What is montelukast and zafirlukast?
Montelukast and Zafirlukast: Leukotriene Receptors Antagonists Montelukast and Zafirlukast are leukotriene D4 receptors antagonists that are used prophylactically for the management of asthma, antigen, exercise, or drug-induced asthma.
Is montelukast a useful cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonist?
The prototype cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonist, montelukast, is generally considered to have a niche application in the therapy of exercise- and aspirin-induced asthma.
What is the role of montelukast in asthma?
The prototype cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonist, montelukast, is generally considered to have a niche application in the therapy of exercise- and aspirin-induced asthma. It is also used as add-on therapy in patients whose asthma is poorly controlled with inhaled corticosteroid monotherapy, o …
Which leukotriene receptor antagonists are used in asthma?
•Leukotriene receptor antagonist, such as montelukast and zafirlukast, is used in asthma, COPD, and allergic rhinitis. • Montelukast is the most prescribed CysLT<sub>1</sub> antagonist used in asthmatic patients.

What medication is a leukotriene receptor antagonist?
Montelukast and zafirlukast are leukotriene receptor antagonists. They block the effects of leukotrienes.
Does montelukast lower leukotrienes?
Montelukast, a leukotriene receptor antagonist, reduces the concentration of leukotrienes in the respiratory tract of children with persistent asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999 Dec;104(6):1162-7.
What receptor does montelukast bind to?
Montelukast and other LTRAs target the cysteinyl leukotriene receptor 1, which is expressed in a variety of cells, including airway smooth-muscle and various inflammatory cells (e.g., eosinophils), therefore inhibiting the activation of this receptor by cysteinyl leukotrienes (Figure 28.7).
What happens if you take montelukast in the morning?
There were no statistical differences between taking the drug in the morning or evening. In conclusion, montelukast, taken for 2 weeks, is equally effective in exercise-induced bronchoconstriction when dosing either in the morning or in the evening.
Why is montelukast taken at night?
The authors of this trial concluded that montelukast exerts an increased action at night, either because of higher plasma concentration at the moment of the challenge test, or because of anti-inflammatory effect during the first hours of the morning, or both.
Why is montelukast not used for acute asthma?
Montelukast establishes its effect tardy, so that it is not among first-line options for the treatment of the patients presenting with acute asthma attack.
What does montelukast do to your brain?
Montelukast has been described to be neuroprotective, for example, in the aging brain and after focal cerebral ischemia7,8. In the aging brain, increased activation of microglia is accompanied with decreased hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive decline7.
Can montelukast damage your liver?
Clinically apparent liver injury from montelukast is rare; but more than a dozen cases reported in the literature. In these cases, the latency to onset of injury was highly variable, ranging from a few days to several years. Patients presented with anorexia, nausea, right upper quadrant pain, dark urine, and jaundice.
What can you not mix with montelukast?
It's usually safe to take everyday painkillers with montelukast. However, do not take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin or ibuprofen if they have ever made your asthma symptoms worse.
What is contraindicated with montelukast?
Montelukast is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to the drug or its components. In addition, for patients with phenylketonuria (PKU), caution should be exercised with phenylalanine-containing formulations.
What antihistamine can I take with montelukast?
Combination Therapy with Montelukast and Antihistamines (desloratadine or Levocetirizine) Improves Quality of Life in Patients with Persistent Allergic Rhinitis: a Double Blind Placebo Controlled Study.
What are the long term side effects of montelukast?
Although montelukast is considered to be a safe drug, there are concerns regarding adverse drug reactions, including the rare occurrence of Churg-Strauss syndrome and, despite insufficient data, the possibility of neuropsychiatric events such as anxiety, depression, sleep disturbance, and suicidality.
Can you take montelukast long term?
Montelukast oral tablets are meant to be used as a long-term treatment. If you and your doctor determine that montelukast oral tablets are safe and effective for you, you'll likely take the drug long term.
Can I suddenly stop montelukast?
Do not stop taking these medicines and do not reduce the dose, even if your asthma seems better, unless you or your child are told to do so by your doctor. Talk to your doctor or get medical care right away if: Your or your child's symptoms do not improve after using this medicine or if they become worse.
