
Full Answer
What is the pectoralis major?
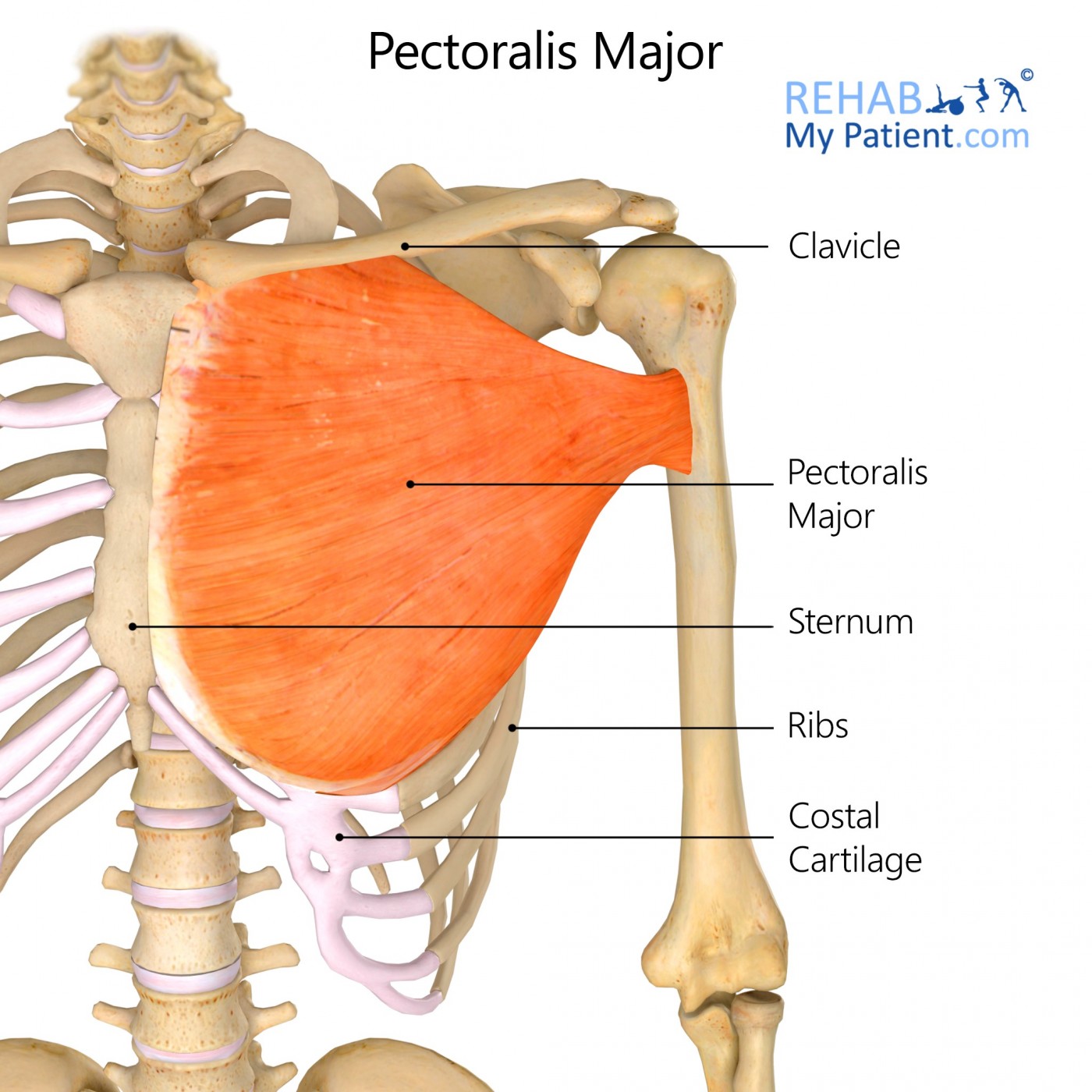
Pectoralis major. The pectoralis major muscle is a large muscle in the upper chest, fanning across the chest from the shoulder to the breastbone. The two pectoralis major muscles, commonly referred to as the 'pecs,' are the muscles that create the bulk of the chest. A developed pectoralis major is most evident in males,...
