Do proton pump inhibitors inhibit metformin?
Is metformin an insulin inhibitor? Metformin is regarded as an antihyperglycemic agent because it lowers blood glucose concentrations in T2D without causing overt hypoglycemia. Metformin is also frequently described as an insulin sensitizer leading to reduction in insulin resistance and significant reduction of plasma fasting insulin level.
What type of drug is metformin?
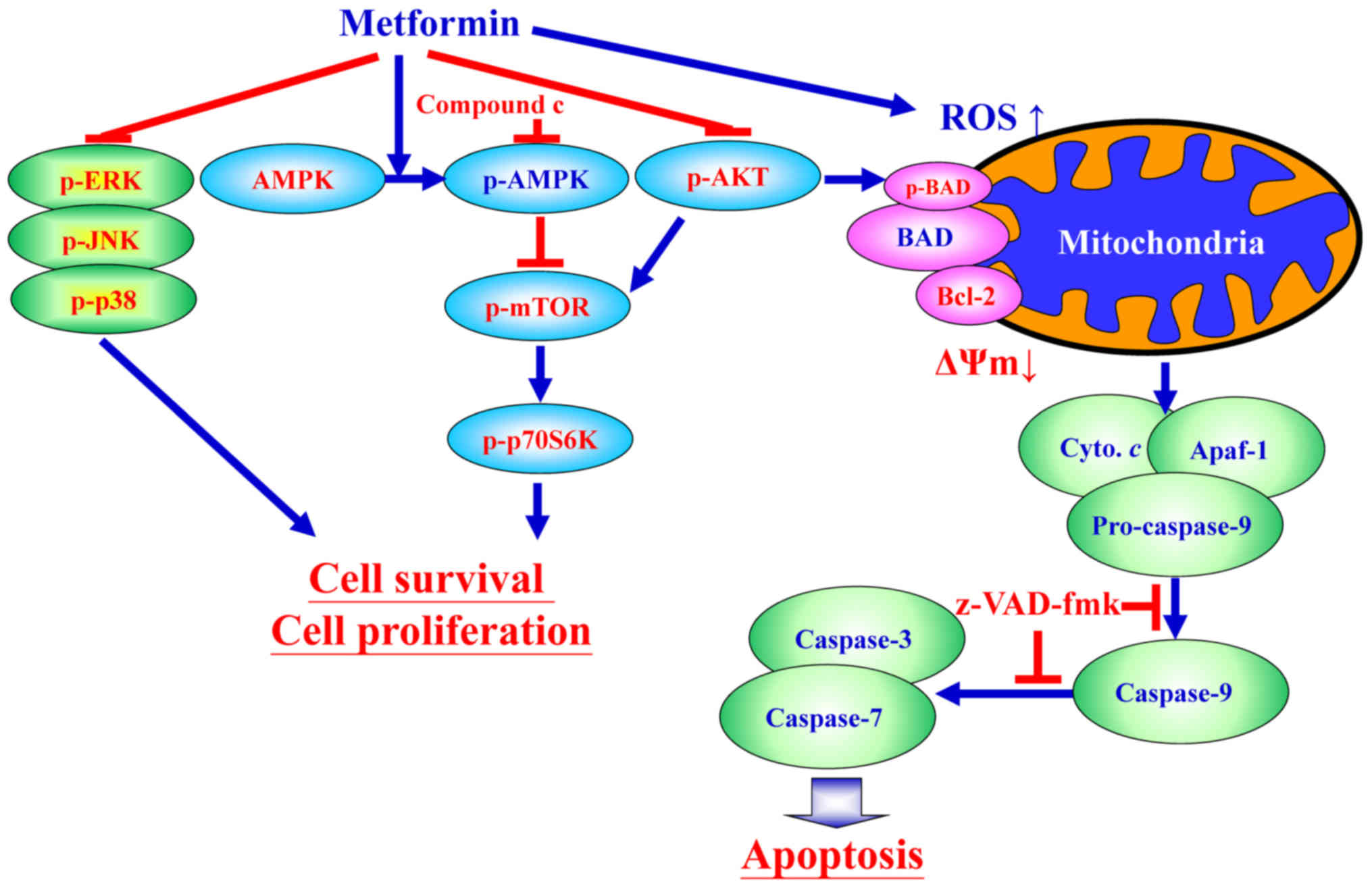
Since most of the effects of metformin have been replicated by other inhibitors of Complex I, it has been suggested that the mechanism of action of metformin involved the inhibition of Complex I. However, compared to conventional Complex I inhibitors, the metformin-induced inhibition of Complex I has unique characteristics.
What is the mechanism of action of metformin?
Apr 21, 2022 · Metformin is a Workhorse for Type 2 Diabetes. Metformin, the generic name commonly known by other brands such as: Glumetza. Riomet. has been available for the oral treatment of type 2 diabetes since 1995. Metformin helps to control blood sugar (glucose) levels and is sometimes used in combination with insulin or other medications.
Does metformin have anticancer properties?