How safe is montelukast?
Safety profile The most commonly reported clinical adverse events of montelukast treatment were fever, upper respiratory infection, and asthma exacerbation. However, montelukast is considered a safe drug because its reported incidence of adverse drug reactions (ADRs) was similar to that of the control group [40].
Does montelukast make you gain weight?
Does Singulair (montelukast) cause weight gain? Weight gain is not a common side effect of Singulair (montelukast).
Does montelukast affect anxiety?
Findings In this cohort study of electronic health records for 72 490 patients with asthma and 82 456 patients with allergic rhinitis, montelukast was associated with higher odds of incident neuropsychiatric outcomes, including anxiety and insomnia.
Can montelukast cause lung problems?
The most common side-effects of montelukast are respiratory infections, tummy (abdominal) pain and headache.
Which is better inhaler or montelukast?
Conclusion: Montelukast is equally effective as inhaled corticosteroids in prevention of mild persistent asthma among 1-5 years and additional significant benefit in controlling rhinitis.
Which antihistamine is best for asthma?
In contrast, loratadine, a potent, nonsedating, histamine-1-receptor antagonist with activity in seasonal and perennial allergic rhinitis, has demonstrated effective control of asthma symptoms, improved pulmonary function, and long duration of action in patients with allergic bronchial asthma.
How do you reduce leukotrienes in the body?
Drugs such as montelukast (Singulair) and zafirlukast (Accolate) are widely prescribed to treat exercise and allergy-induced asthma. A third drug called zileuton (Zyflo) indirectly inhibits leukotriene synthesis. Montelukast is also prescribed for the treatment of year-round and seasonal allergic rhinitis.
How do you stop leukotrienes naturally?
Some natural compounds may block either the production of leukotrienes or their binding to their receptors. These include active compounds from plants such as aloe, butterbur, black cumin, and boswellia, as well as the well known antioxidant resveratrol.
Does montelukast reduce inflammation?
Montelukast reduces eosinophilic inflammation by inhibiting both epithelial cell cytokine secretion (GM-CSF, IL-6, IL-8) and eosinophil survival. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents.
What causes high levels of leukotrienes?
Leukotrienes are proinflammatory lipid mediators that have been shown to be upregulated in several diseases, including asthma, aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD), inflammatory bowel disease, and acute respiratory distress syndrome.
What is the montelukast?
The prototype cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonist, montelukast, is generally considered to have a niche application in the therapy of exercise- and aspirin-induced asthma.
Is montelukast an anti-inflammatory?
Recently, however, montelukast has been reported to possess secondary anti-inflammatory properties, apparently unrelated to conventional antagonism of cysteinyl leukotriene receptors. These novel activities enable montelukast to target eosinophils, monocytes, and, in particular, the corticosteroid-insensitive neutrophil, suggesting that this agent may have a broader spectrum of anti-inflammatory activities than originally thought. If so, montelukast is potentially useful in the chemotherapy of intermittent asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cystic fibrosis, and viral bronchiolitis, which, to a large extent, involve airway epithelial cell/neutrophil interactions. The primary objective of this mini-review is to present evidence for the cysteinyl leukotriene-independent mechanisms of action of montelukast and their potential clinical relevance.
What is the purpose of Montelukast?
Montelukast and zafirlukast are cysteinyl leukotriene receptor antagonists indicated for the prevention and treatment of chronic asthma. This activity will highlight the mechanism of action, adverse event profile, and monitoring pertinent for members of the interprofessional team in the management of patients with asthma and related conditions with leukotriene receptor antagonists.
What is Zafirlukast used for?
Zafirlukast indications include the prophylaxis and chronic treatment of asthma in children five years and older and adults. It is used off-label for allergic rhinitis and the prophylaxis of exercise-induced bronchospasm.
What is the first line of treatment for exercise-induced bronchospasm?
