Is peptide bond formation a spontaneous process?
Then, peptide bond formation occurs spontaneously at the surface of water, facilitated by the formation of the copper complex at the interface.
Is peptide bond formation anabolic?
Bonds called peptide bonds form between separate amino acids, joining them together to form a polypeptide chain. This reaction is anabolic because a large molecule is made from smaller ones.
What reaction is peptide bond formation?
A peptide bond is formed by a dehydration synthesis or reaction at a molecular level. This reaction is also known as a condensation reaction which usually occurs between amino acids. As depicted in the figure given below, two amino acids bond together to form a peptide bond by the dehydration synthesis.
Does peptide bond formation require energy?
The formation of the peptide bond consumes energy, which, in organisms, is derived from ATP. Peptides and proteins are chains of amino acids held together by peptide bonds (and sometimes by a few isopeptide bonds).
Which bonds are formed by anabolic reactions?
Anabolism of proteins The amino acids are joined together in a chain by peptide bonds to form polypeptide chains.
Is anabolic Exergonic or endergonic?
endergonic reactionsAnabolic reactions are endergonic reactions, meaning that they require an input of energy. Catabolism is the process of breaking down complex molecules into simpler molecules.
Is peptide bond formation a hydrolysis reaction?
These peptide bonds are formed via the dehydrolysis reaction (also known as condensation). In the dehydrolysis reaction, a covalent bond is formed between the carbon of the carbonyl group of one amino acid and the nitrogen of the amino group of the other amino acid. In the process, a water molecule is released.
What happens in peptide bond formation of translation?
During translation, peptide bonds are formed from the amino (N) to the carboxyl (C) terminus by removal of water (also referred to as dehydration or condensation) and catalyzed by RNA (referred to as a ribozyme) that forms part of the ribosome.
What causes peptide bonds?
Peptide bonds are formed when the amine group of one amino acid binds with the carbonyl carbon of another amino acid.
Which of the following statements about peptide bonds is true?
Answer and Explanation: The correct equation is b. Peptides are the polymers of amino acids and peptides combine to form proteins. A peptide bond is an amide-type of covalent chemical bond that links two amino acids.
Why is peptide bond formation unfavorable?
Peptide bond formation is kinetically unfavorable because of how long the process is. It has a half-life of 1000 years and another bond could easily form in the place of a peptide bond in that time.
How is a peptide bond formed between two amino acids?
A peptide bond is formed between two amino acid molecules when the carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of the other molecule, releasing a molecule of water (H 2 O). The two amino acids joined by a peptide bond (-CO-NH-).
Is peptide bond formation A hydrolysis reaction?
These peptide bonds are formed via the dehydrolysis reaction (also known as condensation). In the dehydrolysis reaction, a covalent bond is formed between the carbon of the carbonyl group of one amino acid and the nitrogen of the amino group of the other amino acid. In the process, a water molecule is released.
What type of bond is A peptide bond?
covalent bondPeptide bond: A covalent bond joining the α-amino group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of another with the loss of a water molecule.
Which statements about A peptide bond are correct?
Answer and Explanation: The correct equation is b. Peptides are the polymers of amino acids and peptides combine to form proteins. A peptide bond is an amide-type of covalent chemical bond that links two amino acids.
How are peptide bonds formed between amino acids in the elongation process of the translation of MRNA?
The energy for each step of the ribosome is donated by an elongation factor that hydrolyzes GTP. Peptide bonds form between the amino group of the amino acid attached to the A-site tRNA and the carboxyl group of the amino acid attached to the P-site tRNA.
What is a Peptide Bond?
Proteins are found in all living species from bacteria to humans. Proteins are the multifunctional molecules in our bodies and are composed of the elements carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen. They make up our hair, nails, skin and blood.
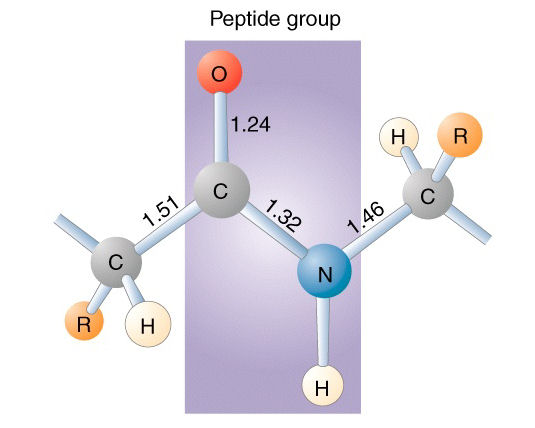
Peptide Bond Formation
A peptide bond is a covalent bond that links amino acids together to form a polypeptide. A peptide bond is formed through a process called dehydration synthesis. Dehydration synthesis, also referred to as polymerization, is an anabolic process in which a water molecule is removed to link monomers together to form a polymer.
About This Quiz & Worksheet
This quiz/worksheet combination will help you test your understanding of the vital peptide bond structures and formations. The questions on the quiz will test you on the chemical groups involved in peptide bonds and the meaning of endergonic.
Skills Practiced
This quiz and worksheet will allow you to test your skills in the following areas:
Additional Learning
To learn more about this topic, review the accompanying lesson called Peptide Bond: Definition, Formation & Structure. This lesson covers the following objectives:
Why does breaking ATP release energy?
