How does monosodium glutamate release into the atmosphere?
Why is monosodium glutamate not hydrolyzed?
What is the pH of monosodium glutamate?
What is glutamate in the nervous system?
What is the pathway of glutamate metabolism?
How is glutamate absorbed?
How is glutamic acid metabolized?
See 4 more
About this website
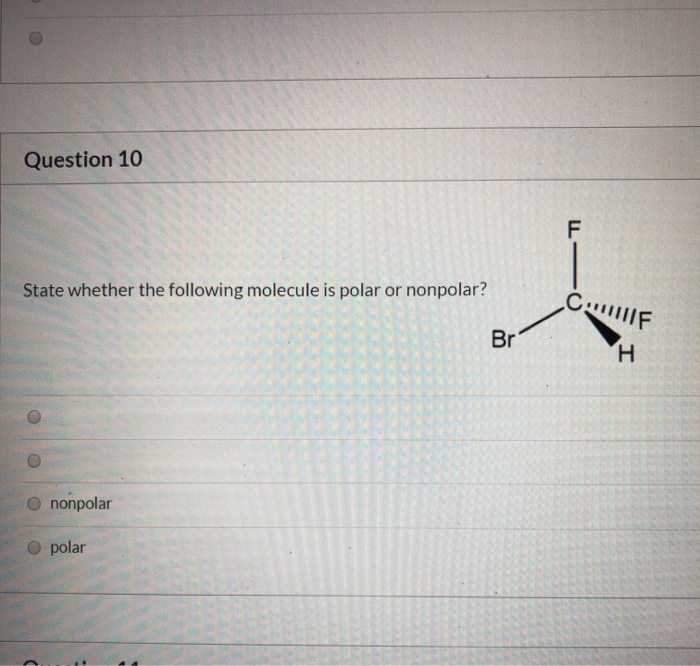
What type of bond is MSG?
MSG molecules feature an ionic bond between Na+ and C5H8NO4–. The structure of a monosodium glutamate molecule is illustrated below. In solid MSG, the glutamate ion exists in its zwitterion form – –O(C=O)CH(NH3+)(CH2)2(C=O)O–.
Will MSG dissolve in water?
Chemical properties MSG is freely soluble in water, but it is not hygroscopic and is insoluble in common organic solvents (such as ether).
Why does MSG dissolve in water?
MSG is made of a positive sodium ion (Na+) and a negative glutamate ion, which has the molecular formula (C5H8NO4−). Polar water interacts with these oppositely charged ions to dissolve the MSG. Salt—sodium chloride is an ionic compound.
What are the properties of MSG?
Physical Properties of MSGIt is a solid, white-coloured compound.MSG is extremely soluble in water but not soluble in organic solvents. The solubility level of monosodium glutamate in water corresponds to 740 grams/L.MSG has no odour or smell.Its melting point is 232 oC.
Does MSG dissolve in oil?
MSG is also soluble in oil or organic solvents (17). It is a common glutamic acid salt which contains 78% glutamic acid, 22% sodium salt and also water (18).
Does MSG melt?
At room temperature, MSG (C5H8NNaO4• H2O) is a salt, which typically exists as a white, odorless crystalline powder that is soluble in water and alcohol. It does not have a melting point per se, but it decomposes when it is heated.
What does MSG in water taste like?
MSG has a specific taste known as umami — the fifth basic taste alongside sweet, sour, salty, and bitter. Umami has a meaty flavor that refers to the presence of proteins in food ( 2 , 6 ).
Is MSG different than salt?
"MSG has two-thirds less sodium than table salt and imparts umami - a savory taste. Taste is a key factor in what people decide to eat. Using MSG as a replacement for some salt in the diet and to increase the appeal of nutritious foods can help make healthy eating easier, likely leading to a positive impact on health."
Why is MSG so thirsty?
Usually, after eating a dish, you feel thirsty because you have consumed too much salt. This includes the intake of MSG, which is actually also because it contains the same sodium ions as salt.
Is MSG a base or acid?
