...
Nitrous oxide.
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Molar mass | 44.013 g/mol |
| Appearance | colourless gas |
| Density | 1.977 g/L (gas) |
| Melting point | −90.86 °C (−131.55 °F; 182.29 K) |
What happens when nitrogen combines with oxygen?
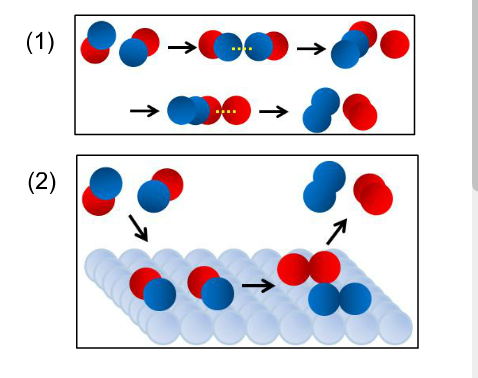
nitrogen + oxygen → nitrogen monoxide N 2 (g) + O 2 (g) → 2NO(g) When this nitrogen monoxide is released from vehicle exhaust systems, it combines with oxygen in the air to form nitrogen dioxide .
What is the reaction between nitrogen and oxygen?
When nitrogen and oxygen mix at room temperature under standard atmospheric conditions, nothing happens. In fact, air is comprised of 78 percent nitrogen and 21 percent oxygen. The nitrogen is inert, or inactive. At much higher temperatures, nitrogen reacts with oxygen to form nitric oxide, but this takes a considerable spark of energy.
How does nitrogen dioxide cause air pollution?
Nitrogen dioxide, or NO 2, is a gaseous air pollutant composed of nitrogen and oxygen and is one of a group of related gases called nitrogen oxides, or NOx. NO 2 forms when fossil fuels such as coal, oil, gas or diesel are burned at high temperatures. NO 2 and other nitrogen oxides in the outdoor air contribute to particle pollution and to the chemical reactions that make ozone. It is one of six widespread air pollutants that have national air quality standards to limit them in the outdoor air.
What is the formula for dinitrogen oxide?
What is in dinitrogen oxide? Nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas or nitrous, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula N2O. At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, with a slight metallic scent and taste.

Is nitrous oxide a gas or liquid?
It is a slightly sweet-smelling colorless gas. B. The boiling point of N2O, which is − 88.5° C (− 127° F), indicates that it is a gas at room temperature.
What type of oxide is n2o2?
nitrous oxide (N2O), also called dinitrogen monoxide, laughing gas, or nitrous, one of several oxides of nitrogen, a colourless gas with pleasant, sweetish odour and taste, which when inhaled produces insensibility to pain preceded by mild hysteria, sometimes laughter.
Is dinitrogen dioxide a gas?
Nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas, nitrous, or nos, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula N2O. At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, and has a slightly sweet scent and taste....CHEBI:17045 - dinitrogen oxide.ChEBI Namedinitrogen oxideChEBI IDCHEBI:1704511 more rows•Oct 13, 2017
Is nitrous oxide a real gas?
Nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas or happy gas, is a colorless, non-flammable gas. This gas is used in medical and dental procedures as a sedative.
What is laughing gas made of?
It's nitrous oxide. Often called laughing gas, most people know it as something dentists give patients so they don't feel pain during a procedure. Formed from two nitrogen atoms and one oxygen atom, the gas is present in much smaller quantities in the atmosphere than carbon dioxide or methane.
Why do they call it laughing gas?
Nitrous Oxide common use is also called laughing gas or happy gas due to its intoxicating effects when inhaled.
Is n2o2 a solid?
O. At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, and has a slightly sweet scent and taste. At elevated temperatures, nitrous oxide is a powerful oxidiser similar to molecular oxygen.
How n2o2 is formed?
It is formed by adding pounded carbonate of ammonia to pure nitric acid, which is concentrated may be previously diluted with half its bulk of water so long as there is effervescence and a small excess of the carbonate may be left at the end in the liquor.
Is n2o2 stable?
Up to 500 GPa, only three stable N-O compounds were found (NO2, N2O5 and NO), as seen in Fig. 1. Most of them retain their molecular structures even under high pressure. Experimentally known “laughing gas” N2O is metastable.
Why does laughing gas make you laugh?
Yes, Laughing Gas Can Make You Laugh Nitrous oxide earned its nickname because of how it interacts with the brain's neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, to make patients feel relaxed and euphoric. Most people do laugh after a dentist administers this sedative, whereas others may feel giddy or lightheaded.
Is laughing gas illegal in England?
The sale of nitrous oxide for its psychoactive effects was made illegal after the Psychoactive Substances Act in 2016, but it is not currently a crime to be caught in possession of the drug.
