotation away from the centre of the body.
What joints have internal and external rotations?
The ball-and-socket joint of the shoulder allows the humerus of the arm to rotate laterally, or away from the body's midline, which is also called external rotation. It can also rotate medially, or toward the body's midline, which is also called internal rotation.
What muscles perform internal rotation of the shoulder?
Internal Rotators The primary muscles that internally rotate the GH joint are the teres major, pectoralis major, subscapularis, latissimus dorsi, and anterior deltoid. Many of these muscles are also powerful shoulder extensors and adductors. Often, lifting activities incorporate all of these actions.
What is internal and external rotation?
Your shoulder is capable of two kinds of subtle rotation, internal rotation and external rotation. Internal shoulder rotation involves rotating your upper arm toward the front side of your torso. External rotation involves rotating it away from the front side of your torso.
What muscles do internal rotation of shoulder?
Internal Rotators The primary muscles that internally rotate the GH joint are the teres major, pectoralis major, subscapularis, latissimus dorsi, and anterior deltoid. Many of these muscles are also powerful shoulder extensors and adductors. Often, lifting activities incorporate all of these actions.
What muscles does internal rotation work?
The internal rotation exercise targets the subscapularis muscle which is a very important muscle of the rotator cuff. The rotator cuff muscles help to provide stability for the shoulder joint. The main function of the subscapularis is to rotate the humerus, or long arm bone, inwards towards the body.
What muscles do internal rotation of knee?
Tibial rotation can occur during passive knee flexion and extension. During daily activities, many muscles are used in tibial internal rotation, such as the popliteal muscle, semitendinosus, semimembranosus, sartorius, and gracilis, and in external rotation, such as the biceps femoris and vastus lateralis [10],[11].
Anatomical Parts
Rotation is a form of movement in which a bone moves around a central axis without undergoing any displacement from this axis; the axis of rotation may lie in a separate bone, as in the case of the pivot formed by the odontoid process of the axis vertebræ around which the atlas turns; or a bone may rotate around its own longitudinal axis, as in the rotation of the humerus at the shoulder-joint; or the axis of rotation may not be quite parallel to the long axis of the bone, as in the movement of the radius on the ulna during pronation and supination of the hand, where it is represented by a line connecting the center of the head of the radius above with the center of the head of the ulna below..
Description
Rotation is a form of movement in which a bone moves around a central axis without undergoing any displacement from this axis; the axis of rotation may lie in a separate bone, as in the case of the pivot formed by the odontoid process of the axis vertebræ around which the atlas turns; or a bone may rotate around its own longitudinal axis, as in the rotation of the humerus at the shoulder-joint; or the axis of rotation may not be quite parallel to the long axis of the bone, as in the movement of the radius on the ulna during pronation and supination of the hand, where it is represented by a line connecting the center of the head of the radius above with the center of the head of the ulna below..
What is the movement of the hip called?
Adduction is a movement towards the midline. Adduction of the hip squeezes the legs together.
What is eversion in physics?
Eversion involves the movement of the sole away from the median plane – so that the sole faces in a lateral direction.
What is the movement of the back when lying flat on the back?
This is the supine position, and so this movement is supination. Again, keeping the elbow and shoulder still, flip your hand onto its front, palm down. This is the prone position, and so this movement is named pronation. These terms also apply to the whole body – when lying flat on the back, the body is supine.
How to do supine position?
With your hand resting on a table in front of you, and keeping your shoulder and elbow still, turn your hand onto its back, palm up. This is the supine position, and so this movement is supination. Again, keeping the elbow and shoulder still, flip your hand onto its front, palm down.
What is the movement of the foot around its long axis called?
Inversion and Eversion . Inversion and eversion are movements which occur at the ankle joint, referring to the rotation of the foot around its long axis. Inversion involves the movement of the sole towards the median plane – so that the sole faces in a medial direction.
What is extension in anatomy?
Extension refers to a movement that increases the angle between two body parts. Extension at the elbow is increasing the angle between the ulna and the humerus. Extension of the knee straightens the lower limb.
What is elevation in psychology?
Elevation refers to movement in a superior direction (e.g. shoulder shrug), depression refers to movement in an inferior direction.
What is the best position to swing a golf club?
When applied correctly, external rotation of the right arm will enable you to achieve the perfect top of the backswing position, where your right triceps are touching your right pectorals, and your right forearm is near vertical. It facilitates a much simpler swing, and helps you to get the golf club perfectly on plane.
What happens to your arm during the transition phase?
The external rotation of your right arm increases slightly during the transition phase, as your right arm moves ahead of your hands and club, stretching your lats, pectorals and deltoid for added power in the downswing. Late in the downswing, your right arm internally rotates as your right elbow extends coming into impact, ...
How to stretch your arm when you swing?