Why does the pectoralis major have a recess at the top?
Due to the different courses of the muscle fibers, the insertion has a recess which is open to the top preventing the muscle from overstretching. The triangular depression between the pectoralis major muscle, deltoid muscle and clavicle is called infraclavicular fossa (Mohrenheim’s fossa).
What is a pennate muscle?
Definition: A pennate muscle (also called a penniform muscle) is a muscle with fascicles that attach obliquely (in a slanting position) to its tendon. … In a pennate muscle, the fascicles will form an angle with its central tendon. Is the gastrocnemius a Pennate muscle?
What is aplasia of the pectoralis?
Clinical Notes. Aplasia of the pectoralis major muscle is one of the most common muscular malformations. In Poland syndrome there is embryonic malformation of the thoracic wall, which is accompanied by a defect of the pectoralis major muscle in combination with other malformations of the upper extremities (e.g., malformations of the fingers).
See more

Is the pectoralis muscle pennate?
Fusiform-shaped muscles (e.g. biceps brachii) have their fibres arranged in near parallel orientation in the belly and converge to a tendon at one or both ends. Muscles that have their fibres oblique to the line of contraction may be triangular (pectoralis, adductor longus) or pennate (feather-like) (Fig.
Is pec major Multipennate?
The pectoralis major (PM) is a complex, multipennate muscle of the anterior shoulder girdle that is responsible for adduction, internal rotation, and flexion of the humerus.
What muscles are pennate?
A pennate or pinnate muscle (also called a penniform muscle) is a type of skeletal muscle with fascicles that attach obliquely (in a slanting position) to its tendon....Pennate muscle.Rectus femorisFMA74993Anatomical terms of muscle11 more rows
What type of parallel muscle is pectoralis major?
convergent muscleThe large muscle on the chest, the pectoralis major, is an example of a convergent muscle because it converges on the intertubercular groove and greater tubercle of the humerus via a tendon (see image 11.3).
What is pectoralis major muscle?
The pectoralis major is the superior most and largest muscle of the anterior chest wall. It is a thick, fan-shaped muscle that lies underneath the breast tissue and forms the anterior wall of the axilla.
Which of the following is not a group of pennate muscles?
Bio 220 Chapter 6-12QuestionAnswerWhich of the following is not a group of pennate muscles?TripennateA muscle is attached to the femur and tibia. Its function or action is to bend the knee. When it contracts, it is acting as the:TrapeziusThe posterior arm muscle that extends the forearm is the:triceps brachii.62 more rows
What is the difference between fusiform and pennate muscle?
Fusiform or spindle-shaped fibers run parallel to the muscle's long axis (e.g., biceps brachii) and taper at the tendinous attachment. In contrast, pennate or fan-shaped fibers' fasciculi (bundles of fibers) lie at an oblique pennation angle.
Which of the following is a Proprioceptor associated with muscle tissue?
Muscle spindles are proprioceptors that consist of intrafusal muscle fibers enclosed in a sheath (spindle). They run parallel to the extrafusal muscle fibers and act as receptors that provide information on muscle length and the rate of change in muscle length.
Is biceps brachii a pennate?
Biceps is composed of two short-fibred pennate muscle heads separated longitudinally by a thick internal tendon (Fig. 2) running continuously from the muscle's origin on the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula to its insertion on the medial radial tuberosity.
What muscles are parallel muscles?
Parallel muscles have fibres that, as the name suggests, run parallel to each other and are sometimes called strap muscles. They are normally long muscles which cause large movements, and are not very strong but have good endurance. Examples include Sartorius and Sternocleidomastoid.
Is pennate a parallel muscle?
Pennate. Unlike in parallel muscles, fibers in pennate muscles are at an angle to the force-generating axis (pennation angle) and usually insert into a central tendon.
