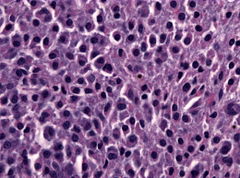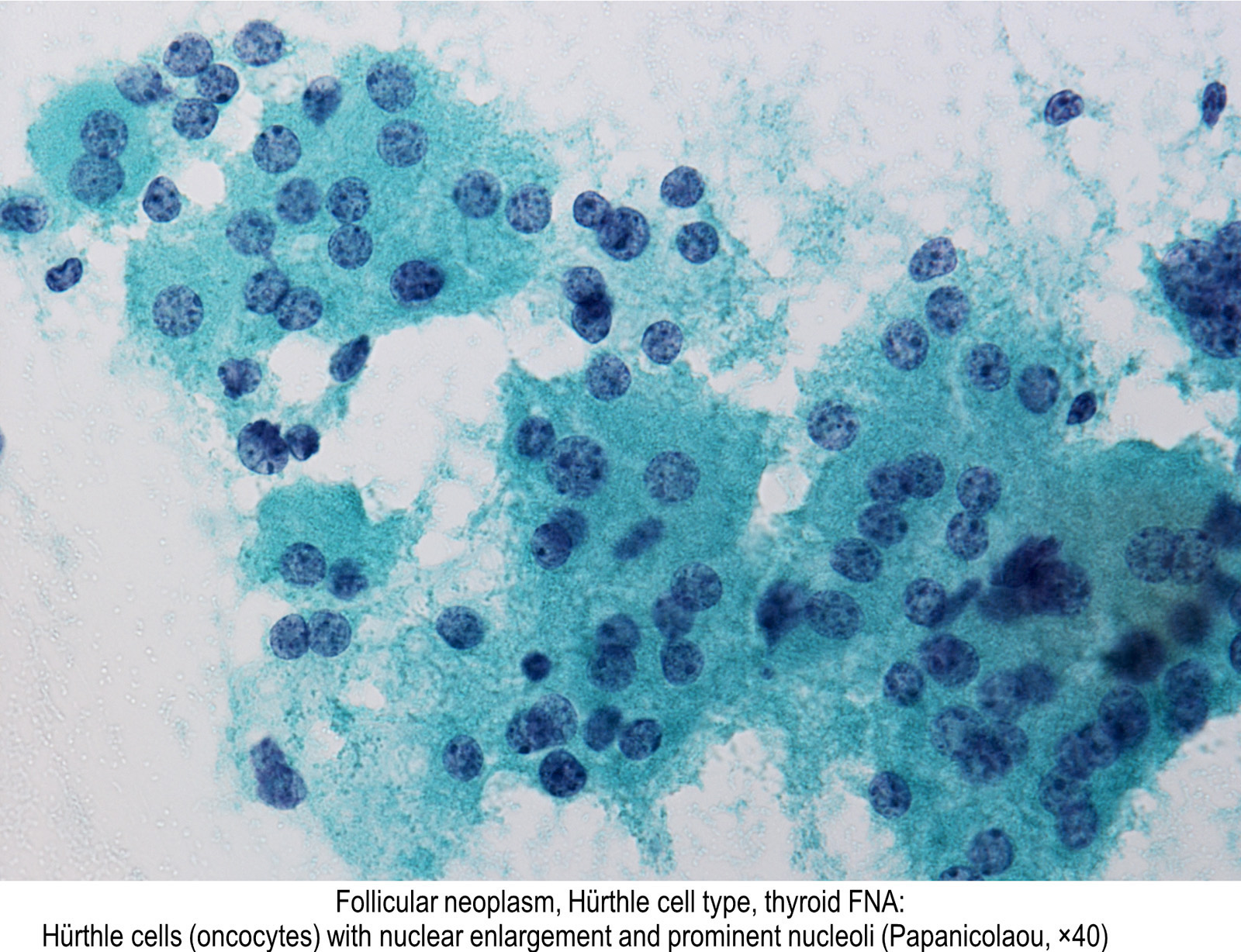
What is the function of a plasma cell?