The FDA has approved fixed-dose combination (FDC) tablets with each of the three available SGLT2 inhibitors (canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and empagliflozin) and metformin. Both drug classes are associated with the rare but serious life-threatening complications that result from metabolic acidosis, including lactic acidosis (with metformin) and euglycemic diabetic …
What type of inhibitor is metformin?
What is the main action of metformin?
Is metformin a glucose inhibitor?
Is metformin competitive or allosteric inhibitor?
When Should metformin be stopped?
What drugs should not be taken with metformin?
- diuretics, such as acetazolamide.
- corticosteroids, such as prednisone.
- blood pressure medication, such as amlodipine (Norvasc)
- anticonvulsants, such as topiramate (Topamax) and zonisamide (Zonegran)
- oral contraceptives.
- antipsychotic drugs, such as chlorpromazine.
Why is metformin the drug of choice?
Can metformin lower your blood pressure?
Does metformin reduce insulin levels?
What are the adverse effects of metformin?
...
The most common side effects of metformin include:
- heartburn.
- stomach pain.
- nausea or vomiting.
- bloating.
- gas.
- diarrhea.
- constipation.
- weight loss.
Does metformin suppress glucagon?
Does metformin help with diabetes?
Metformin helps to control blood sugar (glucose) levels and is sometimes used in combination with insulin or other medications. Metformin is a true workhorse for diabetics: a study published in Diabetes Care showed that the number of people who started metformin as their first treatment has increased since 2005.
Is metformin a first line medicine?
While metformin is a recommended as a first-line medicine, some patients may need to be started on a second drug at the same time to reach blood sugar goals. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) suggests that the A1C measurement should be less than 7% for most nonpregnant adults with diabetes.
Is metformin a work horse?
Metformin is a Workhorse for Type 2 Diabetes. Metformin, commonly known by other names such as: Fortamet. Glumetza. Riomet. has been available for the oral treatment of type 2 diabetes since 1995. Metformin helps to control blood sugar (glucose) levels and is sometimes used in combination with insulin or other medications.
How does metformin affect blood sugar?
Metformin works to make the body's cells more sensitive to insulin and decreases the amount of sugar naturally produced in the liver. Guidelines from the American Diabetes Association (ADA) state that blood sugar levels should be targeted to the individual patient. Blood glucose targets (A1C) are individualized based on:
Does metformin cause nausea?
According to a report published in the Annals of Internal Medicine, some extended-release forms of metformin have a lower odor, and may be less likely to cause nausea.
Does metformin cause lactic acidosis?
Certain metformin drug interactions may increase your risk of lactic acidosis, so be sure to tell your doctor and pharmacists about all of the prescription medicines, herbal, vitamin or other over-the-counter (OTC) medicines you take.
Is lactic acidosis a medical emergency?
It's important you know about it, but it's also a rare side effect. Lactic acidosis is a medical emergency and must be treated in a hospital. Lactic acidosis is a build-up of lactic acid in your blood due to low oxygen levels.
Is metformin FDA approved?
In addition, it is sometimes used to prevent diabetes in patients who are at risk of developing the disease (though it is not FDA approved for prediabetes ).
Why is metformin used for diabetes?
Why? Metformin is the treatment of choice for type 2 diabetes because it works well, is inexpensive, and it has been around for decades. Patients may lose a few pounds of weight on metformin. Metformin is very effective at controlling blood glucose and lowers A1c levels by as much as 1.5% at maximum doses.
Is metformin safe for type 2 diabetes?
Metformin is a commonly recommended initial medication for patients with type 2 diabetes who have mild to moderately uncontrolled blood glucose. In addition, it is sometimes used to prevent diabetes in patients who are at risk of developing the disease (though it is not FDA approved for prediabetes ). On average, most patients find that their HbA1c ...
Does metformin cause diarrhea?
Side effects including diarrhea. However, a slow increase in doses or extended release preparations can often prevent this. In rare cases, metformin can have a serious adverse side effect called lactic acidosis, where the body produces potentially dangerous levels of lactic acid.
Can metformin cause lactic acid?
In rare cases, metformin can have a serious adverse side effect called lactic acidosis, where the body produces potentially dangerous levels of lactic acid. This condition is rare, and occurs more commonly in persons who are older or have from heart failure, history of heavy alcohol use, or advanced kidney disease.
Does metformin lower A1C?
Patients may lose a few pounds of weight on metformin. Metformin is very effective at controlling blood glucose and lowers A1c levels by as much as 1.5% at maximum doses. By itself, metformin does not usually cause low ...
Does metformin reduce cancer risk?
In vivo and in vitro studies have shown that metformin has anti-cancer properties, and population studies have suggested that metformin may reduce the risk of cancer or improve cancer prognosis. It is thought that it exerts its anti-cancer effect through the inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signalling pathway.
Does metformin help with hyperglycaemia?
In addition to its ability to improve the control of hyperglycaemia, metform in has been shown to reduce the burden o,f ageing via effects on damaged DNA and the process of apoptosis. Studies have shown that metformin may reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease through influences on body weight, blood pressure, ...