Mycobacterim abscessus infection is generally spread through contact with contaminated soil, water, or objects. Mycobacterium
Mycobacterium
Mycobacterium is a genus of Actinobacteria, given its own family, the Mycobacteriaceae. Over 190 species are recognized in this genus. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis and leprosy in humans. The Greek prefix myco- mean…
Petri dish
A Petri dish (sometimes spelled "Petrie dish" and alternatively known as a Petri plate or cell-culture dish), named after the German bacteriologist Julius Richard Petri, is a shallow cylindrical glass or plastic lidded dish that biologists use to culture cells – such as bacteria – or small mosses.
What does Mycobacterium abscessus cause?
Apr 08, 2020 · Is Mycobacterium Abscessus contagious? Caused by a mutation, cystic fibrosis (CF) isn't contagious, but one serious complication definitely is: infection with Mycobacterium abscessus, an obscure agent related to the microbe that causes tuberculosis. Between 5% and 10% of CF patients become infected, and that number is growing.
Is Mycoplasma abscessus contagious person-to-person?
Nov 24, 2010 · Infection with M. abscessus is usually caused by injections of substances contaminated with the bacterium or through invasive medical procedures employing contaminated equipment or material. Infection can also occur after accidental injury where the wound is contaminated by soil. There is very little risk of transmission from person to person.
What is the difference between Mycobacterium abscessus and pulmonary infections?
Mar 05, 2022 · Mycobacterium abscessus is not considered contagious from person to person, and usually enters the body through a break in the skin. Bacterial infections can be detected by allowing small samples to culture inside of a petri dish. Infections with Mycobacterium abscessus can often cause serious symptoms.
How is Mycoplasma abscessus transmitted?
Mycobacterium abscessus complex comprises a group of rapidly growing, multidrug-resistant, nontuberculous myco-bacteria that are responsible for a wide spectrum of skin and soft tissue diseases, central nervous system infections, bacteremia, and ocular and other infections. M. abscessus complex is differentiated into 3 subspecies: M. abscessus

How is Mycobacterium abscessus spread?
Transmission of Mycobacterium abscessus abscessus is usually caused by injections of substances contaminated with the bacterium or through invasive medical procedures employing contaminated equipment or material. Infection can also occur after accidental injury where the wound is contaminated by soil.
Is Mycobacterium contagious?
The great majority of NTM lung disease in the U.S. is caused by Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC). Everyone comes into contact with NTM, but it usually only causes infection in people with underlying lung disease, such as bronchiectasis or COPD, a weakened immune system or older age. NTM disease is not contagious.Nov 6, 2020
Can you cure Mycobacterium abscessus?
abscessus complex is notoriously difficult to treat. Although there is no standard treatment, current guidelines suggest the administration of macrolide-based therapy in combination with intravenously administered antimicrobial agents; however, this regimen has been shown to have a substantial cytotoxic effect (2).
Is NTM contagious?
NTM does not cause tuberculosis (TB), and unlike TB, which is spread from person to person, NTM is not contagious.
How is Mycobacterium transmitted?
M. tuberculosis is transmitted through the air, not by surface contact. Transmission occurs when a person inhales droplet nuclei containing M. tuberculosis, and the droplet nuclei traverse the mouth or nasal passages, upper respiratory tract, and bronchi to reach the alveoli of the lungs (Figure 2.2).
How serious is Mycobacterium?
Nontuberculous mycobacteria are tiny germs found in soil, water, and on both tame and wild animals. They're harmless to most people. But sometimes when these bacteria get into your body, they can cause a serious lung disease.Jul 28, 2021
How fast does Mycobacterium Abscessus grow?
The RGM are environmental organisms found worldwide that usually grow in subculture within one week (eg, rapidly, as compared with other mycobacteria). M. abscessus is the most commonly encountered species of this group isolated from clinical respiratory specimens, and M.Sep 18, 2020
What happens if you don't treat Mycobacterium Abscessus?
Without treatment, many people will develop a progressive lung infection. Cough, shortness of breath, fatigue, and often weight loss are symptoms. MAC is the most common species of NTM that causes infections in humans, and the lungs are the most common site for infection.Apr 22, 2021
What antibiotics are used to treat Mycobacterium Abscessus?
M. abscessus is resistant to many antibiotics and thus is very difficult to treat. Isolates are usually susceptible only in vitro to the parenteral agents amikacin, cefoxitin, and imipenem, and to oral macrolides (clarithromycin and azithromycin) (1, 2).May 10, 2009
How long does it take to cure Mycobacterium?