The first-line therapy for the prophylaxis of exercise-induced bronchospasm is inhaled short-acting beta-agonist such as albuterol. Daily use of inhaled corticosteroid or leukotriene receptor antagonists, such as montelukast and zafirlukast, is recommended in patients with exercise-induced bronchospasm who inhaled preventative short-acting beta-agonist but continue to have symptoms or who develop tolerance to continued usage of short-acting beta-agonist. [7]
What receptor antagonists are used for asthma?
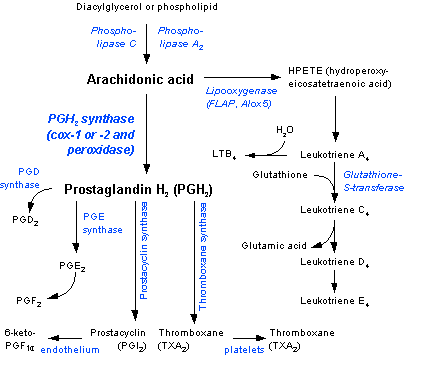
The main indication for leukotriene receptor antagonists is in the treatment of chronic asthma. Leukotrienes are synthesized from arachidonic acid by the action of 5-lipoxygenase in many inflammatory cells in the airways.[9] Arachidonic acid is released from cell membrane phospholipids mainly by phospholipase A2.[10] The cyclooxygenase pathway produces thromboxane and prostaglandins from arachidonic acid. Corticosteroids inhibit phospholipase A2 and subsequent synthesis of eicosanoid inflammatory mediators, including both prostaglandins and leukotrienes. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin inhibit cyclooxygenases. Zileuton inhibits 5-Lipoxygenase.
Which leukotrienes are bind to BLT receptors?
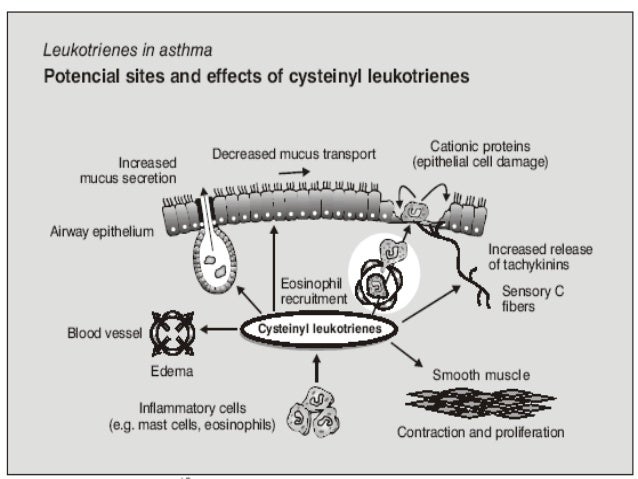
There are two groups of leukotrienes: one with and the other without amino acid moieties.[1] Leukotriene B4 carries hydroxyl moiety only and binds to BLT receptors. The signaling pathway via G protein-coupled BLT receptor activation produces a potent chemotaxis response. Cysteinyl leukotrienes (LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4) have amino acid moiety and bind to cysteinyl leukotriene receptors (CysLT1 and CysLT2). Bronchoconstriction, vascular permeability, eosinophil recruitment, and chronic inflammation are mediated through the G protein-coupled activation of cysteinyl leukotriene receptors. Montelukast and zafirlukast are antagonists to cysteinyl leukotriene CysLT1 receptors but not to CysLT2 receptors. Research has shown that eosinophils are the main source of cysteinyl leukotrienes, and cysteinyl leukotrienes are very important in eosinophil recruitment.[11] Earlier studies have shown that cysteinyl leukotrienes also play an important role in airway remodeling in chronic asthma. [12]
Why do asthmatic children take montelukast?
Parents of asthmatic children prefer montelukast because the once-a-day oral dosage is more convenient than inhaler use. It also avoids the concerns regarding the side effects of long-term use of corticosteroids, such as growth retardation and metabolic abnormalities.
How long after eating can you take Zafirlukast?
Zafirlukast is administered orally. It should be taken 2 hours after or 1 hour before meals because food decreases bioavailability by 40%.
How long after a nasal smear is eosinophils reduced?
Furthermore, reduced eosinophils in nasal smears and peripheral blood were observed 2 and 6 weeks after treatment.