Acidic salts, such as MONOSODIUM GLUTAMATE, are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydrogen ions and have pH's of less than 7.0. They react as acids to neutralize bases.
Is MSG a salt or sugar?
Monosodium glutamate (MSG) is the sodium salt of the common amino acid glutamic acid. Glutamic acid is naturally present in our bodies, and in many foods and food additives.
Is MSG an ionic compound?
Sodium 2-AminopentanedioateMonosodium glutamate / IUPAC ID
How do you dissolve MSG?
Dissolve the MSG in water by adding 30 mL of water to the flask and swirling until you no longer see any solid. (The amount of water added does not need to be measured accurately.)
What does MSG in water taste like?
MSG has a specific taste known as umami — the fifth basic taste alongside sweet, sour, salty, and bitter. Umami has a meaty flavor that refers to the presence of proteins in food ( 2 , 6 ).
Can you put MSG in drinks?
Using MSG in drinks Can you use MSG in drinks, then? Of course you can. Indeed, if you're fond of knocking back a Bloody Mary then that might be down to the tomato juice; tomato is one of the foods that is rich in glutamates, after all.
Does MSG work in drinks?
You can add a pinch of MSG powder directly to the drink, or create a solution of MSG and water and then add it to the drink with a dropper, much like you would for bitters. Umami is a complex flavor, so adding MSG works best with alcohols that also have complex flavors.
Why is MSG bad? 15 Harmful Effects - ExtraChai
Monosodium glutamate (MSG) has been hailed as a silent killer for several years now. MSG is a flavor enhancer which is a main additive in Chinese cuisine, canned meat and processed food. However, it is a controversial additive which has led to several debates over the years. Why is MSG bad? Harmful effects-
Is MSG Truly Unhealthy? All You Need to Know
Monosodium Glutamate (MSG) is a flavor enhancer that has been widely used for roughly 100 years ().In addition to being naturally present in certain foods, it’s a common food additive in Chinese ...
Monosodium glutamate (MSG): Is it harmful? - Mayo Clinic
Monosodium glutamate (MSG) is a flavor enhancer often added to restaurant foods, canned vegetables, soups, deli meats and other foods. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has classified MSG as a food ingredient that's generally recognized as safe. But its use is still debated.
How do you know if a molecule is nonpolar or polar?
How Do I Know If A Molecule is Nonpolar Or Polar? Nonpolar molecules consist of identical sides around the central atom and therefore have no unshared pairs of electrons. The atoms in a molecule have equal or nearly equal electronegativities and have zero or very small dipole moments.
How many electrons does a molecule have?
Molecules have an odd number of electrons (e.g., NO). Molecules in one or more atoms have more than eight electrons (e.g., SF6). Molecules with less than eight electrons; an example is the BF3. There are molecules with a polar bond, but the molecular geometry is symmetrical. As a result, they are nonpolar molecules by nature (examples: CO2, SO3).
Why is a molecule polar?
A molecule is polar if there’s a significant difference in the electronegativity charges between elements. The bonds don’t cancel each other out and are asymmetrical. A nonpolar molecule has no separation of electric charges or difference in electronegativity. The bonds cancel each other out, are symmetrical, and there’s no lone electron pair.
What is polarity in biology?
Polarity is one of the properties of a compound related to other properties such as boiling and melting point, solubility, and molecular interactions between molecules. Polar and nonpolar molecules differ significantly. Here are the steps to help you determine if a molecule is polar or nonpolar. Table of Contents [ Show]
What is the electronegativity difference between bonded atoms?
The electronegativity difference between bonded atoms is less than 0.4. Polar bonds: The electronegativity difference is greater than 0.4 between bonded atoms. There is at least one side of the molecule with more negative or positive charge than another side.1. 3.
What type of bond is the arrows of an atom?
Nonpolar covalent bond: The arrows are equal in length, and the arrangement is symmetrical. All the atoms attached to the middle atom are identical. They share all electron pairs. Polar covalent bond: The arrows are of different lengths, and the arrangement is asymmetrical or uneven. The atoms attached to the atom aren’t all the same.
