What are the differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
- Most prokaryotes have peptidoglycan cell walls but eukaryotes don’t. Prokaryotic viruses therefore need a way to degrade peptidoglycan.
- Prokaryotic viruses usually inject only their nucleic acids. ...
- Animal viruses are coated with a bilayer membrane that facilitates fusion with the host cell.
What are five characteristics of prokaryotes?
What are the characteristics of prokaryotes quizlet?
- they have no nuclear membrane.
- their DNA is not wound around histones.
- the cell walls are made of a chemical called peptidoglycan.
- they do not have complex membrane-bound organelles.
Is Oscillatoria autotroph or heterotroph?
This part is dominated by cyanobacteria and aerobic heterotrophic bacteria and is considered to be biologically the most active layer in mats with respect to carbon cycling. There is no doubt that cyanobacteria play an important role in microbial mats, e.g. by establishing oxygen gradients and supplying nutrient for heterotrophic bacteria.
What are some examples of prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
What are some examples of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Examples of prokaryotes are bacteria and archaea. Examples of eukaryotes are protists, fungi, plants, and animals (everything except prokaryotes). What is the main function of cell membrane? The plasma membrane, or the cell membrane, provides protection for a cell.
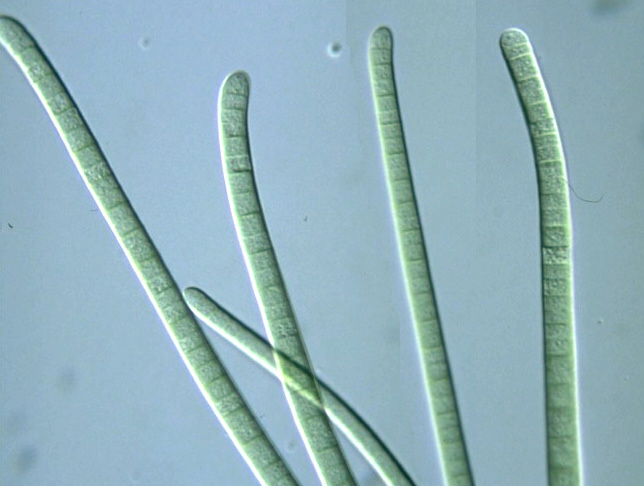
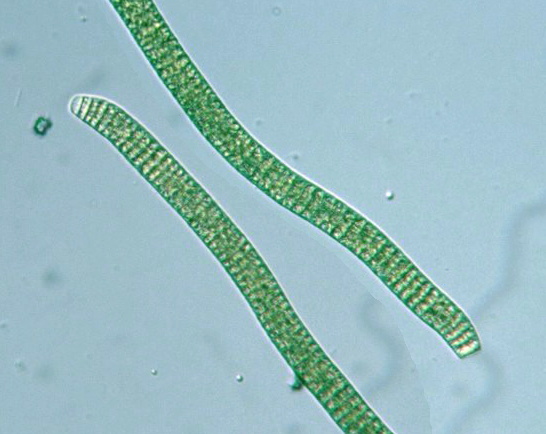
Are Oscillatoria prokaryotic?
blue-green algae, also called cyanobacteria, any of a large, heterogeneous group of prokaryotic, principally photosynthetic organisms.
What cell type is the Oscillatoria organism?
Oscillatoria uses photosynthesis to survive and reproduce. Each filament of oscillatoria consists of trichome which is made up of rows of cells. The tip of the trichome oscillates like a pendulum....OscillatoriaOscillatoria princepsScientific classificationDomain:BacteriaPhylum:Cyanobacteria9 more rows
Which one is a prokaryote Oscillatoria?
Thus, the correct answer is 'Oscillatoria'
Is Oscillatoria a eubacteria?
Cyanobacteria (“blue-green algae”), such as Oscillatoria sp., are a ubiquitous group of bacteria found in freshwater systems worldwide that are linked to illness and in some cases, death among humans and animals. Exposure to cyanobacteria occurs via ingestion of contaminated water or food-products.