A great stretch for this shown in Figures 7 and 8 . Stand with your right arm bent at the elbow, at about 100 degrees, and with your elbow up in front of, and a little lower than, your shoulder. This position mirrors the position of your right arm at the top of the backswing. Then hold a golf club in your fingers and down the outside of your humerus, just above the elbow. Hold the bottom end of the club with your left hand (see Figure 7) and pull gently, keeping your elbow still, to stretch the external rotation of your right arm — see Figure 8.
How to get golf club on plane?
It enables you to generate more width and to get the club on-plane more simply, just by bending your right elbow as you move towards the top of the backswing.
Which way do you rotate your elbow?
This means rotating the front of your elbow counter-clockwise for your right arm, or clockwise for your left arm. The muscles involved in the internal rotation of the arm are the subscapularis, latissimus dorsi, teres major, pectoralis major, and the anterior fibres of the deltoid.
What is the power of the right hand in golf?
This power is why the right hand is often referred to as the “speed hand ” in the golf swing.
Why should the back of my left elbow be facing the target?
The back of your left elbow should be facing the target at impact to avoid injury and discomfort (golfer’s elbow) caused by the vibrations of the golf club as it strikes the ground. The precise angle of the club face through impact is controlled by supinating your left wrist rather than rotating the arm, this promotes stability and control.
What is medial rotation?
Medial rotation The act of turning about an axis passing through the center of the leg, which occurs with closed chain pronation; the talus acts as an extension of the leg in the frontal and transverse planes. Cf External rotation.
What is the function of the rotator cuff?
In this way, the rotator cuff stabilizes the glenohumeral joint, controls humeral head translation, and performs multiple functions including shoulder abduction, internal rotation, and external rotation.
Which fluoroscopic view is most useful?
The most useful "live" fluoroscopic view according to the majority of survey participants is the obturator oblique while testing the hip in flexion, adduction, and internal rotation with axial load applied to the femur.
Does MTSS cause higher internal rotation range?
reported that higher internal rotation range, more plantar flexion and positive navicular drop test are related to prevalence of MTSS while higher BMI just prolongs recovery time (20).
Does hip adduction decrease?
Strong evidence was found for a decrease in hip external rotation, abduction, and extension strength, moderate evidence for a decrease in flexion and internal rotation strength, but no evidence for a decrease in hip adduction strength compared with healthy controls.
Where is the movement of a joint?
Movement of a joint, around its long axis, toward the midline of the body.
Is the internal rotation of the tibia relative to the femur positive or negative?
Internal rotation of the tibia relative to the femur was denoted as positive and external rotation was negative.
What pulls the inferior portion of the scapula toward the thorax?
The triangular-shaped inferior fibers of the serratus as well as the tendinous attachment to the inferior aspect of the scapula will pull the inferior portion of the scapula toward the thorax. When the lower trapezius and the serratus anterior contract together, the scapula will rotate on its axis posteriorly, giving us the action of tilting.
What is posterior tilt?
Posterior tilt occurs around an axis that goes through the glenoid and spine of the scapula. It is a result of coupled motion between the lower trapezius and serratus anterior. 15, 16, 17 If you are confused as to how the serratus anterior functions differently in this case compared to upward rotation, let’s look at the anatomy to help create some clarity.
Why do scapular spines rotate?
These rotations only occur due to the clavicular attachment connecting the scapula to the manubrium. This anatomical construct is why the scapular rotations are accessory motions—in other words, involuntary. While you do not consciously control your ability ...
What is external rotation?
External rotation occurs around a vertical axis that bisects the supraspinous fossa. It occurs as a result of coupled motion between the rhomboids and serratus anterior. 18, 19, 20, 21
Which muscle is attached to the medial scapula?
The diagonal orientation as well as the attachment of the lower trapezius to the medial scapula at the scapular spine helps us see that when the muscle contracts toward the vertebral column, the scapula will be pulled inferiorly. It needs assistance from the serratus anterior, but this time the inferior fibers perform this action.
Which part of the body is positioned to assist the middle trapezius and serratus anterior?
The upper trapezius, which has a limited and distal attachment site, is well positioned to assist the middle trapezius and serratus anterior by elevating the acromion while the lower trapezius stops excessive elevation from occurring.
Which direction does the serratus anterior rotate?
Since the muscle attaches on the upper portion of the bone, the bottom portion will, in turn, rotate laterally and in an upward direction. Similarly, the serratus anterior has a broad, multi-directional fibrous design. Hopefully, you can envision this as when the arm moves into flexion or abduction, the upper fibers of the serratus, ...

Internal Rotation
- Anatomical terms are used to divide the body into distinct sectors and identify motions about these sectors. Beginning with an assumption of a fixed anatomical position, movements are described with reference to set sectors or locations. Medial rotation refers to a rotational movement toward the median plane.
External Rotation
Internal and External Rotation of The Arms in The Golf Swing
You May Also Like…