Plasma cells, as antibody factories, are important contributors to humoral immunity. Though the production and secretion of antibodies were long thought to be the sole functions of plasma cells, recent studies indicate plasma cell involvement in immune response regulation.
What does plasma carry to the cells?
plasma, also called blood plasma, the liquid portion of blood. Plasma serves as a transport medium for delivering nutrients to the cells of the various organs of the body and for transporting waste products derived from cellular metabolism to the kidneys, liver, and lungs for excretion.
What is an abnormal plasma cell?
Plasma cell neoplasms are diseases in which abnormal plasma cells or myelomacells form tumors in the bones or soft tissues of the body. The plasma cells also make an antibody protein, called M protein, that is not needed by the body and does not help fight infection.
What do you know about plasma cell disorders?
When signs and symptoms do occur, they can include:
- Bone pain, especially in your spine or chest
- Nausea
- Constipation
- Loss of appetite
- Mental fogginess or confusion
- Fatigue
- Frequent infections
- Weight loss
- Weakness or numbness in your legs
- Excessive thirst
What is the most common type of neoplasm in middle aged people?
What is the disease that causes a tumor in the bones?
What is the condition that causes peripheral nerves to fail?
What is plasma cell neoplasm?
What is targeted therapy?
What is immunoglobulin study?
Why do plasma cells make antibodies?
See 4 more
About this website
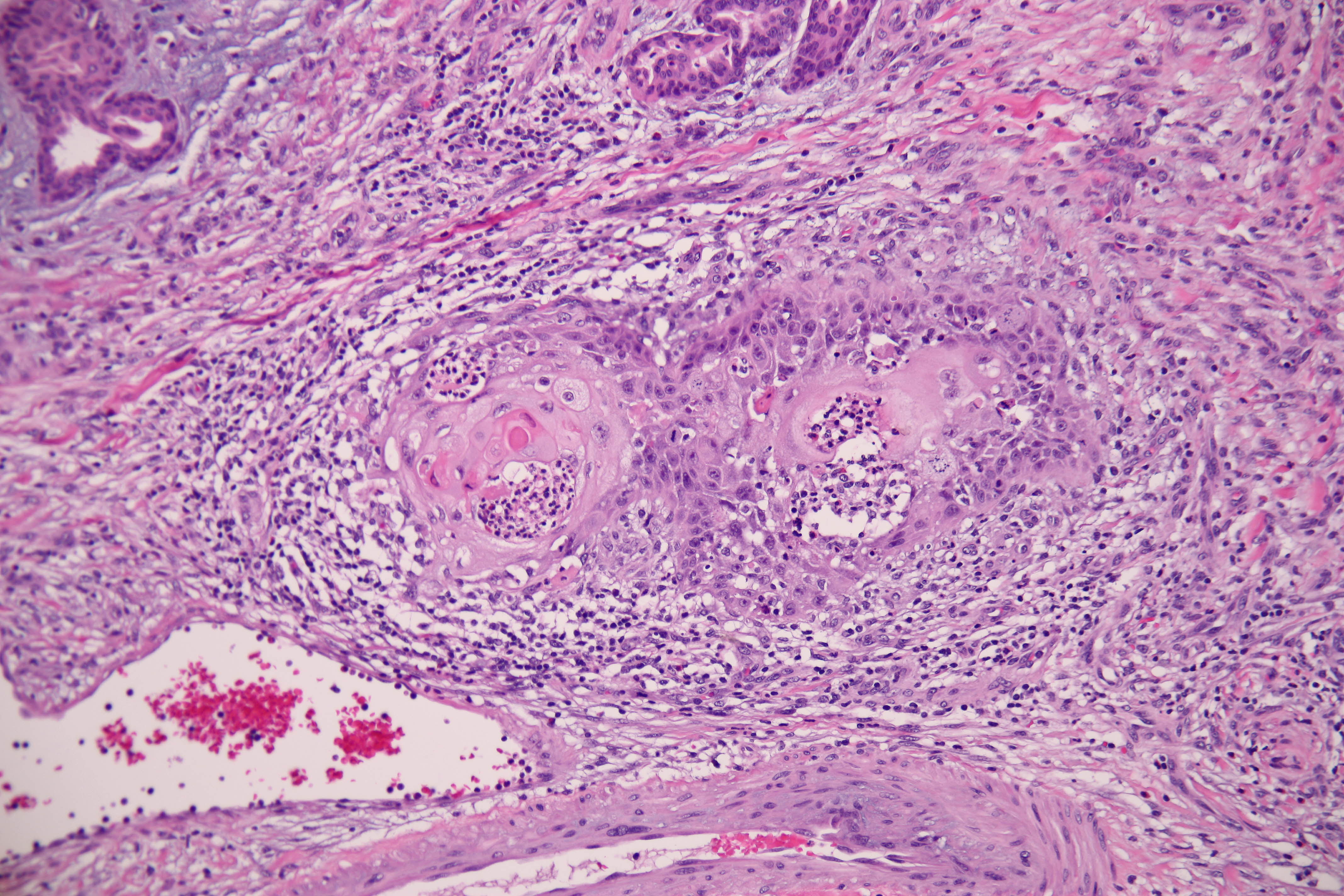
Is plasma cell neoplasm the same as myeloma?
Overview. Plasma cell neoplasms occur when abnormal plasma cells form cancerous tumors in bone or soft tissue. When there is only one tumor, the disease is called a plasmacytoma. When there are multiple tumors, it is called multiple myeloma.
What are neoplastic plasma cells?
Plasma cell neoplasms are diseases in which abnormal plasma cells or cells form tumors in the bones or soft tissues of the body. The plasma cells also make an antibody protein , called M protein , that is not needed by the body and does not help fight infection.
Is plasma cell myeloma a form of cancer?
Myeloma, also called multiple myeloma, is a cancer of the plasma cells. Plasma cells are white blood cells that make antibodies that protect us from infection. In myeloma, the cells grow too much, crowding out normal cells in the bone marrow that make red blood cells, platelets, and other white blood cells.
