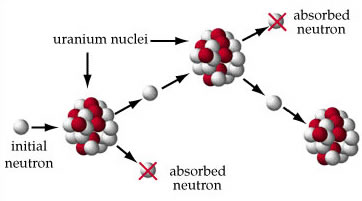
How many neutrons must be released during nuclear fission?
Controlled Nuclear Fission To maintain a sustained controlled nuclear reaction, for every 2 or 3 neutrons released, only one must be allowed to strike another uranium nucleus. If this ratio is less than one then the reaction will die out; if it is greater than one it will grow uncontrolled (an atomic explosion).
What is the difference between controlled fission and chain reactions?
Controlled fission reactions can be carried out in the presence of moderators. Nuclear power plants use controlled chain reactions. There, the chain reactions are controlled by controlling the rate of nuclear reactions. Controlled chain reactions can easily be converted into uncontrolled form.
How does nuclear fission differ from other types of nuclear reactions?
Nuclear fission differs importantly from other types of nuclear reactions, in that it can be amplified and sometimes controlled via a nuclear chain reaction (one type of general chain reaction). In such a reaction, free neutrons released by each fission event can trigger yet more events, which in turn release more neutrons and cause more fission.
How can a nuclear chain reaction be controlled?
And also, by regulating the time of the reaction, a nuclear chain reaction can be made into a controlled reaction. When the time of reaction is reduced, the probability of a neutron interacting with a fissile isotope is low. Then the reaction can easily be controlled.
Is nuclear fission uncontrolled?
In uncontrolled nuclear fission, one fission reaction starts a chain reaction, in which neutrons produced in one reaction cause other reactions, which cause more reactions, and so on. Energy released by nuclear fission is used to produce electrical energy in nuclear power plants.
Is nuclear energy controlled or uncontrolled?
Nuclear fission carried out in a nuclear power plant is a controlled chain reaction which can be controlled to stop if required.
Which nuclear reaction is uncontrolled?
Uncontrolled nuclear fission reactionUncontrolled nuclear fission reaction is production of ATOM BOMB.
Is fission or fusion controlled?
Fission is used in nuclear power reactors since it can be controlled, while fusion is not utilized to produce power since the reaction is not easily controlled and is expensive to create the needed conditions for a fusion reaction.
Can nuclear fusion be controlled?
Reaching ignition For this reason, a way to create efficient fusion reactions has been sought for decades to produce clean energy using few resources. However, fusion reactions have proven difficult to control and to date, no fusion experiment has produced more energy than has been put in to get the reaction going.
Which is used to control nuclear fission?
Control rods are used in nuclear reactors to control the rate of fission of the nuclear fuel – uranium or plutonium. Their compositions include chemical elements such as boron, cadmium, silver, hafnium, or indium, that are capable of absorbing many neutrons without themselves decaying.
How can the fission chain reaction be controlled?
The chain reaction is controlled by absorbing some of the neutrons emitted in the fission process by means of the cadmium rods and then making them slow by the moderators such as graphite, heavy water, etc, the energy obtained in fission can be utilized for the constructive purposes.
What is controlled uncontrolled reaction?
In an uncontrolled chain reaction, the reaction occurs rapidly so that the energy is released instantaneously and therefore, we can't convert any of that into any useful form of energy. In a controlled chain reaction, we can control the speed of reaction and thereby control the rate of release of energy.
How is fission controlled in a nuclear reactor?
Inside the reactor vessel, the fuel rods are immersed in water which acts as both a coolant and moderator. The moderator helps slow down the neutrons produced by fission to sustain the chain reaction. Control rods can then be inserted into the reactor core to reduce the reaction rate or withdrawn to increase it.
How is nuclear energy controlled?
In nuclear power plants, neutrons collide with uranium atoms, splitting them. This split releases neutrons from the uranium that in turn collide with other atoms, causing a chain reaction. This chain reaction is controlled with "control rods" that absorb neutrons.