Will laughing gas put you to sleep?
Will Nitrous Oxide Put You to Sleep? Unlike general anesthesia, nitrous oxide is not intended to put you to sleep. You will still be conscious and aware of your surroundings, allowing you to communicate with your dentist and follow any instructions they give you.
How does nitrous oxide work in racing?
In vehicle racing, nitrous oxide (often referred to as just " nitrous ") allows the engine to burn more fuel by providing more oxygen during combustion. The increase in oxygen allows for an increase in the injection of fuel, allowing the engine to produce more engine power. The gas is not flammable at a low pressure/temperature, but it delivers more oxygen than atmospheric air by breaking down at elevated temperatures, about 570 degrees F (~300C). Therefore, it often is mixed with another fuel that is easier to deflagrate. Nitrous oxide is a strong oxidising agent, roughly equivalent to hydrogen peroxide, and much stronger than oxygen gas.
What are the processes that produce nitrous oxide?
Natural processes that generate nitrous oxide may be classified as nitrification and denitrification. Specifically, they include: 1 aerobic autotrophic nitrification, the stepwise oxidation of ammonia ( NH#N#3) to nitrite ( NO−#N#2) and to nitrate ( NO−#N#3) 2 anaerobic heterotrophic denitrification, the stepwise reduction of NO−#N#3 to NO−#N#2, nitric oxide (NO), N#N#2O and ultimately N#N#2, where facultative anaerobe bacteria use NO−#N#3 as an electron acceptor in the respiration of organic material in the condition of insufficient oxygen ( O#N#2) 3 nitrifier denitrification, which is carried out by autotrophic NH#N#3 -oxidising bacteria and the pathway whereby ammonia ( NH#N#3) is oxidised to nitrite ( NO−#N#2 ), followed by the reduction of NO−#N#2 to nitric oxide (NO), N#N#2O and molecular nitrogen ( N#N#2) 4 heterotrophic nitrification 5 aerobic denitrification by the same heterotrophic nitrifiers 6 fungal denitrification 7 non-biological chemodenitrification
What is the name of the gas that is a laughing gas?
Nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas or nitrous, is a chemical compound, an oxide of nitrogen with the formula N. 2O. At room temperature, it is a colourless non-flammable gas, with a slight metallic scent and taste. At elevated temperatures, nitrous oxide is a powerful oxidiser similar to molecular oxygen.
How is nitrogen oxide released into the atmosphere?
Nitrous oxide is released into the atmosphere through agriculture, when farmers add nitrogen-based fertilizers onto the fields, through the breakdown of animal manure. Approximately 79 percent of all nitrous oxide released in the United States came from nitrogen fertilization.
What is 2O used for?
2O tanks used in dentistry. Nitrous oxide has been used in dentistry and surgery, as an anaesthetic and analgesic, since 1844. In the early days, the gas was administered through simple inhalers consisting of a breathing bag made of rubber cloth.
What is the purpose of Whippit remnants?
Whippit remnants (the small steel canisters) of recreational drug use, the Netherlands, 2017. Recreational inhalation of nitrous oxide, with the purpose of causing euphoria and/or slight hallucinations, began as a phenomenon for the British upper class in 1799, known as "laughing gas parties".
How does air affect butterfat?
Used in this way, it produces whipped cream which is four times the volume of the liquid, whereas whipping air into cream only produces twice the volume. If air were used as a propellant, oxygen would accelerate rancidification of the butterfat, but nitrous oxide inhibits such degradation.
Preparation and reactions
Nitrogen dioxide typically arises via the oxidation of nitric oxide by oxygen in air:
Ecology
NO 2 is introduced into the environment by natural causes, including entry from the stratosphere, bacterial respiration, volcanos, and lightning. These sources make NO 2 a trace gas in the atmosphere of Earth, where it plays a role in absorbing sunlight and regulating the chemistry of the troposphere, especially in determining ozone concentrations.
Uses
NO 2 is used as an intermediate in the manufacturing of nitric acid, as a nitrating agent in manufacturing of chemical explosives, as a polymerization inhibitor for acrylates, as a flour bleaching agent ., : 223 and as a room temperature sterilization agent.
Human-caused sources and exposure
For the general public, the most prominent sources of NO 2 are internal combustion engines burning fossil fuels. Outdoors, NO 2 can be a result of traffic from motor vehicles.
Toxicity
Gaseous NO 2 diffuses into the epithelial lining fluid (ELF) of the respiratory epithelium and dissolves. There, it chemically reacts with antioxidant and lipid molecules in the ELF.
Environmental effects
Interaction of NO 2 and other NO x with water, oxygen and other chemicals in the atmosphere can form acid rain which harms sensitive ecosystems such as lakes and forests. Elevated levels of NO 2 can also harm vegetation, decreasing growth, and reduce crop yields.