Why is the Lewis dot structure important?
It’s essential for predicting molecular geometry, molecule polarity, and reactivity in a compound.
What do polar and non-polar mean?
In simple terms, polar means oppositely charged, and non-polar means equally charged. Covalent bonds can be polar or non-polar. To understand the difference between polar and non-polar bonds, it is essential to comprehend electronegativity.
What is electronegativity?
Electronegativity is the measurement of how much an atom wants to bond to another atom. Electronegativity increases from left to right and down each column on the periodic table. The Pauling scale describes the electronegativity of an element, with a scale from 0.7 to 4. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, with an electronegativity of 4. Cesium is the least electronegative element with an electronegativity of 0.7.
What makes a bond non-polar?
Non-polar bonds are also a type of covalent bond. Unlike polar bonds, non-polar bonds share electrons equally. A bond between two atoms or more atoms is non-polar if the atoms have the same electronegativity or a difference in electronegativities that is less than 0.4. An example of a non-polar bond is the bond in chlorine. Chlorine contains two chlorine atoms. The electrons are shared equally because the electronegativity difference between the two atoms is zero.
What is polar bond?
A polar bond is a type of covalent bond. A bond between two or more atoms is polar if the atoms have significantly different electronegativities (>0.4). Polar bonds do not share electrons equally, meaning the negative charge from the electrons is not evenly distributed in the molecule. This causes a dipole moment.
What is the term for a molecule with two poles?
Polar molecules can have ionic or polar covalent bonds. A molecule with two poles is called a dipole. When you measure the amount of polarity of a molecule, the result is called the dipole moment.
What is the difference between polar and non-polar bonds?
What do polar and non-polar mean? In simple terms, polar means oppositely charged, and non-polar means equally charged. Covalent bonds can be polar or non-polar. To understand the difference between polar and non-polar bonds, it is essential to comprehend electronegativity.
What is polar chemistry?
In chemistry, the definition of a polar molecule, is a molecule that has a charge on one side of the molecule, that is not cancelled out. It has a region of partial charge. One end is slightly positive one end is slightly negative. They are generally asymmetrical, with an uneven distribution of the electrons.
Why is SiCl4 Nonpolar in nature?
In order to check the polarity of any inorganic compound, three major points have to be analyzed:
What is the difference between Si and Cl?
In SiCl4, the electronegativity of the silicon (Si) atom is 1.9 whereas the chlorine (Cl) atom is 3.16. The electronegativity difference between Si and Cl atoms is about 1.26 which is greater than 0.4.
What is the color of SiCl4?
SiCl4 is a colorless volatile liquid, which produces fumes when kept in the moist air. A violent reaction between SiCl4 and water produces white-colored solid silicon dioxide and steamy fumes of HCl. Due to this, the water vapor present in moist air generates fumes of liquid SiCl4.
How many valence electrons does SiCl4 have?
In SiCl4, silicon is the center atom of the molecule, and the four valence electrons of the silicon share a single bond with four chlorine atoms around it.
What is SiCl4 used for?
Silicon tetrachloride (SiCl4) is an inorganic compound that is used in commercial applications to produce highly pure silicon or silica. Various silicon compounds such as ferrosilicon, silicon carbide, or mixtures of silicon dioxide and carbon can be chlorinated to prepare SiCl4.
What reacts with water to produce orthosilicic acid and hydrogen chloride?
Silicon tetrachloride reacts with water to produce orthosilicic acid and hydrogen chloride.
Why are Si and Cl polar?
In all the forms, the covalent bonds between Si and Cl are polar due to the greater electronegativity difference between them.
How does monosodium glutamate release into the atmosphere?
