Why is a phospholipid both hydrophilic and hydrophobic?
Why are phospholipids hydrophobic and hydrophilic? As the phosphate groups are polar and hydrophilic, they are attracted to water in the intracellular fluid. The hydrophobic tails associate with one another, forming the interior of the membrane. The polar heads contact the fluid inside and outside of the cell. Watch out a lot more about it.
What is meant by hydrophobic and hydrophilic?
Hydrophobic is any substance or surface that resists water. They act the same way as similar magnet poles by repelling each other. The word hydrophilic is also Greek, meaning water-loving. Hydrophilic is any substance that’s attracted to water. These types of materials easily mix and interact with one another.
Which part(s) of a phospholipid is hydrophobic?
The hydrophobic, or “water-fearing,” part of a phospholipid consists of its lengthy, nonpolar fatty acid tails. The fatty acid tails can simply work together with different nonpolar molecules, however they work together poorly with water.
Are phospholipids both hydrophilic and hydrophobic in nature?
The phospholipid bilayer is amphipathic, meaning it has both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties in water. When placed in water, phospholipids tend to naturally form small spheres called...
Why is phosphate group hydrophilic?
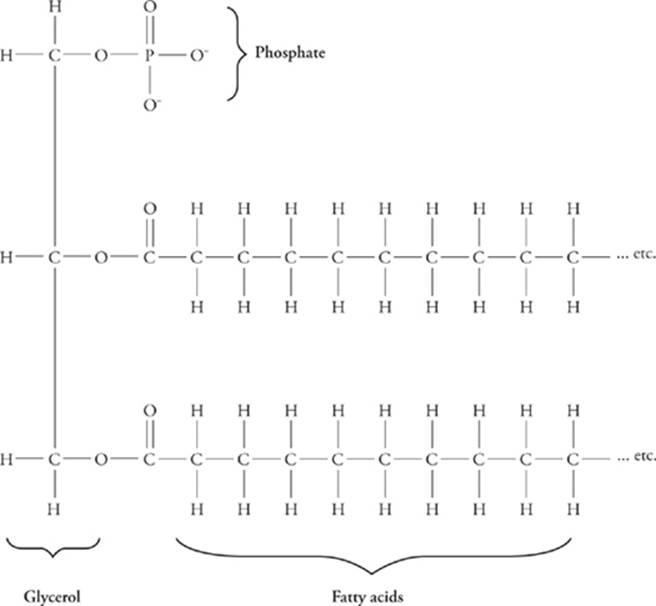
In general, phospholipids are composed of a phosphate group, two alcohols, and one or two fatty acids. On one end of the molecule are the phosphate group and one alcohol; this end is polar, i.e., has an electric charge, and is attracted to water (hydrophilic).
Is phospholipid a hydrophilic?
Phospholipids, are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule).
Does phosphate attract water?
There are two important parts of a phospholipid: the head and the two tails. The head is a phosphate molecule that is attracted to water (hydrophilic).
Are phosphate tails polar or nonpolar?
The heads (the phospho part) are polar while the tails (the lipid part) are non-polar.
Which part of phospholipid is hydrophobic?
Phospholipids consist of two hydrophobic “tails,” which are fatty acid chains, and one hydrophilic “head,” which is phosphate group.
What parts of a phospholipid are hydrophobic and hydrophilic?
1: A phospholipid consists of a head and a tail. The "head" of the molecule contains the phosphate group and is hydrophilic, meaning that it will dissolve in water. The "tail" of the molecule is made up of two fatty acids, which are hydrophobic and do not dissolve in water.
Is hydrophilic polar or nonpolar?
If a molecule has areas where there is a partial positive or negative charge, it is called polar, or hydrophilic (Greek for "water-loving"). Polar molecules dissolve easily in water.
Why is a phospholipid both hydrophobic and hydrophilic?
Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules. This means that they have a hydrophilic, polar phosphate head and two hydrophobic fatty acid tails. These components of the phospholipids cause them to orientate themselves, so the phosphate head can interact with water and the fatty acid tails can't, hence forming a bilayer.
Which part of a phospholipid is attracted to water?
In all phospholipids, the phosphatidic acid is hydrophobic while amino alcohol is hydrophilic. Ernest Z. The end containing the phosphate group is attracted to water.
Is a phospholipid nonpolar and polar?
Phospholipids are amphiphilic. They have a polar head and two hydrocarbon tails, which are nonpolar. The phospholipids that make up the cell membranes of plants, bacterial or animal cells often have fatty acids tails. Of these two fatty acid tails one is unsaturated (contains double bonds) and the other is saturated.
Is the phospholipid bilayer hydrophobic?
The phospholipid bilayer consists of two layers of phospholipids, with a hydrophobic, or water-hating, interior and a hydrophilic, or water-loving, exterior. The hydrophilic (polar) head group and hydrophobic tails (fatty acid chains) are depicted in the single phospholipid molecule.
Is the cell membrane hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
All of the lipid molecules in cell membranes are amphipathic (or amphiphilic)—that is, they have a hydrophilic (“water-loving”) or polar end and a hydrophobic (“water-fearing”) or nonpolar end. The most abundant membrane lipids are the phospholipids.
Are phospholipids hydrophobic?
Phospholipids are amphiphilic molecules that contain a polar head group and a hydrophobic tail with various degrees of instauration (Kelly et al., 2015).
Why is a phospholipid both hydrophobic and hydrophilic?
Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules. This means that they have a hydrophilic, polar phosphate head and two hydrophobic fatty acid tails. These components of the phospholipids cause them to orientate themselves, so the phosphate head can interact with water and the fatty acid tails can't, hence forming a bilayer.
Is a phospholipid nonpolar and polar?
Phospholipids are amphiphilic. They have a polar head and two hydrocarbon tails, which are nonpolar. The phospholipids that make up the cell membranes of plants, bacterial or animal cells often have fatty acids tails. Of these two fatty acid tails one is unsaturated (contains double bonds) and the other is saturated.
What is true about phospholipids?
Phospholipids are amphipathic molecules, having both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions; nonpolar tails (hydrophobic) are directed inward, polar heads (hydrophilic) are directed outward to face both extracellular and intracellular fluid. the plasma membrane. They are tucked in between the phospholipid molecules.
Why does water move through a semipermeable membrane?
Water moves through a semipermeable membrane in osmosis because there is a concentration gradient across the membrane of solute and solvent. The solute cannot effectively move to balance the concentration on both sides of the membrane, so water moves to achieve this balance.
Does osmosis move water?
Where as diffusion transports osmosis transports material across membranes and within cells, Osmosis moves only water across the membrane and the membrane limits the diffusion of solutes in the water.