How much carbon dioxide is in a tonne of nitrous oxide?
One tonne of nitrous oxide is equivalent to 298 tonnes of carbon dioxide. Nitrous oxide has an atmospheric lifetime of 110 years. The process that removes nitrous oxide from the atmosphere also depletes ozone. So nitrous oxide is not only a greenhouse gas, but also an ozone destroyer.
How much carbon dioxide is in a tonne?
One tonne of nitrous oxide is equivalent to 298 tonnes of carbon dioxide.
Where does nitrous oxide come from?
But the nitrous oxide in the atmosphere doesn’t come from dentists — it comes from nitrogen-based fertilisers. Globally, about 1% of all the nitrogen fertiliser applied to the soil to grow our food is emitted to the atmosphere as nitrous oxide.
How to prevent frostbite?
Skin: Wear appropriate personal protective clothing to prevent skin from becoming frozen from contact with the liquid or from contact with vessels containing the liquid. Eyes: Wear appropriate eye protection to prevent eye contact with the liquid that could result in burns or tissue damage from frostbite. Wash skin: No recommendation is made specifying the need for washing the substance from the skin (either immediately or at the end of the work shift). Remove: No recommendation is made specifying the need for removing clothing that becomes wet or contaminated. Change: No recommendation is made specifying the need for the worker to change clothing after the work shift. Provide: Quick drench facilities and/or eyewash fountains should be provided within the immediate work area for emergency use where there is any possibility of exposure to liquids that are extremely cold or rapidly evaporating. (NIOSH, 2016)
What temperature does oxidation occur?
To oxidize organic compounds at temperatures greater than 300 °C; to make nitrites from alkali metals at their boiling points; in rocket fuel formulations (with carbon disulfide ); in the preparation of whipped cream.
How to treat frozen eye tissue?
Eye: If eye tissue is frozen, seek medical attention immediately; if tissue is not frozen, immediately and thoroughly flush the eyes with large amounts of water for at least 15 minutes , occasionally lifting the lower and upper eyelids. If irritation, pain, swelling, lacrimation, or photophobia persist, get medical attention as soon as possible. Skin: If frostbite has occurred, seek medical attention immediately; do NOT rub the affected areas or flush them with water. In order to prevent further tissue damage, do NOT attempt to remove frozen clothing from frostbitten areas. If frostbite has NOT occurred, immediately and thoroughly wash contaminated skin with soap and water. Breathing: If a person breathes large amounts of this chemical, move the exposed person to fresh air at once. Other measures are usually unnecessary. (NIOSH, 2016)
What are the advantages of inhalation anesthesia?
Inhalation anesthetics have advantages over intravenous agents in that the depth of anesthesia can be changed rapidly by altering the inhaled concentration. Because of their rapid elimination, any postoperative respiratory depression is of relatively short duration. (From AMA Drug Evaluations Annual, 1994, p173) (See all compounds classified as Anesthetics, Inhalation .)
What is Nitrous Oxide used for?
It is used as anesthetic in dentistry and surgery, propellant gas in food aerosols, leak detection. HUMAN EXPOSURE AND TOXICITY: The main complication following inhalation of nitrous oxide is varying degrees of hypoxia, affecting the functions of the heart and the brain.
Where is nitrogen oxide found?
Nitrous oxide is found in the air as part of the earth's natural nitrogen cycle. The compound remains in the atmosphere for about 114 years (1). It is present in the environment at concentrations ranging from 0.25 to 0.29 ppm, arising from biodegradation of organic nitrogen compounds that occur in soil (2).
Is Cameo Chemicals copyrighted?
CAMEO Chemicals and all other CAMEO products are available at no charge to those organizations and individuals (recipients) responsible for the safe handling of chemicals. However, some of the chemical data itself is subject to the copyright restrictions of the companies or organizations that provided the data.
What is NO 2 and how does it get in the air?
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO 2) is one of a group of highly reactive gases known as oxides of nitrogen or nitrogen oxides (NO x ). Other nitrogen oxides include nitrous acid and nitric acid. NO 2 is used as the indicator for the larger group of nitrogen oxides.
Effects of NO 2
Breathing air with a high concentration of NO 2 can irritate airways in the human respiratory system. Such exposures over short periods can aggravate respiratory diseases, particularly asthma, leading to respiratory symptoms (such as coughing, wheezing or difficulty breathing), hospital admissions and visits to emergency rooms.
What is being done to reduce NO 2 pollution?
EPA’s national and regional rules to reduce emissions of NO 2 and NO x will help state and local governments meet the National Ambient Air Quality Standard (NAAQS).