If released to air, monosodium glutamate will exist solely in the particulate phase in the atmosphere since it is a salt. Particulate-phase monosodium glutamate will be removed from the atmosphere by wet or dry deposition. Monosodium glutamate does not contain chromophores that absorb at wavelengths >290 nm and therefore is not expected to be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight. If released to soil, monosodium glutamate is expected to have very high mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 4. Volatilization from soil and water surfaces will not occur since monosodium glutamate is a salt. Several genera of bacteria have been shown to possess enzymatic capability to degrade l-glutamic acid and monosodium glutamate was readily degraded in sediment/ water microcosms using both seawater and estuarine water. If released into water, monosodium glutamate is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc. Hydrolysis is not expected to be an important environmental fate process since this compound lacks functional groups that hydrolyze under environmental conditions. An estimated BCF of 1 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Occupational exposure to monosodium glutamate may occur through dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where monosodium glutamate is produced or used. The general population is exposed to monosodium glutamate primarily via ingestion of food products containing this additive. (SRC)
Why is monosodium glutamate not hydrolyzed?
Monosodium glutamate is not expected to undergo hydrolysis in the environment due to the lack of functional groups that hydrolyze under environmental conditions (1). Monosodium glutamate does not contain chromophores that absorb at wavelengths >290 nm and therefore is not expected to be susceptible to direct photolysis by sunlight (1).
What is the pH of monosodium glutamate?
Monosodium glutamate appears as white or off-white crystalline powder with a slight peptone-like odor. pH (0.2% solution)7.0. (NTP, 1992) CAMEO Chemicals. One of the FLAVORING AGENTS used to impart a meat-like flavor.
What is glutamate in the nervous system?
L-Glutamate and GABA supposedly act as excitatory and inhibitory transmitters , respectively, in the central nervous system. Glutamate is also involved in the synthesis of proteins. / Glutamate /. WHO Food Additive Series 22; L-Glutamic Acid and its Ammonium, Calcium, Monosodium and Potassium Salts.
What is the pathway of glutamate metabolism?
Quantitatively minor but physiologically important pathways of glutamate metabolism involve decarboxylation to gamma-aminobutyrate ( GABA) and amidation to glutamine ... . Decarboxylation to GABA is dependent on pyridoxal phosphate, a coenzyme of glutamic acid decarboxylase ..., as is glutamate transaminase.
How is glutamate absorbed?
Glutamate is absorbed from the gut by an active transport system specific for amino acids. This process is saturable, can be competitively inhibited, and is dependent on sodium ion concentration... . During intestinal absorption, a large proportion of glutamic acid is transaminated and consequently alanine levels in portal blood are elevated. If large amounts of glutamate are ingested, portal glutamate levels increase ... . This elevation results in increased hepatic metabolism of glutamate, leading to release of glucose, lactate, glutamine, and other amino acids, into systemic circulation ... . The pharmacokinetics of glutamate depend on whether it is free or incorporated into protein, and on the presence of other food components. Digestion of protein in the intestinal lumen and at the brush border produces a mixture of small peptides and amino acids; di-and tri-peptides may enter the absorptive cells where intracellular hydrolysis may occur, liberating further amino acids. Defects are known in both amino acid and peptide transport ... .. Glutamic acid in dietary protein, together with endogenous protein secreted into the gut, is digested to free amino acids and small peptides, both of which are absorbed into mucosal cells where peptides are hydrolyzed to free amino acids and some of the glutamate is metabolized. Excess glutamate and other amino acids appear in portal blood. As a consequence of the rapid metabolism of glutamate in intestinal mucosal cells and in the liver, systemic plasma levels are low, even after ingestion of large amounts of dietary protein. / Glutamic acid /
How is glutamic acid metabolized?
Glutamic acid is metabolized in the tissues by oxidative deamination ... or by transamination with pyruvate to yield oxaloacetic acid ... which, via alpha-ketoglutarate, enters the citric acid cycle ... .. Quantitatively minor but physiologically important pathways of glutamate metabolism involve decarboxylation to gamma-aminobutyrate ( GABA) and amidation to glutamine ... . Decarboxylation to GABA is dependent on pyridoxal phosphate, a coenzyme of glutamic acid decarboxylase ..., as is glutamate transaminase. Vitamin B6 -deficient rats have elevated serum glutamate levels and delayed glutamate clearance ... . / Glutamic acid /
