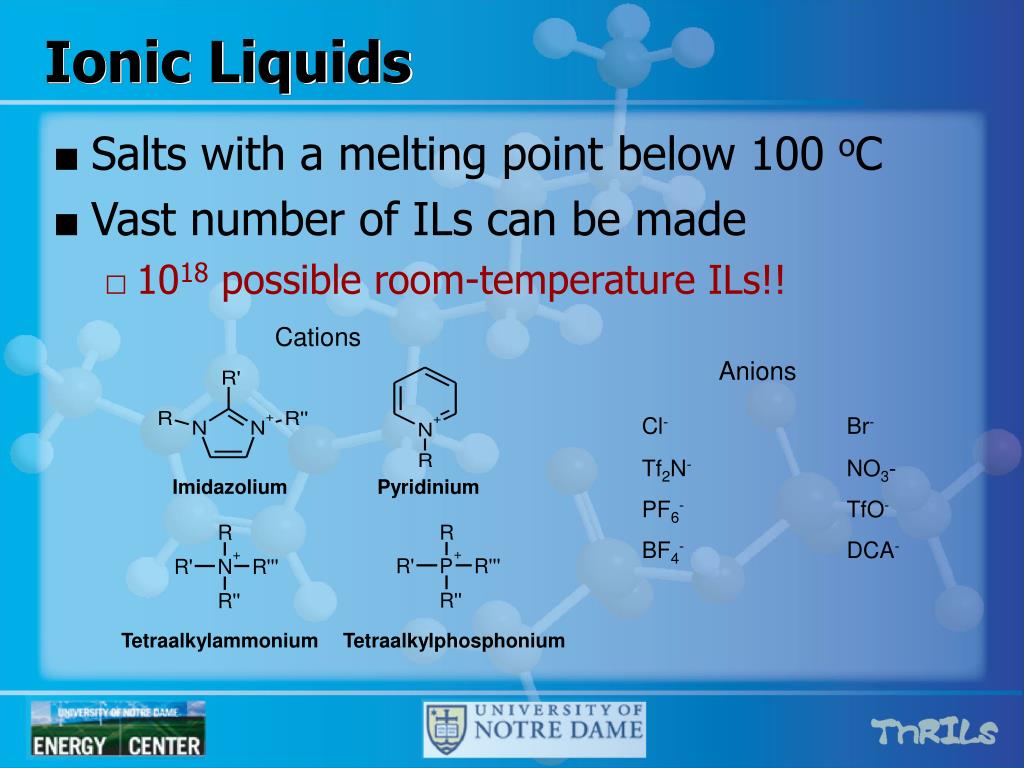
What is meant by cation and anion?
What is meant by cation and anion?
- The electronic configuration of many ions is that of the closest noble gas to them in the periodic table.
- An anion is an ion that has gained one or more electrons, acquiring a negative charge.
- A cation is an ion that has lost one or more electrons, gaining a positive charge.
What are common cations?
Common Cations and Anions Name Formula Charge Name Formula Charge Name Formula Charge aluminum Al 3+ +3 magnesium Mg 2+ +2 carbonate CO 3 2– –2 ammonium NH 4 + +1 manganese (II) Mn 2+ +2 chlorate ClO 3 – –1 barium Ba 2+ +2 manganese (III) Mn 3+ +3 chloride Cl – –1 cadmium Cd 2+ +2 mercury (I)
What are the cations and anions in the periodic table?
Main Differences Between Cation and Anion
- Cation is generally a positively charged atom, whereas Anion is a negatively charged atom.
- Cation is generally smaller in size than the Anion, whereas Anion is generally larger.
- Cation has fewer electrons than the protons, whereas Anion has higher numbers of electrons than the protons.
What elements are cations?
Halogens always form anions, alkali metals and alkaline earth metals always form cations. Most other metals form cations (e.g. iron, silver, nickel), whilst most other nonmetals typically form anions (e.g. oxygen, carbon, sulfur). Similarly, you may ask, what type of elements form anions?