Which of the following cancers starts in plasma cells?
Doctors know that myeloma begins with one abnormal plasma cell in your bone marrow — the soft, blood-producing tissue that fills in the center of most of your bones.
What type of neoplasm is considered cancerous?
Neoplasms may be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer). Benign neoplasms may grow large but do not spread into, or invade, nearby tissues or other parts of the body. Malignant neoplasms can spread into, or invade, nearby tissues.
Why is neoplastic considered cancerous?
A neoplasm is an abnormal growth of tissue that can be benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Benign tumors (noncancerous neoplasms) usually grow slowly and don't spread. However, malignant tumors (cancerous neoplasms) usually grow rapidly and invade other parts of your body.
Are all plasma cell disorders cancer?
Plasma cell neoplasms can be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer). There are several types of plasma cell neoplasms. Multiple myeloma and other plasma cell neoplasms may cause a condition called amyloidosis. Age can affect the risk of plasma cell neoplasms.
Is multiple myeloma considered terminal cancer?
Multiple myeloma is classified as stage 1, 2, or 3. In multiple myeloma cases, stage 3 is the terminal stage. This means it's the most advanced stage of this type of rare cancer. Doctors use the international staging system to determine the stage of the cancer.
Is plasma cancer curable?
There's no cure, but treatments can slow its spread and sometimes make symptoms go away. A type of white blood cell called a plasma cell makes antibodies that fight infections in your body.
What is the most common plasma cell disorder?
Plasma cell dyscrasias are diseases of the hematologic system; the most common plasma cell dyscrasia is multiple myeloma. Caers J, Garderet L, Kortüm KM, et al. European Myeloma Network recommendations on tools for the diagnosis and monitoring of multiple myeloma: what to use and when.
What causes abnormal plasma cells?
Abnormal plasma cells make M proteins that block the filtering process and damage your kidneys. This disease happens when abnormal proteins (amyloid proteins) build up in your organs. This condition happens when damaged or weakened bones release too much calcium into your bloodstream.
What are the symptoms of plasma cell disorder?