Is the latissimus dorsi parallel or pennate?
triangular pennate muscleThe latissimus dorsi (LD) is a triangular pennate muscle. In pennate muscles, the excursion length of muscles is much less than that in strap muscles.
What do you mean by Multipennate muscle?
Adjective. multipennate (not comparable) (anatomy) Of a muscle: having the fibers arranged at multiple angles in relation to the axis of force generation.
What is the function of a Multipennate muscle?
a bundle of long slender cells (muscle fibers) that have the power to contract and hence to produce movement. Muscles are responsible for locomotion and play an important part in performing vital body functions. They also protect the contents of the abdomen against injury and help support the body.
What type of muscle is the deltoid muscle?
skeletal musclesDeltoid muscles help you move your arms in different directions. They also protect and stabilize your shoulder joint. Like most other muscles in your body, the deltoids are skeletal muscles. Tendons attach them to bones.
What does Unipennate mean?
Medical Definition of unipennate : having the fibers arranged obliquely and inserting into a tendon only on one side in the manner of a feather barbed on one side a unipennate muscle.
What are the parts of the pectoralis major?
The pectoralis major has a broad origin, based on which it is divided into three parts: clavicular part, sternocostal part and abdominal part. All three parts converge laterally and insert onto the greater tubercle of humerus. The main function of this chest muscle as a whole is the adduction and internal rotation of the arm on the shoulder joint.
What is the deep surface of the pectoralis minor?
In females, it is covered by the breast. The deep surface of the muscle covers the pectoralis minor and serratus anterior muscles and the anterior surface of the upper six ribs.
Why is the pectoralis major muscle important?
This action is important in activities such as climbing. When acting from the humeral attachment, the pectoralis major muscle also facilitates the act of inspiration. This is particularly important during forced breathing in physical distress.
How long does it take to read a pectoralis major?
Reading time: 5 minutes. Pectoralis major muscle (Musculus pectoralis major) The pectoralis major is a paired, superficial muscle located on the anterior surface of the thoracic cage. If you’re a gym lover, you’ll hear these muscles also being referred to as the pecs muscles. The pectoralis major has a broad origin, ...
What is the triangular depression between the pectoralis and the deltoid muscle?
The triangular depression between the pectoralis major muscle, deltoid muscle and clavicle is called i nfraclavicular fossa (Mohrenheim’s fossa) which serve s as an important landmark in the surgical procedures on the subclavian artery.
Which artery is the pectoralis muscle vascularized by?
The pectoralis major muscle is vascularized by the pectoral branches of thoracoacromial artery and the perforating branches of internal thoracic artery .
Where does the clavicular part originate?
The clavicular part originates from the anterior surface of the medial half of the clavicle. The sternocostal part originates from the anterior surface of sternum and the anterior aspects of the costal cartilages of ribs 1-6. The smallest, abdominal part originates from the anterior layer of the rectus sheath.
What is the function of the pectoralis major?
The pectoralis major's primary functions are flexion, adduction, and internal rotation of the humerus. The pectoral major may colloquially be referred to as "pecs", "pectoral muscle" or "chest muscle" due to it being the largest and most superficial muscle in the chest area.
How does hypertrophy of the pectoralis major occur?
Hypertrophy of the pectoralis major increases functionality. Maximal activation of the pectoralis major occurs in the transverse plane through pressing motions. Both multi-joint and single-joint exercises induce pectoralis major hypertrophy. A combination of both single-joint and multi-joint exercises will result in a maximum hypertrophic response. [Aesthetic contours of regions in the muscle may be specifically-addressed (“targeted”) by specific exercises; for instance, “plating” or “stitching” of the pectoralis major —towards the center of the sternum —-may be targeted by a wider hand position.] The pectoralis major can be targeted from numerous training angles along the sternum and clavicle. Exercises that include horizontal adduction and elbow extensions such as the barbell bench press, dumbbell bench press, and machine bench press induce high activation of the pectoralis major in the sternocostal region. Heavy loads are strongly correlated with pectoralis major activation.
