Monosaccharides are carbohydrate molecules that cannot be broken down by hydrolysis2 into simpler (smaller) carbohydrate molecules. Hence, monosaccharides are at times referred to as “simple sugars” or just :sugars,” which infers that they are the simplest (smallest) of the carbohydrates.
What are monosaccharides?
Three or more monosaccharides Ex: glycogen, starch, cellulose, chitin Glycogen Storage form of glucose in animals (humans) Found in liver and muscles Made of long chains of glucose Starch Storage form of glucose in plants Long chain of glucose Found in breads, pasta, rice, potatoes
Is lipid A polymeric molecule?
Unlike carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids, lipids are not polymeric molecules. Lipids play a great role in the cellular structure and are the chief source of energy. Learn more in detail about the Biomolecules, different types, their structure, functions, importance and other related topics a BYJU’S Biology.
What are carbohydrates and polysaccharides?
Carbohydrates - polysaccharide - glycogen, starch, chitin, cellulose Phospholipid Primary component of cell membrane Glycerol + 2 fatty acids + phosphate group Cholesterol in nutrition body makes all it needs but also found in animal based foods (saturated foods) makes fat based hormones (sex hormones) excessive levels risks heart disease
What is the structure of the monosaccharide C6H12O6?
Contain C, H, & O 1:2:1 ratio C6H12O6 Short term energy source Maintains structure In plant cells Monosaccharides Simple sugars Glucose Most important monosaccharide Main source of energy for cells Structure: Hexagon shape Structural formula: C6H12O6 Fructose Found in fruits Source of energy Sweetest monosaccharide Structure: pentagon
What is lipids?
What are the three atoms in carbohydrates?
About this website

Is monosaccharide a lipid or carbohydrate?
Monosaccharides are carbohydrate monomers. Carbohydrate monomers are called monosaccharides, or single sugars. The various types of monosaccharides are classified based on size, location of their characteristic carbonyl group (a carbon double bonded to oxygen), and the spatial arrangement of atoms around the carbons.
Is monosaccharide a nucleic acid?
Monosaccharides are the monomers that make up carbohydrates. Glucose is an example of a monosaccharide. Glycerol and fatty acids are the monomers that make up lipids. Nucleotides are the monomers that make up nucleic acids.
Is disaccharide a carbohydrate lipid or protein?
Carbohydrates are classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides, depending on the number of monomers in the molecule. Lipids are a class of macromolecules that are nonpolar and hydrophobic in nature.
Is glucose a lipid protein or carbohydrate?
Answer and Explanation: The molecule "glucose" is characterized as a simple sugar which indicates that it is a type of carbohydrate.
How do you classify monosaccharides?
Monosaccharides can be classified by the number of carbon atoms in the structure and/or the type of carbonyl group they contain (aldose or ketose). Most monosaccharides contain at least one chiral carbon and can form stereoisomers. Enantiomers are a specific type of stereoisomers that are mirror images of each other.
What are examples of lipids?
Examples of lipids include fats, oils, waxes, certain vitamins (such as A, D, E and K), hormones and most of the cell membrane that is not made up of protein. Lipids are not soluble in water as they are non-polar, but are thus soluble in non-polar solvents such as chloroform.
Is monosaccharide a carbohydrate?
Monosaccharides are the simplest carbohydrates; most of them are sugars. Monosaccharides may have between three and eight carbon atoms, but only those with five carbons (pentoses) and six carbons (hexoses) are common.
What are monosaccharides disaccharides and polysaccharides?
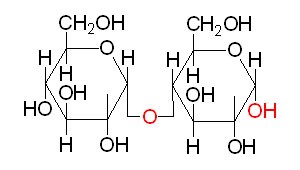
One monosaccharide serves as the acetal or ketal center that reacts with the hydroxyl group of the next monosaccharide. Disaccharides are oligosaccharides that contain two monosaccharide units. Polysaccharides contain a large number of monosaccharide units bonded to each other by a series of glycosidic bonds.
Is maltose a carbohydrate lipid or protein?
Since there are two units connected, maltose is referred to as a disaccharide: 'di' meaning two and saccharide is another name for a simple carbohydrate or sugar (such as glucose). So, it is a carbohydrate with two sugar units.
Is glucose a monosaccharide?
Glucose is classified as a monosaccharide because it cannot be broken down further by hydrolysis. It is further classified as a hexose because of its six-carbon skeleton and as an aldose, because of the presence of an aldehyde group on carbon 1.