People with plasma cell disorders may experience a range of symptoms, such as bone pain, anemia, increased infections, kidney problems, and fatigue.
What does positive for neoplastic cells mean?
A “positive” or “involved” margin means there are cancer cells in the margin. This means that it is likely that cancerous cells are still in the body. Lymph nodes. The pathologist will also note whether the cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or other organs.
Can neoplastic cells be benign?
A tumor (also called neoplasm) is an abnormal mass of cells in the body. It is caused by cells dividing more than normal or not dying when they should. Tumors can be classified as benign or malignant. Benign tumors are those that stay in their primary location without invading other sites of the body.
How does a cell become neoplastic?
To become neoplastic, a normal cell must develop mutations that allow it to no longer obey boundaries of adjacent cells, thus allowing for uncontrolled growth, and the neoplasm must be able to produce its own blood supply.
What is the difference between a tumor and a neoplasm?
The difference between a tumor and a neoplasm is that a tumor refers to swelling or a lump like swollen state that would normally be associated with inflammation, whereas a neoplasm refers to any new growth, lesion, or ulcer that is abnormal.
What Are Plasma Cell Neoplasms? What Causes Them? - WebMD
Plasma cell neoplasms are a group of diseases – some cancerous – where certain blood cells don’t work like they should. Learn the symptoms, tests you might need, and options for treatment.
Plasma Cell Neoplasms (Including Multiple Myeloma) Treatment (PDQ ...
Evaluation of patients with monoclonal (or myeloma) protein (M protein) Idiotypic myeloma cells can be found in the blood of myeloma patients in all stages of the disease.[4,5] For this reason, when treatment is indicated, systemic treatment must be considered for all patients with symptomatic plasma cell neoplasms.Patients with MGUS or asymptomatic smoldering myeloma do not require immediate ...
Plasma Cell Myeloma - Cancer Therapy Advisor
At a Glance. Plasma cell myeloma is a bone marrow-based clonal plasma cell proliferation. It comprises 10-15% of hematopoietic neoplasms. It is typically diagnosed as a result of evaluations for ...
Significance of Bone Marrow Plasma Cell Percentage in Patients with ...
Introduction: Monoclonal gammopathies are characterized by the detection of a monoclonal immunoglobulin in the serum or urine and underlying proliferation of a plasma cell/B lymphoid clone. (1) Patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) have a clonal plasma cell population in the marrow (<10%) and secrete a monoclonal protein in the serum (<3g/dL) and/or urine.
Overview of Plasma Cell Disorders - Merck Manuals Consumer Version
Plasma cell disorders are uncommon. They begin when a single plasma cell B cells One of the body's lines of defense ( immune system) involves white blood cells (leukocytes) that travel through the bloodstream and into tissues, searching for and attacking microorganisms and... read more multiplies excessively. The resulting group of genetically identical cells (called a clone) produces a large ...
Overview
Plasma cell neoplasms occur when abnormal plasma cells form cancerous tumors in bone or soft tissue. When there is only one tumor, the disease is called a plasmacytoma. When there are multiple tumors, it is called multiple myeloma.
Causes & Prevention
NCI does not have PDQ evidence-based information about prevention of plasma cell neoplasms (including multiple myeloma).
Screening
NCI does not have PDQ evidence-based information about screening for plasma cell neoplasms (including multiple myeloma).
Statistics
Plasma cell neoplasms (including multiple myeloma) statistics based on data from large groups of patients to be used as a general guide.
Coping with Cancer
The information in this section is meant to help you cope with the many issues and concerns that occur when you have cancer.
How is multiple myeloma staged?
Multiple myeloma is staged by estimating the myeloma tumor cell mass on the basis of the amount of monoclonal (or myeloma) protein (M protein) in the serum and/or urine, along with various clinical parameters, such as hemoglobin and serum calcium concentrations, the number of lytic bone lesions, and the presence or absence of renal failure. Impaired renal function worsens prognosis regardless of stage. [ 1]
What is Venetoclax?