What is LTC4 in asthma?
Of particular interest are numerous theories regarding the pathogenesis of aspirin intolerance with subsequent hyperproduction of leukotrienes and inhibition of cyclooxygenase.
Does leukotriene blockade cause eosinophil inflammation?
Conclusion: Leukotriene 1 receptor blockade led to a significant decrease in eosinophil inflammation accompanied by a reduction in other mediators such as neurokinin A and substance P in the nasal lavage fluid of patients with nasal polyps and asthma, with or without aspirin intolerance.
How does Montelukast work?
It works by blocking the action of leukotriene D4 in the lungs resulting in decreased inflammation and relaxation of smooth muscle. Montelukast was approved for medical use in the United States in 1998. It is available as a generic medication.
What is the role of Montelukast?
Montelukast functions as a leukotriene receptor antagonist ( cysteinyl leukotriene receptors) and consequently opposes the function of these inflammatory mediators ; leukotrienes are produced by the immune system and serve to promote bronchoconstriction, inflammation, microvascular permeability, and mucus secretion in asthma and COPD. Leukotriene receptor antagonists are sometimes colloquially referred to as leukasts .
What is Montelukast used for?
Montelukast is used for a number of conditions including asthma, exercise induced bronchospasm, allergic rhinitis, and urticaria. It is mainly used as a complementary therapy in adults in addition to inhaled corticosteroids, if inhaled steroids alone do not bring the desired effect. It is also used to prevent allergic reactions and asthma flare-ups during the administration of intravenous immunoglobulin. It may also be used as an adjunct therapy in symptomatic treatment of mastocytosis. It is taken by mouth, as a tablet, chewable tablet, or as granules.
What is the name of the brand of Montelukast?
Montelukast is sold under a variety of brand names including Monalast (Ziska Pharmaceuticals Ltd) Montenaaf (NAAFCO Pharma ) Montelon-10 (Apex), Montene (Square), Montair-10, Montelo-10, Monteflo, and Tukast L in India, Reversair (ACI Bangladesh), Monas, Miralust, Montiva, Provair, Montril, Lumona, Lumenta, Arokast and Trilock in Bangladesh, Ventair in Nepal, Montika in Pakistan, Montelair in Brazil, Zykast in the Philippines though combined with levocetirizine, Notta in Turkey, Topraz in South Africa and AirOn in Venezuela.
When did the FDA require a boxed warning for montelukast?
In March 2020 , the FDA required a boxed warning for montelukast to strengthen an existing warning about the risk of neuropsychiatric events associated with the drug in the wake of an increase in case reporting of neuropsychiatric events around the time of the initial communications about the concern from FDA in 2008.
When did Singulair expire?
Singulair was covered by U.S. Patent No. 5,565,473 which expired on August 3, 2012. The same day, the FDA approved several generic versions of montelukast.
What are the genes that are involved in the biosynthesis of leukase?
Leukotriene receptor antagonists are sometimes colloquially referred to as leukasts . Two genes of interest are ALOX5 and LTC4S, which catalyze two major steps in the biosynthetic pathway of leukotrienes.
What is the mean FEV 1 before exercise?
The mean (±SD) FEV 1 before exercise was similar in the placebo and montelukast groups at the second base-line measurement (3.33±0.69 and 3.35±0.66 liters, respectively) and at week 12 (3.33±0.71 and 3.45±0.65 liters, respectively).
How long does montelukast therapy last?
Twelve weeks of montelukast therapy significantly improved the control of asthma, as determined by the patients' global assessment scores (P=0.009). In the montelukast group, 73.1 percent of patients characterized the control of asthma as better, 21.2 percent as unchanged, and 5.8 percent as worse, as compared with respective values of 44.4 percent, 46.3 percent, and 9.3 percent in the placebo group. Significantly fewer patients in the montelukast group than in the placebo group required rescue therapy with a β-agonist after exercise challenge at each visit during the treatment period. The respective values for the montelukast and placebo groups were 7.8 percent and 27.8 percent at week 4, 8.0 percent and 24.5 percent at week 8, and 14.3 percent and 36.0 percent at week 12 (P<0.05 for all comparisons).