What is the clavicular head?
Clavicular head: anterior surface of the medial half of the clavicle. Depression and abduction of the scapula. The pectoralis major (from Latin pectus ' breast ') is a thick, fan-shaped or triangular convergent muscle, situated at the chest of the human body.
What is the name of the muscle that makes up the bulk of the chest muscles?
The pectoralis major (from Latin pectus ' breast ') is a thick, fan-shaped or triangular convergent muscle, situated at the chest of the human body. It makes up the bulk of the chest muscles and lies under the breast. Beneath the pectoralis major is the pectoralis minor, a thin, triangular muscle.
Which head flexes the humerus?
The clavicular head flexes the humerus, and the sternocostal head adducts the humerus. As a whole the action is to adduct and medially rotate the humerus. It also draws the scapula anteriorly and inferiorly. The pectoralis major has four actions which are primarily responsible for movement of the shoulder joint.
Which nerves innervate the pectoralis major?
The pectoralis major receives dual motor innervation by the medial pectoral nerve and the lateral pectoral nerve, also known as the lateral anterior thoracic nerve. The sternal head receives innervation from the C7, C8 and T1 nerve roots, via the lower trunk of the brachial plexus and the medial pectoral nerve.
Can pectoralis major muscle be excision?
Pectoralis major muscle in rare occasions may develop intramuscular lipomas. Such rare tumors may mimic malignant breast tumors as they look like enlargements of the breasts. They are well-encapsulated radiolucent tumours of fat density. Their location can be accurately identified through computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The treatment in these cases involves complete surgical excision because of the risk of liposarcoma they post especially large intramuscular liposomas. Partial excision is risky because recurrence may occur.
What are pennate muscles?
Pennate muscles have a large number of muscle fibres per unit and so are very strong, but tire easily. They can be divided into: 1 Unipennate: These muscles have their fibres arranged to insert in a diagonal direction onto the tendon, which allows great strength. Examples include the Lumbricals (deep hand muscles) and Extensor Digitorum Communis (wrist and finger extensor) 2 Bipennate: Bipennate muscles have two rows of muscle fibres, facing in opposite diagonal directions, with a central tendon, like a feather. This allows even greater power but less range of motion. An example is the Rectus Femoris 3 Multipennate: As the name suggests Multipennate muscles have multiple rows of diagonal fibres, with a central tendon which branches into two or more tendons. An example is the Deltoid muscle which has three sections, anterior, posterior and middle.
What are some examples of bipennate muscles?
Examples include the Lumbricals (deep hand muscles) and Extensor Digitorum Communis (wrist and finger extensor) Bipennate: Bipennate muscles have two rows of muscle fibres, facing in opposite diagonal directions, with a central tendon, like a feather.
Which muscle is circular?
These muscles appear circular in shape and are normally sphincter muscles which surround an opening such as the mouth, surrounded by Obicularis Oris and Obicularis Oculi surrounding the eyes .
Which muscle is very strong?
Pennate Muscles . Pennate muscles have a large number of muscle fibres per unit and so are very strong, but tire easily. They can be divided into: Unipennate: These muscles have their fibres arranged to insert in a diagonal direction onto the tendon, which allows great strength.
Which muscle group is not very strong but has good endurance?
They are normally long muscles which cause large movements, are not very strong but have good endurance. Examples include Sartorius and Sternocleidomastoid. Some textbooks include Fusiform muscles in the parallel group.
Which muscle group is more spindle shaped?
Fusiform Muscles. Sometimes, included in the parallel muscle group, these muscles are more spindle-shaped, with the muscle belly being wider than the origin and insertion. Examples are, Biceps Brachii and Psoas major.
Which muscles have a spiral shape?
the sternocostal fibres of the pectoralis major and latissimus dorsi muscles). Others spiral around a bone (e.g. supinator in the forearm) or have fibres orientated in different directions in a cruciate fashion (e.g. adductor magnus muscle). Many muscles have more than one of the above arrangements to allow for different functional roles.
