
Which is more dangerous Gram positive or negative?
Mar 24, 2020 · Penicillin is effective only against Gram-positive bacteria because Gram negative bacteria have a lipopolysaccharide and protein layer that surrounds the peptidoglygan layer of the cell wall, preventing penicillin from attacking.
Which Gram negative or Gram positive bacteria more dangerous?
For this reason Gram-positive bacteria are very susceptible to penicillin (as first evidenced by the discovery of penicillin in 1928). Penicillin, or any other molecule, enters Gram-negative bacteria in a different manner. The bacteria have thinner cell walls but the external surface is coated with an additional cell membrane, called the outer membrane.
Do sulfa antibiotics attack Gram positive or Gram negative?
Gram-negative bacteria have peptidoglycan between membranes. Penicillin works best on gram-positive bacteria by inhibiting peptidoglycan production, making the cells leaky and fragile. The cells burst open and are much easier for the immune system to break down, which helps the sick person heal more quickly.
Is Campylobacter jejuni Gram positive or Gram negative?
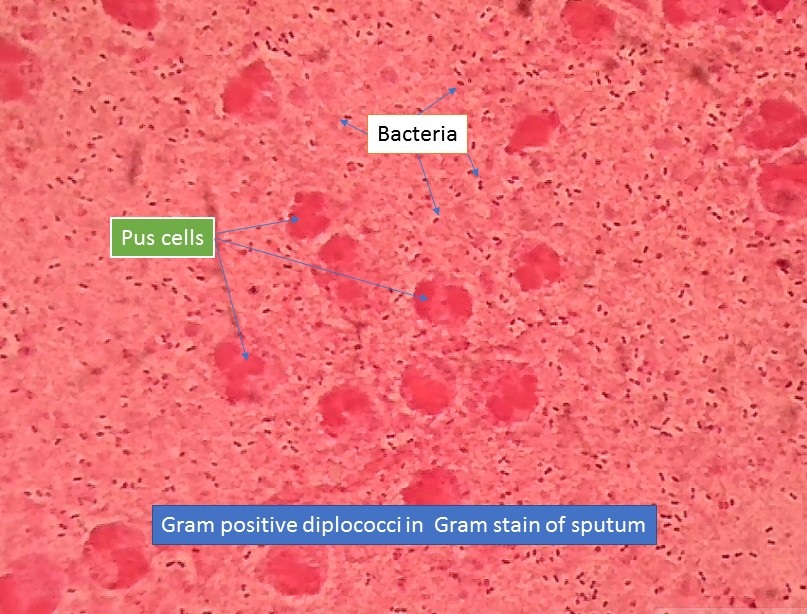
•Bacteria are divided into two groups, Gram-positive (Figure 7) and Gram-negative, based on their cell wall formation and staining properties. Penicillin is effective only against Gram-positive bacteria because Gram negative bacteria have a lipopolysaccharide and protein layer that surrounds the peptidoglygan layer of
Is Penicillium gram-positive or Gram-negative?
The genus includes a wide variety of species molds that are the source molds of major antibiotics. Penicillin, a drug produced by P. chrysogenum (formerly P. notatum), was accidentally discovered by Alexander Fleming in 1929, and found to inhibit the growth of Gram-positive bacteria (see beta-lactams).
What type of bacteria is Penicillium?
Penicillium is a diverse fungal genus of ascomycetous fungi and contains more than 350 species (Visagie et al., 2014). Penicillium is often referred as Deuteromycetes.
Is penicillin positive or negative?
Antimicrobial resistance can be classified into three groups: intrinsic, mutational and acquired. Penicillin, tetracycline and erythromycin are broad-spectrum drugs, effective against gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms.
What type of fungus is Penicillium?
Penicillium, genus of blue or green mold fungi (kingdom Fungi) that exists as asexual forms (anamorphs, or deuteromycetes). Those species for which the sexual phase is known are placed in the Eurotiales.