Venetoclax is a selective BCL-2 inhibitor that induces apoptosis in myeloma cells, particularly in those with t (11;14) which expresses high levels of bcl2.
How long does multiple myeloma survival last?
Revised text to state that improvements in multiple myeloma prognosis have occurred because of the introduction of newer biologic therapies and better salvage options, with median survivals now exceeding 60 to 90 months (cited van de Donk et al. as reference 46). Added text to state that racial disparities because of biology, socioeconomic factors, and structural racism are under evaluation (cited Marinac et al. as reference 48).
What age is considered a transplant eligible patient?
Newly diagnosed patients who require therapy fall into two categories: 1) the younger fit patient who is transplant-eligible or 2) the older more unfit patient with comorbidities who is not transplant eligible. Patients younger than 65 years are usually considered younger and fit, while patients older than 75 years are usually not transplant eligible. Comorbidities and performance status are important determinants at all ages, especially between the ages of 65 years and 75 years, to help decide about transplant eligibility. Nomograms exist for geriatric patients to define life expectancy independent of the myeloma diagnosis. [ 8] Age, organ dysfunction, and risk of cardiovascular and thrombotic complications influence the choice of induction therapies and consideration of consolidation therapies, such as autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) consolidation. Most patients also receive medication with a bisphosphonate or RANKL inhibitor to prevent skeletal-related complications. [ 9, 10]
What is the condition of amyloidosis?
Amyloidosis Associated With Plasma Cell Neoplasms. Multiple myeloma and other plasma cell neoplasms may cause a condition called amyloidosis. Primary amyloidosis can result in severe organ dysfunction, especially in the kidney, heart, or peripheral nerves. [ 49] . Clinical symptoms and signs include the following:
What are plasma cell neoplasms?
These diseases are all associated with a monoclonal (or myeloma) protein (M protein). They include monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), isolated plasmacytoma of the bone, extramedullary plasmacytoma, and multiple myeloma.
Where are idiotypic myeloma cells found?
Idiotypic myeloma cells can be found in the blood of myeloma patients in all stages of the disease. [ 4, 5] For this reason, when treatment is indicated, systemic treatment must be considered for all patients with symptomatic plasma cell neoplasms. Patients with MGUS or asymptomatic smoldering myeloma do not require immediate treatment but must be followed carefully for signs of disease progression.
How do you know if you have a tumor in your bones?
Feeling very tired. Getting sick often. Pain in your bones. Problems breathing. Other Problems. The tumors you get with plasma cell neoplasms can also damage your bones. This may cause hypercalcemia, where your blood has too much calcium.
What age is MGUS most common?
Age (most common in adults 65 and older ; very rare in people under 35) Sex (men a little more likely to get it) Race (African-Americans more likely to get it) Symptoms. These depend on which type of plasma cell neoplasm you have. MGUS doesn’t usually cause any symptoms.
What causes blood to thicken?
It can also cause your blood to thicken due to high M protein levels. You may also hear this condition called Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia, or WM. Plasmacytoma is another type of cancer where plasma cells form a single tumor, usually in a bone, but sometimes in soft tissue outside the bone.
What is plasma cell neoplasm?
But in the center of your body’s long, flat bones (like your breastbone), you have soft, spongy tissue called bone marrow. Your bone marrow makes stem cells.
What type of cells make antibodies?
Plasma cells are a type of white blood cell. Normally, they make antibodies -- proteins to help kill germs that enter your body. But with the group of diseases known as plasma cell neoplasms, your body makes too many plasma cells. They make an antibody called “M protein,” which you don’t even need and can cause your blood to thicken.
What is the tissue in the center of the body called?
But in the center of your body’s long, flat bones (like your breastbone), you have soft, spongy tissue called bone marrow. Your bone marrow makes stem cells. Some of them become white blood cells, which are an important part of your body’s immune system. Plasma cells are a type of white blood cell. Normally, they make antibodies -- proteins ...
What is the cause of weak bones and fewer healthy blood cells?
Multiple myeloma. The tumors crowd out normal cells, which leads to fewer healthy blood cells and weaker bones.