Which muscle has a tendon at one end?
Fusiform-shaped muscles (e.g. biceps brachii) have their fibres arranged in near parallel orientation in the belly and converge to a tendon at one or both ends. Muscles that have their fibres oblique to the line of contraction may be triangular (pectoralis, adductor longus) or pennate (feather-like) ( Fig. 60.3). Pennate muscles can be further subdivided into unipennate (e.g. flexor pollicis longus), bipennate (e.g. rectus femoris, dorsal interossei), multipennate (e.g. deltoid), and circumpennate or cylindrical (e.g. tibialis anterior).
Why is the spontaneous return to normal sarcomere number following the removal of external constraints?
The spontaneous return to normal sarcomere number following the removal of external constraints suggests a physiological mechanism to restore homeostasis and optimal muscle mechanics.
Can a pennate muscle contract?
It has been suggested that loss of muscle fibre diameter may cause contracture in pennate muscles, through shortening of the aponeuroses. A recent study, using ultrasound imaging to examine the architecture of medial gastrocnemius, found no difference in fibre length between normal children and those with spastic diplegia and plantarflexion contractures (Shortland et al., 2002 ). On relating the findings to those in the literature from animal studies, where fibre length was normal but diameter was reduced, the investigators concluded that muscle shortening was due to fibre atrophy.
Which axis of the muscle runs parallel to the long axis of the muscle?
The long axes of the fascicles run parallel to the long axis of the muscle is a description of this type of fascicle arrangement.
Which muscle has a fascicle pattern?
In addition to the Pectoralis major, another muscle that displays this pattern of fascicle arrangement is Latissimus dorsi.
Which muscle has a triangular fascicle?
This arrangement of muscle fascicles tends to be triangular in shape. The Pectoralis major is an example of a muscle with this type of muscle fascicle arrangement.
Which joint is an example of a fulcrum?
The elbow joint is an example of a fulcrum as the biceps brachii flexes the forearm.
Overview
The pectoralis major (from Latin pectus 'breast') is a thick, fan-shaped or triangular convergent muscle, situated at the chest of the human body. It makes up the bulk of the chest muscles and lies under the breast. Beneath the pectoralis major is the pectoralis minor, a thin, triangular muscle. The pectoralis major's primary functions are flexion, adduction, and internal rotation of the humerus. Th…
Structure
It arises from the anterior surface of the sternal half of the clavicle from breadth of the half of the anterior surface of the sternum, as low down as the attachment of the cartilage of the sixth or seventh rib; from the cartilages of all the true ribs, with the exception, frequently, of the first or seventh, and from the aponeurosis of the abdominal external oblique muscle.
Function
The pectoralis major has four actions which are primarily responsible for movement of the shoulder joint. The first action is flexion of the humerus, as in throwing a ball underhand, and in lifting a child. Secondly, it adducts the humerus, as when flapping the arms. Thirdly, it rotates the humerus medially, as occurs when arm-wrestling. Fourthly the pectoralis major is also responsible f…
Clinical significance
Tears of the pectoralis major are rare and typically affect otherwise healthy individuals. This type of injury is known to affect the athletic population, namely in high-impact contact sports such as powerlifting, and may result in pain, weakness, and disability. Most lesions are located at the musculotendinous junction and result from violent, eccentric contraction of the muscle, such as d…
See also
• Pectoralis minor, an inferior, smaller muscle to the pectoralis major
• Sternalis, an accessory muscle found in some individuals that may have embryonic origin from the pectoralis major
• Tra Telligman, a retired American mixed martial artist and boxer having only one pectoral muscle
External links
• Illustration: upper-body/pectoralis-major from The Department of Radiology at the University of Washington
• UCC
• www.polands-syndrome.com
• MRI Imaging sequence demonstrating a pectoralis major muscle tear