Is Penicillium eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Edible mushrooms, yeasts, black mold, and Penicillium notatum (the producer of the antibiotic penicillin) are all members of the kingdom Fungi, which belongs to the domain Eukarya. As eukaryotes, a typical fungal cell contains a true nucleus and many membrane-bound organelles.
Is Penicillium multicellular or unicellular?
MulticellularGenus/species: Penicillium Sp. Morphology: Cell: Multicellular, elipsoid.
Does penicillin affect gram-negative bacteria?
Penicillin is effective only against Gram-positive bacteria because Gram negative bacteria have a lipopolysaccharide and protein layer that surrounds the peptidoglygan layer of the cell wall, preventing penicillin from attacking.
Is gram-positive cell wall sensitive to lysozyme?
Gram-positive bacteria are more susceptible to the action of lysozyme because their cell wall contains up to 90% peptidoglycan, whereas Gram-negative bacteria are more resistant because of the smaller amount of peptidoglycan in their cell wall.
Does ampicillin cover gram-negative?
Ampicillin, an extended spectrum penicillin, is effective against gram positive as well as gram negative microorganisms. Also, being acid resistant, it can be given orally.
Is Penicillium an imperfect fungi?
The imperfect fungi are not placed in the Ascomycota phylum because classification of that group is based on the morphology of sexual structures which the Deuteromycota do not have. The best known fungus in this phylum is Penicillium.
How do I identify my Penicillium?
Important characters used for describing Penicillium include colony texture, degree of sporulation, the colour of conidia, the abundance, texture and colour of mycelia, the presence and colours of soluble pigments and exudates, colony reverse colours, and degree of growth and acid production (in some species acid ...Sep 22, 2014
Is Penicillium a penicillin?
Penicillium mold naturally produces the antibiotic penicillin.
What is penicillin G?
Penicillin G (benzylpenicillin) was first produced from a penicillium fungus that occurs in nature. The strain of fungus used today for the manufacture of penicillin G was created by genetic engineering to improve the yield in the manufacturing process. None of the other natural penicillins (F, K, N, X, O, U1 or U6) are currently in clinical use.
What are the side effects of penicillin?
Common (≥ 1% of people) adverse drug reactions associated with use of the penicillins include diarrhoea, hypersensitivity, nausea, rash, neurotoxicity, urticaria, and superinfection (including candidiasis ).
Why is penicillin used as a first line antibiotic?
Because penicillin resistance is now so common, other antibiotics are now the preferred choice for treatments. For example, penicillin used to be the first-line treatment for infections with Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis, but it is longer recommended for treatment of these infections.
What is the name of the mold that is used to make penicillin?
The term "penicillin" is defined as the natural product of Penicillium mould with antimicrobial activity. It was coined by Alexander Fleming on 7 March 1929 when he discovered the antibacterial property of Penicillium rubens. The name was "to avoid the repetition of the rather cumbersome phrase 'Mould broth filtrate,' the name 'penicillin' will be used," as Fleming explained in his 1929 paper in the British Journal of Experimental Pathology. The name thus refers to the scientific name of the mould, as described by Fleming in his Nobel lecture in 1945:
How is penicillin G destroyed?
Penicillin G is destroyed by stomach acid, so it cannot be taken by mouth, but doses as high as 2.4 g can be given (much higher than penicillin V). It is given by intravenous or intramuscular injection. It can be formulated as an insoluble salt, and there are two such formulations in current use: procaine penicillin and benzathine benzylpenicillin, which are used only in the treatment of syphilis. When a high concentration in the blood must be maintained, penicillin G must be administered at relatively frequent intervals, because it is eliminated quite rapidly from the bloodstream by the kidney.
Where is penicillin stored?
A single 8 gram batch of pure crystalline penicillin G sodium was stored at The National Institute for Medical Research at Mill Hill in London (the International Standard). One penicillin unit was defined at 0.6 micrograms of the International Standard.
Who was the first person to use penicillin?
Fleming's student Cecil George Paine was the first to successfully use penicillin to treat eye infection ( ophthalmia neonatorum) in 1930. The purified compound (penicillin F) was isolated in 1940 by a research team led by Howard Florey and Ernst Boris Chain at the University of Oxford.