Is glucose a carbohydrate?
Simple carbohydrates: These carbohydrates are composed of sugars (such as fructose and glucose) which have simple chemical structures composed of only one sugar (monosaccharides) or two sugars (disaccharides).
Is sugar a protein or carbohydrate?
carbohydratesSugars, starches and fiber are carbohydrates. Other macronutrients include fat and protein. Your body needs these macronutrients to stay healthy.
Which substance is a nucleic acid?
The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). DNA is the master blueprint for life and constitutes the genetic material in all free-living organisms and most viruses.
What are nucleic acids examples?
Two examples of nucleic acids include deoxyribonucleic acid (better known as DNA) and ribonucleic acid (better known as RNA). These molecules are composed of long strands of nucleotides held together by covalent bonds. Nucleic acids can be found within the nucleus and cytoplasm of our cells.
Which monosaccharides is present in nucleic acids?
The sugar in the DNA molecule is deoxyribose and the one in RNA is ribose sugar.
What 2 monosaccharides are a part of nucleic acids?
Furthermore, carbohydrates such as pentose sugars ribose and deoxyribose are important components of RNA and DNA respectively.
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Carbohydrates, Carbohydrates, monosaccharide and more.
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids - Quizlet
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like monomer, polymer, C,H,O and more.
Proteins, Lipids, Carbohydrates, and nucleic acids - Quiz
Preview this quiz on Quizizz. Whats the number 1 function of lipids?
1. Carbohydrates 2. Lipids 3. Proteins 4. Nucleic Acids
Importance of Carbon Organic molecules contain C & H: • methane (CH 4), glucose (C 6H 12O 6) are organic • water (H 2O), carbon dioxide (CO 2) are inorganic • organic molecules are typically derived from living things Special features of the element Carbon: • can form bonds with up to 4 other atoms • can form complex linear, branched, ringed structures ...
What is lipids?
Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Supply energy. and are primary source of fat in the body. Click again to see term 👆.
What are the three atoms in carbohydrates?
Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. These are sugars and starches. They are all composed of only three atoms: carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, in a ratio of 1:2:1. Three types of these which are: 1.
What are the three monosaccharides?
Three or more monosaccharides. Ex: glycogen, starch, cellulose, chitin. Glycogen. Storage form of glucose in animals (humans) Found in liver and muscles . Made of long chains of glucose. Starch. Storage form of glucose in plants. Long chain of glucose.
How many double bonds are there between fatty acids?
at least one double or triple bond between carbons of fatty acid (vegetable oil)
How many units are in a monosaccharide?
Depending on the number of constituting sugar units obtained upon hydrolysis, they are classified as monosaccharides (1 unit ), oligosaccharides (2-10 units) and polysaccharides (more than 10 units).
What is the monomeric unit of nucleic acids?
The monomeric unit of nucleic acids is known as nucleotide and is composed of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and phosphate. The nucleotides are linked by a 3’ and 5’ phosphodiester bond. The nitrogen base attached to the pentose sugar makes the nucleotide distinct.
What are the different types of biomolecules?
Types of Biomolecules. There are four major classes of Biomolecules – Carbohydrates, Proteins, Nucleic acids and Lipids. Each of them is discussed below.
What are lipids in water?
Lipids are organic substances that are insoluble in water , soluble in organic solvents, are related to fatty acids and are utilized by the living cell. They include fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins, mono-, di- or triglycerides, phospholipids, etc. Unlike carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids, lipids are not polymeric molecules.
What are the four nitrogenous bases in DNA?
There are 4 major nitrogenous bases found in DNA: adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. In RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil. The DNA structure is described as a double-helix or double-helical structure which is formed by hydrogen bonding between the bases of two antiparallel polynucleotide chains.
What is the function of nucleic acids?
There are two types of nucleic acids namely, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). The main function of nucleic acid is the transfer of genetic information and synthesis ...
What are the most essential organic molecules?
Biomolecules are the most essential organic molecules, which are involved in the maintenance and metabolic processes of living organisms. These non-living molecules are the actual foot-soldiers of the battle of sustenance of life.
What is lipids?
Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. Energy-rich organic compounds, such as fats, oils, and waxes, that are made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Supply energy. and are primary source of fat in the body. Click again to see term 👆.
What are the three atoms in carbohydrates?
Click card to see definition 👆. Tap card to see definition 👆. These are sugars and starches. They are all composed of only three atoms: carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, in a ratio of 1:2:1. Three types of these which are: 1.