Is Gloeocapsa prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
prokaryotesCells of Gloeocapsa are surrounded by a thick, gelatinous sheath that holds the cells together in a colony. We will also look at bacteria that are found in the yogurt that we eat. Both of these are examples of prokaryotes.
Is Oscillatoria multicellular or unicellular?
Oscillatoria annae include unicellular, colonial and filamentous forms some filamentous cyanophytes form differentiated cells called heterocyst, that are speciallized for hydrogen fixation, and resting or spore cells called aconites.
What are examples of prokaryotes?
Prokaryotes are single celled, microscopic entities. They neither have specialized organelles nor a prominent nucleus with a membrane. Examples of prokaryotes include cyanobacteria, E. coli, mycoplasma etc.
What is not a prokaryote?
They also lack membrane-bound organelles. In the given options, Saccharomyces is not a prokaryote as it is a fungus and hence a eukaryote. They have a well-defined nucleus and membrane-bound nucleus. Their cell structure is more complicated than a prokaryotic cell.
What are 5 examples of prokaryotic cells?
What Are 5 Examples Of Prokaryotic Cells?E. coli (Escherichia Coli Bacterium)Corynebacterium diphtheriae.Bacillus anthracis.Bacillus cereus.
Is Anabaena prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
prokaryotic cellsAnabaena are a genus of Blue-green Algae or Cyanobacteria. Specifically, Anabaena are known for their nitrogen-fixing abilities. These prokaryotic cells are not true algae (which are eukaryotic) but also aren't truly bacterial cells as they produce energy via photosynthesis.
Is Oscillatoria single-celled?
Oscillatoria Morphology It consists of a single row of cells forming trichomes or un-branched filaments with a very thin gelatinous sheath. The cells are broader than longer but cylindrical.
What is the phylum of Oscillatoria?
CyanobacteriaOscillatoria / PhylumCyanobacteria, also known as Cyanophyta, are a phylum of Gram-negative bacteria that obtain energy via photosynthesis. Wikipedia
What are the characteristics of prokaryotic cells?
Although prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have many differences, they share some common features, including the following: 1 DNA: Genetic coding that determines all the characteristics of living things. 2 Cell (or plasma) membrane: Outer layer that separates the cell from the surrounding environment and acts as a selective barrier for incoming and outgoing materials. 3 Cytoplasm: Jelly-like fluid within a cell that is composed primarily of water, salts and proteins. 4 Ribosomes: Organelles that make proteins.
What is the difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
There are several differences between the two, but the biggest distinction between them is that eukaryotic cells have a distinct nucleus containing the cell's genetic material, while prokaryotic cells don't have a nucleus and have free-floating genetic material instead.
What are the organisms in the Eukarya domain?
Organisms in the Eukarya domain are made of the more complex eukaryotic cells. These organisms, called eukaryotes, can be unicellular or multicellular and include animals, plants, fungi and protists. Many people are unclear on whether yeasts or fungi are prokaryotes or eukaryotes. Both are eukaryotes and share similar cell structure ...
How long ago did eukaryotes develop?
Both are eukaryotes and share similar cell structure to all other eukaryotes. Eukaryotes developed at least 2.7 billion years ago, following 1 to 1.5 billion years of prokaryotic evolution, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Which cells have smaller ribosomes?
The ribosomes in prokaryotic cells also have smaller subunits. All ribosomes (in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells) are made of two subunits — one larger and one smaller. In eukaryotes, these pieces are identified by scientists as the 60-S and 40-S subunits. In prokaryotes, the ribosomes are made of slightly smaller subunits, ...
What is the outer layer of a cell?
Cell (or plasma) membrane: Outer layer that separates the cell from the surrounding environment and acts as a selective barrier for incoming and outgoing materials. Cytoplasm: Jelly-like fluid within a cell that is composed primarily of water, salts and proteins. Ribosomes: Organelles that make proteins.
Which bacterium has two circular chromosomes?
For example, Vibrio cholerae, the bacterium that causes cholera, has two circular chromosomes. Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells: Eukaryotic cells have several other membrane-bound organelles not found in prokaryotic cells.