Is nitrate a monovalent or a conjugate?
Is nitrate an inorganic or aqueous solution?
Can organic compounds react with oxidizing agents?
About this website
What anion is NO3?
nitrate ionThe nitrate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula NO3- and a molecular mass of 62.01 daltons; it consists of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identical oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a negative one formal charge.
Is co3 a cation or anion?
Solution : The formula of carbonate is `CO_3^(2-)`. It is an anion.
Is so3 a cation or anion?
Simple ions:Hydrogen sulfateHSO4-NitriteThiosulfateS2O32-SulfiteSO32-PerchlorateClO4-Iodate28 more rows
Is nh4 a cation or anion?
The ammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula [NH 4] +.
What is a cation and anion?
Cations are positively-charged ions (atoms or groups of atoms that have more protons than electrons due to having lost one or more electrons). Anions are negatively-charged ions (meaning they have more electrons than protons due to having gained one or more electrons).
How do you identify an anion?
2:245:11Cations and Anions Explained - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBecause it has a negative charge and so that's the difference between cations and anions rememberMoreBecause it has a negative charge and so that's the difference between cations and anions remember cations are ions with positive charges they have more protons than electrons.
What are examples of cation?
They are formed when a metal loses its electrons. They lose one or more than one electron and do not lose any protons. Therefore, they possess a net positive charge. Some examples of cations are Calcium (Ca2+), Potassium (K+), hydrogen (H+).
Is SO3 an ion?
Is SO3 covalent or ionic? Sulfur trioxide is a covalent compound. In the case of sulfur trioxide, the bonds are formed between the two non-metals i.e. sulfur and oxygen, and the electrons are shared between the participating atoms. Therefore, the bonds formed in this molecule are covalent in nature.
Which of the following are cation?
The correct answer is option 3, i.e. Ammonium. Ammonium ion (NH4+) is a cation. It is a positively charged polyatomic cation.
Why is NH4 a cation?
During the formation of the ammonium ion, the nitrogen atom gains a positive charge as it loses a lone pair of electrons. Since the produced ammonium ion possesses a positive charge, it is also known as ammonium cation.
What type of ion is NH4+?
ammonium cationThe ammonium cation is a positively charged polyatomic ion with the chemical formula [NH4]+.
Is NH4 2 an anion?
Answer and Explanation: The compound (NH4)2S ( N H 4 ) 2 S is formed from the cation ammonium (NH+4 N H 4 + ) and the sulfide anion (S2− ). Compounds made from cations and anions are ionic compounds. To write the name of an ionic compound, we write the name of the cation first, followed by the anion.
What is CO3 called?
CO3 : SummaryCodeCO3Molecule nameCARBONATE IONSystematic namesProgram Version Name ACDLabs 10.04 carbonate OpenEye OEToolkits 1.5.0 carbonateFormulaC O3Formal charge-25 more rows
Why does CO3 have a 2 charge?
The valency of carbonate is two because it can combine with two hydrogen atoms. Carbon with valency 4 forms a double bond with one among the three O atoms and a single bond each with two O– ions.
What is the formal charge of CO3?
C=4−4=0.
How do you identify CO3?
2:175:21Chemical Tests for Carbonate - MeitY OLabs - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe can see that carbonate reacts with dilute sulfuric acid to produce brisk effervescence with theMoreWe can see that carbonate reacts with dilute sulfuric acid to produce brisk effervescence with the evolution of colorless odorless gas of carbon dioxide. Cover the test tube containing salt.
What is the factor to convert from NO3-N and NO3?
You have been directed to this answer based on an ID match. Click here to see search results of this phrase. X
Which element can form both cations and anions?
However, some elements are capable of forming both cations and anions given the right conditions. One example is hydrogen , which may gain (H -) or lose (H +) an electron, forming hydride compounds such as ZnH 2 (where it is an anion) and hydron compounds such as H 2 O (where it is a cation).