However, even the bond breaking in ATP requires energy input. The reason ATP can store energy is because when the free phosphate is released, it forms a ton of hydrogen bonds with the water around it, releasing energy ( also there is some increased entropy due to resonance in ADP). So even when a bond is breaking in ATP, the net reaction results in greater energy release due to bond formation between phosphate and water. Tricky!
Is a bond exergonic or endergonic?
Forming a bond is always exergonic. Breaking a bond is always endergonic. But let’s say it takes 10 joules of energy to break a bond and then you form a bond which releases 20 joules, then the overall process ends up so being exergonic because you have a net yield of 10 joules. Maybe that’s what your teacher meant? Or maybe they just slipped there words up, that can happen sometimes. Hope that helped!

What Is A Peptide?
- A peptide is a short-chain made up of amino acidwhich, together with other peptides, forms a protein.
- The number of amino acids in a peptide can range from two amino acids to fifty amino acids.
- Based on the number of amino acids present in the peptide, peptides are of many types; peptides with ten or fewer amino acids are termed oligopeptides, and the peptides with mor…
- A peptide is a short-chain made up of amino acidwhich, together with other peptides, forms a protein.
- The number of amino acids in a peptide can range from two amino acids to fifty amino acids.
- Based on the number of amino acids present in the peptide, peptides are of many types; peptides with ten or fewer amino acids are termed oligopeptides, and the peptides with more than ten amino aci...
- Polypeptides with around 100 amino acids are then considered proteins.
Peptide Bond Definition
- A peptide bond is a special type of amide bond formed between two molecules where an α-carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the α-amino group of another molecule releasing a water molecule.
- The peptide bond is also referred to as the isopeptide bond where the amide bond forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid a…
- A peptide bond is a special type of amide bond formed between two molecules where an α-carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the α-amino group of another molecule releasing a water molecule.
- The peptide bond is also referred to as the isopeptide bond where the amide bond forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid at other positions than...
- The process of formation of the peptide bond is an example of a condensation reaction resulting in dehydration (removal of water).
- Peptide bonds are covalent bonds that exist between any two amino acids resulting in a peptide chain.
Peptide Bond Formation Mechanism
- The mechanism of peptide bond formation is a dehydration synthesis process.
- During the formation of a peptide bond, the carboxyl group of one amino acid moves towards the amino group of another amino acid.
- Subsequently, one hydrogen and one oxygen atoms are lost from the carboxyl group (COOH) of the first amino acid. In contrast, one hydrogen is lost from the amino group (NH2) of the ot…
- The mechanism of peptide bond formation is a dehydration synthesis process.
- During the formation of a peptide bond, the carboxyl group of one amino acid moves towards the amino group of another amino acid.
- Subsequently, one hydrogen and one oxygen atoms are lost from the carboxyl group (COOH) of the first amino acid. In contrast, one hydrogen is lost from the amino group (NH2) of the other amino acid.
- This results in the release of a water molecule (H2O) along with the formation of an amide bond (C-N) between the two amino acids.
Peptide Bond Degradation Mechanism
- The degradation of the peptide bond takes place through hydrolysis, thus requires the presence of water molecules.
- The degradation reaction is very slow as the amide bond between the amino acids is stabilized by the partial double bond.
- Because of the partial double bond between carbon and nitrogen molecule, carbon atom gen…
- The degradation of the peptide bond takes place through hydrolysis, thus requires the presence of water molecules.
- The degradation reaction is very slow as the amide bond between the amino acids is stabilized by the partial double bond.
- Because of the partial double bond between carbon and nitrogen molecule, carbon atom generates a slight positive charge.
- In the presence of water, the OH–ions of water attack the carbon atom, which results in degradation of the peptide bond.
Revision Questions/FAQs
- What is a peptide bond? A peptide bond is a special type of amide bond formed between two molecules where an α-carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the α-amino group of another molecule releasing a water molecule. Which parts of amino acids are involved in a peptide bond? The carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid are involved i…
References
- Jain JL, Jain S, and Jain N (2005). Fundamentals of Biochemistry. S. Chand and Company.
- Nelson DL and Cox MM. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry. Fourth Edition.
- Berg JM et al. (2012) Biochemistry. Seventh Edition. W. H Freeman and Company.
- ARLINGHAUS R, SHAEFER J, SCHWEET R. MECHANISM OF PEPTIDE BOND FORMATION IN POLYPEPTIDE SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964; 51(6):1291-1299. DOI:10.1073/p…
- Jain JL, Jain S, and Jain N (2005). Fundamentals of Biochemistry. S. Chand and Company.
- Nelson DL and Cox MM. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry. Fourth Edition.
- Berg JM et al. (2012) Biochemistry. Seventh Edition. W. H Freeman and Company.
- ARLINGHAUS R, SHAEFER J, SCHWEET R. MECHANISM OF PEPTIDE BOND FORMATION IN POLYPEPTIDE SYNTHESIS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964; 51(6):1291-1299. DOI:10.1073/pnas.51.6.1291
Sources
- 4% – https://www.peptidesciences.com/information/peptide-bonds/
- 2% – https://quizlet.com/164305942/study-flash-cards/
- 2% – https://quizlet.com/116549295/chapter-4-bio-302-flash-cards/
- 1% – https://www.sciencedaily.com/terms/peptide_bond.htm