For skin and soft tissue infections, treatment is typically given for at least two to three months after any skin symptoms have resolved.
What is the second most common nontuberculous mycobacteria to cause lung disease?
Figure 2 shows the distribution of mycobacterial species among patients with definite pulmonary NTM disease in Asia, according to ATS criteria. MAC was the most frequently reported (68% of all cases) cause of NTM disease; RGM were second (14% of all cases).
Can Mycobacterium go away on its own?
Once you have a diagnosis of an NTM infection, you will be closely monitored. NTM infections continue because phlegm gets trapped in the lungs. Chest physiotherapy and regular exercise can help NTM infections go away without treatment.
General Information About Mycobacterium abscessus
Mycobacterium abscessus [mī–kō–bak–tair–ee–yum ab–ses–sus] (also called M. abscessus) is a bacterium distantly related to the ones that cause tuber...
Symptoms of Mycobacterium abscessus
Skin infected with M. abscessus is usually red, warm, tender to the touch, swollen, and/or painful. Infected areas can also develop boils or pus-fi...
Transmission of Mycobacterium abscessus
Transmission of M. abscessus can occur in several ways. Infection with M. abscessus is usually caused by injections of substances contaminated with...
Prevention of Mycobacterium abscessus
Anyone who touches or cares for the infected site should wash their hands carefully with soap and water. Patients should follow all instructions gi...
Treatment of Mycobacterium abscessus
Treatment of infections due to M. abscessus consists of draining collections of pus or removing the infected tissue and administering the appropria...
Recommendations and Guidelines
For more information about prevention and treatment of HAIs, see the resources below: 1. CDC. Guidelines for preventing the transmission of mycobac...
How to tell if mycobacterium abscessus is a bacterial infection?
Bacterial infections can be detected by allowing small samples to culture inside of a petri dish. Symptoms of a Mycobacterium abscessus infection may include chills and fever.
How does Mycobacterium abscessus spread?
Mycobacterim abscessus infection is generally spread through contact with contaminated soil, water, or objects. Mycobacterium abscessus is not considered contagious from person to person, and usually enters the body through a break in the skin.
What are the symptoms of mycobacterium abscessus?
Symptoms of a Mycobacterium abscessus infection may include chills and fever. Chronic respiratory conditions, open wounds and lowered immunity are some of the primary risk factors for the contraction of this mycobacterial infection.
How to diagnose mycobacterium abscess?
A definitive diagnosis of Mycobacterium abscesses can often be made by culturing pus from an infected boil, or by examining a biopsy sample of infected skin. Antibiotics can be prescribed to treat this infection, but are often effective only after prolonged use.
Is mycobacterium abscessus related to tuberculosis?
Mycobacterium abscessus is closely related to the bacteria that causes tuberculosis. Mycobacterium abscessus is a mycobacterium of the same genus as the microbes that cause the diseases leprosy and tuberculosis. While this mycobacterium can infect various parts of the body, it usually infects the skin and the tissues beneath the skin.
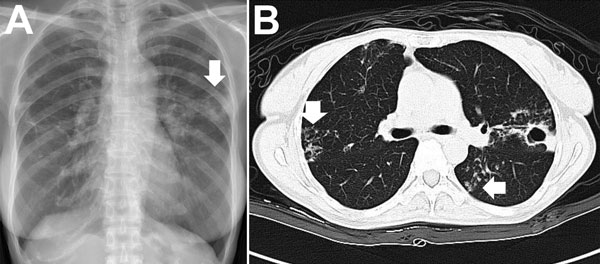
Can mycobacterium abscessus infect the lungs?
These mycobacteria mostly infect the skin, but can, in rare cases, infect the lungs, especially in those with a history of chronic lung afflictions.
How big is a Mycobacterium abscessus cell?
Mycobacterium abscessus cells are Gram-positive, nonmotile, acid-fast rods about 1.0–2.5 µm long by 0.5 µm wide. They may form colonies on Löwenstein–Jensen medium that appear smooth or rough, white or greyish, and nonphotochromogenic .
Why is M. abscessus complex so difficult to treat?
Amongst NTM species responsible for disease, infection caused by M. abscessus complex are more difficult to treat due to antimicrobial drug resistance. M. abscessus grown in starch-based medium on a Petri dish: Colonies appear as light yellow streaks.
What bacteriophages killed M. abscessus?