Causes & Prevention
NCI does not have PDQ evidence-based information about prevention of plasma cell neoplasms (including multiple myeloma).
Screening
NCI does not have PDQ evidence-based information about screening for plasma cell neoplasms (including multiple myeloma).
Statistics
Plasma cell neoplasms (including multiple myeloma) statistics based on data from large groups of patients to be used as a general guide.
Supportive & Palliative Care
We offer evidence-based supportive and palliative care information for health professionals on the assessment and management of cancer-related symptoms and conditions.
What is a tumor made of abnormal plasma cells called?
A tumour made up of abnormal plasma cells is called a plasmacytoma. When a plasmacytoma forms outside the bone it is called an extraosseous plasmacytoma. If only a single tumour is found in a bone without injury to other parts of the body, it is called a solitary plasmacytoma of the bone. Plasma cell leukemia.
What is the name of the part of a cell that sticks to abnormal cells?
Immunoglobulins can also stick to abnormal cells or cells that have stopped functionally normally. Immunoglobulins are made up of four parts and each part is called a chain. One immunoglobulin is made up of two heavy chains and two light chains.
How to diagnose a plasma cell neoplasm?
The diagnosis of plasma cell neoplasm is usually made after your doctor takes a small piece of your bone marrow in a procedure called a biopsy. For some patients, the abnormal plasma cells form a tumour outside of the bone. In that situation, your doctor may perform a biopsy of that tumour instead. Rarely, the plasma cells can be seen in your blood. The tissue is then sent to your pathologist who examines it under the microscope.
What is plasma cell myeloma?
Plasma cell myeloma – This diagnosis is made when there are more than 10% plasma cells in your bone marrow and the immunoglobulins found in your blood or urine are above a certain threshold.#N#If there is no evidence of damage to your organs, this is called an asymptomatic (or smoldering) plasma cell myeloma.#N#If there is evidence of damage to your organs or more than 60% of plasma cells in your bone marrow, this is called a plasma cell myeloma or multiple myeloma. 1 If there is no evidence of damage to your organs, this is called an asymptomatic (or smoldering) plasma cell myeloma. 2 If there is evidence of damage to your organs or more than 60% of plasma cells in your bone marrow, this is called a plasma cell myeloma or multiple myeloma.
What is it called when white blood cells are more than 20%?
If they represent more than 20% of the white blood cells in the blood, it will be called plasma cell leukemia. Amyloidosis. Sometimes, the abnormal immunoglobulins produced by the plasma cells will build up in tissues. When this happens, it can create a substance called amyloid.
Why is it important to have an abnormal plasma cell?
Each type of immune cell plays an important role in protecting your body from infections and helping you heal after an injury.
Why do people with a plasma cell neoplasm have fewer red blood cells?
As a result, patients with a plasma cell neoplasm often produce fewer red blood cells because of the damage to their kidneys and bones. This condition is called anemia. Types of plasma cell neoplasms.
Why is bone marrow core biopsy performed?
Bone marrow core biopsy is performed for examining clustering of plasma cells in the bone marrow because a normal bone marrow contains less than 5% plasma cells. But a bone marrow riddled with myeloma tissue would contain excessive plasma cells. Imaging. Thoracic, abdominal and skeletal survey radiographs, bone mineral density analysis (DEXA scan) ...
What is plasma cell neoplasm?
Plasma Cell Neoplasms. It is a type of neoplasm in which the white blood cells called plasma cells multiply abnormally and become malignant. There are several types of them including multiple myeloma, IgM (Waldenstrom’s) macroglobulinemia, and solitary plasmacytoma, (comprising solitary osseous plasmacytoma and extramedullary plasmacytoma). ...
How long does hypercalcemia go into remission?
Moderate hypercalcemia goes into remission 2-3 days after the commencement of melphalan/prednisone chemotherapy.
How long does a dog's survival after a colorectal tumor last?
According to studies, 9 dogs treated for colorectal plasmacytoma showed a median survival time of 15 months. Metastatic tumors generally develop from non-cutaneous locations. Therefore the site of the primary tumor plays an instrumental role in determining the prognosis.