What is the difference between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria?
Within bacteria, there are two types of bacterial cell walls. Gram-positive bacteria have a peptidoglycan layer on the outside of the cell wall. Gram-negative bacteria have peptidoglycan between membranes. Penicillin works best on gram-positive bacteria by inhibiting peptidoglycan production, making the cells leaky and fragile.
How do bacteria become resistant to antibiotics?
Bacteria can become resistant to antibiotics through the process of selection and evolution. Penicillin kills most of the bacterial cells, but it does not kill them all. Bacteria resistant to the effects of the antibiotic remain, but in small numbers they can be eliminated from the body by the immune system.
Why are antibiotics not helpful?
Antibiotics are highly specific to a certain bacterial function, and are not helpful for treating non-bacterial illnesses. Viruses are unaffected by antibiotics because they do not have peptidoglycan cell walls or ribosomes, and they do not replicate their own DNA.
What was the first antibiotic?
One of the first antibiotics discovered was penicillin. Penicillin was first used to treat bacterial infections in 1942 and is derived from the fungus Penicillium sp. When used as an antibiotic treatment, penicillin operates by a very specific mechanism. Penicillin interferes with the production of a molecule called peptidoglycan.
What are the cell walls of algae made of?
Algae cell walls can be made of cellulose, xylan, silica, carrageenan or a variety of other materials. The cell walls of most fungi are made from chitin. Composition of the cell wall in the archaea is more diverse. Within bacteria, there are two types of bacterial cell walls.

Overview
Penicillium is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that is part of the mycobiome of many species and is of major importance in the natural environment, in food spoilage, and in food and drug production.
Some members of the genus produce penicillin, a molecule that is used as an antibiotic, which kills or stops the growth of certain kinds of bacteria. Other sp…
Taxonomy
The genus was first described in the scientific literature by Johann Heinrich Friedrich Link in his 1809 work Observationes in ordines plantarum naturales; he wrote, "Penicillium. Thallus e floccis caespitosis septatis simplicibus aut ramosis fertilibus erectis apice penicillatis", where penicillatis means "having tufts of fine hair". Link included three species—P. candidum, P. expansum, and P. …
Characteristics
The thallus (mycelium) consists of highly branched networks of multinucleated, usually colourless hyphae, with each pair of cells separated by a septum. Conidiophores are at the end of each branch accompanied by green spherical constricted units called conidia. These propagules play a significant role in reproduction; conidia are the main dispersal strategy of these fungi.
Ecology
Species of Penicillium are ubiquitous soil fungi preferring cool and moderate climates, commonly present wherever organic material is available. Saprophytic species of Penicillium and Aspergillus are among the best-known representatives of the Eurotiales and live mainly on organic biodegradable substances. Commonly known in America as molds, they are among the main causes of food spoilage, especially species of subgenusPenicillium. Many species produce highl…
Economic value
Several species of the genus Penicillium play a central role in the production of cheese and of various meat products. To be specific, Penicillium molds are found in Blue cheese. Penicillium camemberti and Penicillium roqueforti are the molds on Camembert, Brie, Roquefort, and many other cheeses. Penicillium nalgiovenseis used in soft mold-ripened cheeses, such as Nalžovy (ellischau) …
Reproduction
Although many eukaryotes are able to reproduce sexually, as much as 20% of fungal species had been thought to reproduce exclusively by asexual means. However recent studies have revealed that sex occurs even in some of the supposedly asexual species. For example, sexual capability was recently shown for the fungus Penicillium roqueforti, used as a starter for blue cheese production. This finding was based, in part, on evidence for functional mating type(MAT) genes t…
External links
• Samson, R.A.; Pitt, J.I. (2000). Integration of Modern Taxonomic Methods For Penicillium and Aspergillus Classification. CRC Press. p. 66. ISBN 978-9058231598.
• Asan, A. (2004). "Aspergillus, Penicillium, and Related Species Reported from Turkey" (PDF). Mycotaxon. 89 (1): 155–7.