What is the primary end point of FEV 1?
The primary end point was the area under the curve (AUC) for FEV 1 (expressed as the percent change from base-line values) in the first 60 minutes after exercise challenge, summarizing the extent and duration of bronchoconstriction after exercise ( Figure 1 ). The maximal decrease in FEV 1 after exercise and the length of time from the maximal decrease in FEV 1 to the return to within 5 percent of the FEV 1 value measured before exercise were secondary end points.
What is the PC 20 value of montelukast?
The mean PC 20 values in the montelukast group and the placebo group were similar at base line (0.46±0.41 vs. 0.45±0.35 mg per milliliter). During the methacholine challenge, patients in the montelukast group required proportionately more doubling doses than patients in the placebo group (0.45 vs. 0.14), but the difference between the two groups was not significant (P=0.16).
What are the adverse effects of montelukast?
The three most commonly reported adverse effects were headache (32 percent of patients in the placebo group, as compared with 20 percent of patients in the montelukast group), upper respiratory tract infections (23 percent vs. 28 percent), and worsening asthma (10 percent vs. 4 percent). One patient in each group had elevations in serum aminotransferase levels to more than three times the upper limit of normal. In each case, the elevations were transient and self-limiting. Withdrawal of montelukast during the washout period did not cause an increased incidence of worsening asthma as compared with placebo.
What is the degree of protection afforded by a drug against exercise-induced bronchoconstriction?
Accordingly, the degree of protection afforded by a drug against exercise-induced bronchoconstriction may be used to assess therapeutic benefit in patients with mild asthma who have near-normal airway function and minimal symptoms.
Why did one patient stop treatment for montelukast?
In the montelukast group, one patient stopped treatment because of sinusitis, one patient stopped treatment because of respiratory distress , one stopped treatment because of pregnancy, one was withdrawn because of a protocol deviation, one was lost to follow-up, and one withdrew consent.
What are leukotrienes?
Leukotrienes are fatty acid-derived mediators that contain a conjugated triene structure. Leukotrienes are products of arachidonic acid metabolism and are formed when arachidonic acid is liberated from the cell membrane of cells, as a result of cell activation by an allergen.
What is the role of LTB4 in asthma?
They are generated by 5-Lipoxygenase and converts arachidonic into 5-HPETE, which in turn is converted into LTB4 which is a potent mediator of inflammation and Cysteinyl-LTs (LTC4, LTD4, LTE4 that mediate asthmatic responses. LTB4 is a potent pro-inflammatory chemo-attractant.
How long does Montelukast stay in your system?
This drug is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The mean plasma half-life is 2.7–5.5 hours. The drug is 60-70% metabolized in the liver by cytochrome 3A and 2C9 and is mainly excreted in the bile. It has a half-life of 10 hours. When Montelukast is administered, it binds the cysteine leukotriene 1 receptor.
What is the difference between Montelukast and Zafirlukast?
Montelukast and Zafirlukast: Leukotriene Receptors Antagonists. Montelukast and Zafirlukast are leukotriene D4 receptors antagonists that are used prophylactically for the management of asthma, antigen, exercise, or drug-induced asthma. Montelukast is used as add-on therapy in adults and children ...
What are the two classes of leukotriene inhibitors?
Leukotriene Esterase Inhibitors are classified into two classes. 5-Lipoxygenase inhibitor such as Zileuton. Cysteinyl Leukotriene Receptor antagonists: Montelukast and Zafirlukast. For an easier understanding of these Leukotriene antagonist medications, it is important that we have a basic understanding of what are leukotrienes.
How often is Zafirlukast given?
Zafirlukast and Montelukast are administered orally, 1–2 times per day usually in the evening.
How is LTC4 activated?
LTC4 is activated to an active metabolite ( LTD4) by the removal of the terminal amino acid in the peptide side-chain. Removal of a second amino acid results in a less active metabolite known as LTE4. LTC4, LTD4 and LTE4, the ‘cysteinyl leukotrienes’, account for ‘slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis’ (SRS-A).