What is bone lysis in dogs?
Bony lysis or diffuse osteoporosis (dissolution of bones due to lack of calcium) is evident on radiographs of one-fourth to two-third of dogs .
What is malignant plasma cell?
It is basically a proliferation of plasma cells which mimic the existing single cells that usually have multiple bone marrow sites. Unlike normal plasma cells, the malignant plasma cells look large and round with a high mitotic index (measure of the proliferation of a cell population) in early stages of cellular differentiation.
Which bone is involved in solitary osseous plasmacytoma?
Most of the solitary osseous plasmacytomas aggravate to systemic multiple myeloma. The most common sites involved are the zygomatic arch (cheek bone) and the ribs.
Does Daratumumab work with Lenalidomide?
Results from a phase III trial showed that adding daratumumab to lenalidomide and dexamethasone improved progression-free survival among patients with relapsed or refractory disease, compared with lenalidomide and dexamethasone alone.
Does Revlimid delay smoldering myeloma?
The drug lenalidomide (Revlimid) may delay the progression of smoldering myeloma to multiple myeloma, according to preliminary results from a clinical trial. CAR T Cells: Expanding into Multiple Myeloma. Posted: June 12, 2017.
Is lenalidomide a maintenance drug?
The FDA has approved lenalidomide for use as a maintenance therapy in patients with multiple myeloma who have undergone an autologous stem cell transplant, to help keep the cancer from coming back. A phase III clinical trial demonstrates that adding the drug bortezomib to a commonly used two-drug regimen extends survival in patients ...
Can MGUS change over time?
A person’s risk of progressing from a benign condition called monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) to the blood cancer multiple myeloma can change over time, according to a new study.
Does Zoledronic acid cause osteonecrosis?
A recent study quantified the risk of osteonecrosis of the jaw for patients who take zoledronic acid to manage complications from cancer that has spread to the bone. The study also examined risk factors for osteonecrosis of the jaw in these patients.
Is Daratumumab approved by the FDA?
The FDA has approved daratumumab, in combination with either of two other standard therapies, in patients with multiple myeloma whose disease has progressed after only a single prior treatment course.
Does Bortezomib help with multiple myeloma?
A phase III clinical trial demonstrates that adding the drug bortezomib to a commonly used two-drug regimen extends survival in patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma.
What is the most common type of neoplasm in middle aged people?
Plasma cell neoplasms are most common in people who are middle aged or older. For multiple myeloma and plasmacytoma, other risk factors include the following:
What is the disease that causes a tumor in the bones?
Multiple myeloma cells also damage and weaken the bone. Plasma cell neoplasms are diseases in which abnormal plasma cells or myeloma cells form tumors in the bones or soft tissues of the body.
What is the condition that causes peripheral nerves to fail?
This may be caused by a condition called amyloidosis.
What is plasma cell neoplasm?
Plasma cell neoplasms are diseases in which the body makes too many plasma cells. Plasma cell neoplasms can be benign (not cancer) or malignant (cancer). There are several types of plasma cell neoplasms. Multiple myeloma and other plasma cell neoplasms may cause a condition called amyloidosis.
What is targeted therapy?
Targeted therapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs or other substances to identify and attack specific cancer cells. Targeted therapies usually cause less harm to normal cells than chemotherapy or radiation therapy do. Several types of targeted therapy may be used to treat multiple myeloma and other plasma cell neoplasms. There are different types of targeted therapy:
What is immunoglobulin study?
Blood and urine immunoglobulin studies: A procedure in which a blood or urine sample is checked to measure the amounts of certain antibodies (immunoglobulins). For multiple myeloma, beta-2-microglobulin, M protein, free light chains, and other proteins made by the myeloma cells are measured.
Why do plasma cells make antibodies?
Normal plasma cells make antibodies to help the body fight infection and disease. As the number of multiple myeloma cells increases , more antibodies are made. This can cause the blood to thicken and keep the bone marrow from making enough healthy blood cells. Multiple myeloma cells also damage and weaken the bone.