How many electrons do cations lose?
For a cation to form, one or more electrons must be lost, typically pulled away by atoms with a stronger affinity for them. The number of electrons lost, and so the charge of the ion, is indicated after the chemical symbol, e.g. silver (Ag) loses one electron to become Ag +, whilst zinc (Zn) loses two electrons to become Zn 2+.
What are the ionic properties of batteries?
Ionic properties are central to the function of batteries too. Batteries have two electrodes made of conductive material, the cathode which is the positive end where the electrical current leaves/electrons enter, and the anode where the electrical current enters/ electrons leave.
What are ionic properties?
Ionic properties are central to the function of batteries too .
What is it called when an atom is not balanced?
However, if they are not balanced, they will be charged. These charged species are called ions .
When atoms from a metallic and a nonmetallic element combine, do they form ions?
Therefore, when atoms from a metallic and a nonmetallic element combine, the nonmetallic atoms tend to draw one or more electrons away from the metallic atoms to form ions . These oppositely charged ions then attract one other to form ionic bonds and produce ionic compounds with no overall net charge.
Which has more electrons: protons or anion?
An anion has more electrons than protons, consequently giving it a net negative charge. For an anion to form, one or more electrons must be gained, typically pulled away from other atoms with a weaker affinity for them.
What is the difference between an ion and a cation?
But seriously: anions and cations are both ions. The difference is in the electrical charge. Anions have a negative charge, and cations have a positive charge.
Where does the word "anion" come from?
The an- in anion is a form of ana-, meaning “up” (it’s the same root used in anode ). The word ion comes from the Greek ión, meaning “going,” and was introduced by English physicist and chemist Michael Faraday in the 1830s.
What is a cation?
A cation is an ion with positive charge, which means it has more protons (positively-charged particles) than electrons (negatively-charged particles). Cations are formed when an atom loses one or more electrons: the loss of the negatively-charged electron (s) results in an overall positive charge.
Why are cations positively charged?
Remember, cations are positive ions—they are positively charged because they have lost one or more electrons and therefore have more protons than electrons.
How does an atom become negatively charged?
An atom becomes negatively charged if it gains extra electrons, and it becomes positively charged if it loses electrons. We use the word ion to refer to atoms that have a charge one way or another, and we use the words cation and anion to specify whether the charge is positive or negative.
What happens when the number of electrons in a cation goes down?
Remember: the number of electrons in a cation has gone down, resulting in a positive charge. The number of electrons in an anion has gone up, resulting in a negative charge.
Which element is composed of an anion and two electrons?
Many elements can take the form of either anions or cations depending on the situation. Oxygen often exists in a neutral state, but oxygen atoms tend to form anions by gaining two electrons. Atoms of other elements also tend to form anions, including nitrogen, chlorine, and fluorine, among others. By contrast, atoms of calcium, magnesium, aluminum, and sodium tend to lose electrons and form cations. Sodium chloride—what we know as table salt—is actually composed of an anion and a cation (written as NA+CL- ).
Is nitrate a monovalent or a conjugate?
Nitrate is a nitrogen oxoanion formed by loss of a proton from nitric acid. Principal species present at pH 7.3. It is a nitrogen oxoanion, a member of reactive nitrogen species and a monovalent inorganic anion. It is a conjugate base of a nitric acid.
Is nitrate an inorganic or aqueous solution?
It is a nitrogen oxoanion, a member of reactive nitrogen species and a monovalent inorganic anion. It is a conjugate base of a nitric acid. Nitrates, inorganic, aqueous solution, n.o.s. is a liquid which is readily ignited when in contact with organic materials.
Can organic compounds react with oxidizing agents?
Organic compounds, in general, have some reducing power and can in principle react with compounds in this class. Actual reactivity varies greatly with the identity of the organic compound. Inorganic oxidizing agents can react violently with active metals, cyanides, esters, and thiocyanates.