What is difference between fission and fusion?
The main difference between these two processes is that fission is the splitting of an atom into two or more smaller ones while fusion is the fusing of two or more smaller atoms into a larger one.
Is fusion more powerful than fission?
Fusion occurs when two atoms slam together to form a heavier atom, like when two hydrogen atoms fuse to form one helium atom. This is the same process that powers the sun and creates huge amounts of energy—several times greater than fission. It also doesn't produce highly radioactive fission products.
Why is nuclear energy not reliable?
The multiple stages of the nuclear fuel cycle produce large volumes of radioactive waste. No government has yet resolved how to safely manage this waste. Some of this nuclear waste is highly radioactive and will remain so for several thousand years.
Which of the following statement about nuclear energy is true?
(b) is true. Nuclear energy is released when bonds within the nucleus are broken. New elements are formed through these processes, which are known as fission or fusion.
Why do people oppose nuclear energy?
Opponents say that nuclear power poses numerous threats to people and the environment and point to studies in the literature that question if it will ever be a sustainable energy source. These threats include health risks, accidents and environmental damage from uranium mining, processing and transport.
What is the argument against nuclear energy?
Nuclear takes 5 to 17 years longer between planning and operation and produces on average 23 times the emissions per unit electricity generated. In addition, it creates risk and cost associated with weapons proliferation, meltdown, mining lung cancer, and waste risks.
What happens to the nucleus in nuclear fission?
In nuclear fission, the unstable nucleus breaks into fragments, which are themselves complex nuclei, along with such particles as neutrons and protons. The resultant stable nuclei or nuclear fragments are usually in a highly excited state and then reach their low-energy ground state by emitting one…
How are fission reactors classified?
Fission reactors can be classified by the energy of the neutrons that propagate the chain reaction. The most common type, called a thermal reactor, operates with thermal neutrons (those having the same energy distribution as gas molecules at ordinary room temperatures). In such a reactor, the fission neutrons produced (with an average kinetic ...
How do delayed neutrons affect chain reaction?
The delayed-neutron emitters among the fission products increase the time between successive neutron generations in the chain reaction and make the control of the reaction easier to accomplish by the mechanical movement of the control rods. Fission reactors can be classified by the energy of the neutrons that propagate the chain reaction.
What is the chain reaction of a fission?
The emission of several neutrons in the fission process leads to the possibility of a chain reaction if at least one of the fission neutrons induces fission in another fissile nucleus, which in turn fissions and emits neutrons to continue the chain. If more than one neutron is effective in inducing fission ...
What type of neutrons are used in a fast reactor?
In a fast reactor, fast fission neutrons maintain the chain reaction, and no moderator is needed.
Why are reactors important?
Another important use for reactors is the utilization of their high neutron fluxes for studying the structure and properties of materials and for producing a broad range of radionuclides, which, along with a number of fission products, have found many different applications.
How do neutrons get slowed down?
In such a reactor, the fission neutrons produced (with an average kinetic energy of more than 1 MeV) must be slowed down to thermal energy by scattering from a moderator, usually consisting of ordinary water, heavy water (D 2 O), or graphite.
How many neutrons are released in nuclear fission?
Controlled Nuclear Fission. To maintain a sustained controlled nuclear reaction, for every 2 or 3 neutrons released, only one must be allowed to strike another uranium nucleus. If this ratio is less than one then the reaction will die out; if it is greater than one it will grow uncontrolled (an atomic explosion).
Why are neutrons slow?
In addition to the need to capture neturons, the neutrons often have too much kinetic energy. These fast neutrons are slowed through the use of a moderator such as heavy water and ordinary water. Some reactors use graphite as a moderator, but this design has several problems.
What element is responsible for neutron absorbing?
Most reactors are controlled by means of control rods that are made of a strongly neutron-absorbent material such as boron or cadmium. Controlled Nuclear Chain Reaction.