A cocktail of bacteriophages, Muddy, ZoeJ, and BPs, effectively killed a strain of M. abscessus in vitro. The potential this showed encouraged the commencement of patient treatments towards the GD01 infection. Every 12 hours, the patient received a treatment of the bacteriophage cocktail.
What is the M. abscessus complex?
Mycobacterium abscessus complex (MABSC) is a group of rapidly growing, multidrug-resistant, nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) species that are common soil and water contaminants. Although M. abscessus complex most commonly causes chronic lung infection and skin and soft tissue infection (SSTI), the complex can also cause infection in almost all ...
How long does it take for M. abscessus to grow?
M. abscessus shows growth at 28 and 37°C after 7 days, but not at 43°C. It may grow on MacConkey agar at 28°C and even 37°C. It shows tolerance to saline media (5% NaCl) and 500 mg/l hydroxylamine (Ogawa egg medium) and 0.2% picrate (Sauton agar medium). Strains of the species have been shown to degrade the antibiotic p- aminosalicylate. M. abscessus has also been shown to produce arylsulfatase, but not of nitrate reductase and Tween 80 hydrolase. It shows a negative result for the iron uptake test and no use of fructose, glucose, oxalate, or citrate as sole carbon sources.
Which bacteria carry a common antibiotic resistance gene?
M. abscessus subsp. abscessus and bolletii carry a common antibiotic resistance gene, which confers resistance to macrolide antibiotics, while M. a. massiliense is thought to carry a nonfunctional copy, so is more susceptible to antibiotics and more easily treated.
When was the genome sequence of M. abscessus completed?
A draft genome sequence of M. abscessus subsp. bolletii BD T was completed in 2012. Since then, a large number of strains from this subspecies have had their genomes sequenced, leading to a clarification of subspecies boundaries. In 1992, M. abscessus was first recognised as a distinct species. In 2006, this group was separated into three subspecies: M. a. abscessus, M. a. bolletii, and M. a. massiliense. In 2011, the latter two were briefly merged into a single subspecies, but were subsequently separated again following greater availability of genome sequence data, which showed the three subspecies formed genetically distinct groups.
How to tell if mycobacterium is infected?
However, for a definite diagnosis, the organism has to be cultured from the infection site or, in severe cases, from a blood culture.
What is the genus of Mycobacterium?
Mycobacterium is a genus of Actinobacteria, given its own family, the Mycobacteriaceae. Over 190 species are recognized in this genus 1). Mycobacterium genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in humans, including tuberculosis (Mycobacterium tuberculosis) and leprosy (Mycobacterium leprae) in humans.
How is mycobacterium avium complex acquired?
Mycobacterium avium complex is acquired by inhalation and can also be ingested into the gastrointestinal tract, where it adheres to the mucosal epithelial cells and infects the macrophages. From the submucosal tissues and lymph nodes, the organism is then carried by lymphatics to the rest of the body. In most people, disseminated mycobacterium avium complex infection will occur when the CD4 count is less than 50 cell per microliter. In patients who do not have HIV, the most important risk factor for mycobacterium avium complex infection is underlying lung disease. Mycobacterium avium complex has also been associated with bronchiectasis and a hypersensitivity pneumonitis-like reaction 12).
What is the most common risk factor for mycobacterium avium complex infection?
In patients who do not have HIV, the most important risk factor for mycobacterium avium complex infection is underlying lung disease.
How long does it take for a Mycobacterium avium complex to grow?
Mycobacterium avium complex is a nonchromogen and slow growing and takes about 10 to 20 days to develop mature colonies 8). Mycobacterium avium complex belongs to class III of the Runyon classification.
What are the clinical patterns of mycobacterium chelonae?
Mycobacterial infections including mycobacterium chelonae infections can be categorized into several clinical patterns: pulmonary disease, skin and soft tissue infections, musculoskeletal infections, disseminated disease, catheter-associated disease. and lymphadenitis. Skin and soft tissue infections are the most common presentations of mycobacterium chelonae infections. Infections occur in both immunocompetent and in immunocompromised hosts. mycobacterium chelonae has a predilection to extremities as it has a tendency to grow at a lower temperature. Nodules, papular rash, and sporotrichoid pattern have been reported. Skin lesions due to mycobacterium chelonae in the setting of sclerotherapy, acupuncture tattoos, and other injection procedure have been reported. Skin lesions can progress to pustules, hemorrhagic crusts, and abscess formation. Disseminated cutaneous disease and advanced skin lesions are common in immunosuppressed patients. Sweet syndrome can be a presenting feature of mycobacterium chelonae infection particularly if the skin lesions are on the extremities. Skin lesions mimicking lupus vasculitis can occur due to mycobacterium chelonae infection. Disseminated disease can present with multiple lesions, complex lesions and in more proximal location. Umbilicated papules, pustules involving the face and upper trunk may be present.
How old is a person with mycobacterium kansasii?
In one study, the mean age of patients with mycobacterium kansasii infection was 58 years, and 64% were men. However, mycobacterium kansasii can infect adults of any age, sex, or race. Infection results in symptoms in 85% of cases.
Why do humans encounter mycobacterial species?
Humans encounter mycobacterial species due to their ubiquity in different environmental niches. In many individuals, pathogenic mycobacterial species may breach our first-line barrier defenses of the innate immune system and modulate the activation of phagocytes to cause disease of the respiratory tract or the skin and soft tissues, sometimes resulting in disseminated infection. Cutaneous mycobacterial infections may cause a wide range of clinical manifestations, which are divided into four main disease categories: (i) cutaneous manifestations of Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection, (ii) Buruli ulcer caused by Mycobacterium ulcerans and other related slowly growing mycobacteria, (iii) leprosy caused by Mycobacterium leprae and Mycobacterium lepromatosis, and (iv) cutaneous infections caused by rapidly growing mycobacteria. Clinically, cutaneous mycobacterial infections present with widely different clinical presentations, including cellulitis, nonhealing ulcers, subacute or chronic nodular lesions, abscesses, superficial lymphadenitis, verrucous lesions, and other types of findings. Mycobacterial infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissue are associated with important stigma, deformity, and disability. Geography-based environmental exposures influence the epidemiology of cutaneous mycobacterial infections. Cutaneous tuberculosis exhibits different clinical phenotypes acquired through different routes, including via extrinsic inoculation of the tuberculous bacilli and dissemination to the skin from other sites, or represents hypersensitivity reactions to M. tuberculosis infection. In many settings, leprosy remains an important cause of neurological impairment, deformity, limb loss, and stigma. Mycobacterium lepromatosis, a mycobacterial species related to M. leprae, is linked to diffuse lepromatous leprosy of Lucio and Latapí. Mycobacterium ulcerans produces a mycolactone toxin that leads to subcutaneous tissue destruction and immunosuppression, resulting in deep ulcerations that often produce substantial disfigurement and disability. Mycobacterium marinum, a close relative of M. ulcerans, is an important cause of cutaneous sporotrichoid nodular lymphangitic lesions. Among patients with advanced immunosuppression, Mycobacterium kansasii, the Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex, and Mycobacterium haemophilum may cause cutaneous or disseminated disease. Rapidly growing mycobacteria, including the Mycobacterium abscessus group, Mycobacterium chelonei, and Mycobacterium fortuitum, are increasingly recognized pathogens in cutaneous infections associated particularly with plastic surgery and cosmetic procedures. Skin biopsies of cutaneous lesions to identify acid-fast staining bacilli and cultures represent the cornerstone of diagnosis. Additionally, histopathological evaluation of skin biopsy specimens may be useful in identifying leprosy, Buruli ulcer, and cutaneous tuberculosis. Molecular assays are useful in some cases. The treatment for cutaneous mycobacterial infections depends on the specific pathogen and therefore requires a careful consideration of antimicrobial choices based on official treatment guidelines.
What are the clinical presentations of mycobacterial infections?
Clinically, cutaneous mycobacterial infections present with widely different clinical presentations, including cellulitis, nonhealing ulcers, subacute or chronic nodular lesions, abscesses, superficial lymphadenitis, verrucous lesions, and other types of findings. Mycobacterial infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissue are associated ...
What is cutaneous tuberculosis?
Cutaneous tuberculosis exhibits different clinical phenotypes acquired through different routes, including via extrinsic inoculation of the tuberculous bacilli and dissemination to the skin from other sites, or represents hypersensitivity reactions to M. tuberculosis infection.
Where is nontuberculous mycobacteria found?
Nontuberculous mycobacteria are a group of bacteria naturally found in soil, water and dust worldwide. Everyone inhales NTM into their lungs as part of daily life, and in most people the organisms do no harm. But in a small number of vulnerable individuals, NTM gets established in the lungs as an infection.
Is mycobacterium avium contagious?
The other Mycobacterium species are classified as “nontuberculous” to clearly set them apart. Unlike the others, NTM lung disease is not known to be contagious. The most common type of NTM bacteria in the U.S. is Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC). The great majority of NTM lung disease in the U.S. is caused by MAC.
