
Plasma is a component of blood--it includes the non-cellular part of blood. Therefore, plasma glucose and blood glucose are both measuring the amount of blood circulating in your bloodstream. If you have elevated plasma glucose, then you should speak with your doctor about doing further testing for diabetes.
Is 82 a good glucose level?
Men and women with fasting plasma glucose levels in the high-normal range of 87 to 99 mg/dL should be counseled with regard to weight and lifestyle, and assessing their lipid profiles. What is a good fasting glucose level? A fasting blood sugar level less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) is normal. A fasting blood sugar level from 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L) is considered prediabetes. If it's 126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L) or higher on two separate tests, you have diabetes.
What does high plasma glucose mean?
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar (also spelled hyperglycaemia or hyperglycæmia) is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma.
How to naturally lower glucose?
Mind the Fluids You Drink
- Sugary juices and sodas increase your blood sugar fast. ...
- Flavored water has added sugar to make it more appetizing.You can use alternatives flavors such as berries, citrus fruits and strawberries.
- Add lemon or lemon slices, strawberries, or orange juice to spice water instead of adding sugar. ...
What is the normal range of glucose?
The normal blood glucose range is 70-99 mg/dL before meals, and less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating. If you are fasting (not eating anything), your blood sugar should be below 95 mg/dL.
See more
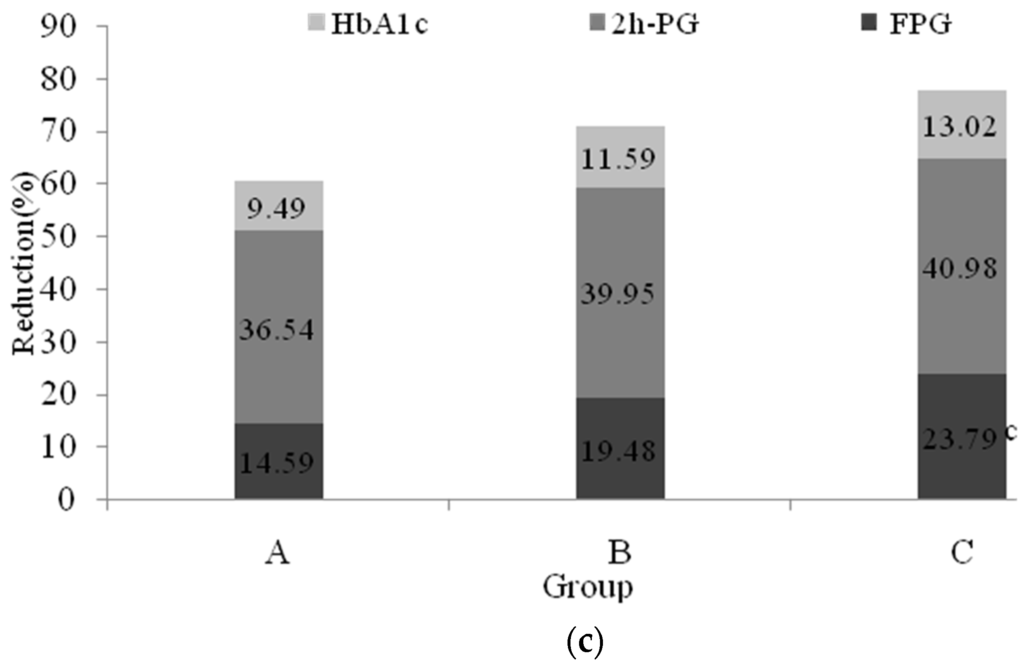
Is fasting blood glucose the same as fasting plasma glucose?
The fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test, also known as the fasting blood glucose test (FBG) or fasting blood sugar test, measures the levels of glucose (sugar) in the blood.
What does plasma glucose indicate?
Increased fasting blood glucose concentration (hyperglycemia) is an indicator of a higher risk to diabetes. An individual's fasting blood plasma glucose (FPG) may be in the normal range because the individual is not diabetic or because of effective treatment with glucose-lowering medication in diabetics.
What is normal plasma glucose level?
Normal plasma glucose levels are defined as under 100 mg/dL during fasting and less than 140 mg/dL 2-hours postprandial. Additionally, glucose levels in healthy individuals can vary with age.
What happens if mean plasma glucose is high?
High blood glucose levels (hyperglycemia) may be a sign of diabetes, a disorder that can cause serious, long-term health conditions. High blood sugar may also be caused by other conditions that can affect insulin or glucose levels in your blood, such as problems with your pancreas or adrenal glands.
Why fasting plasma glucose test is important?
They help people with diabetes manage the condition and understand what factors affect their blood sugar. Fasting blood sugar is a simple, common blood test to diagnose prediabetes, diabetes or gestational diabetes. Before the test, you shouldn't have anything to eat or drink (except water) for 8 to 12 hours.
How do you measure plasma glucose?
A blood glucose test is a blood test that screens for diabetes by measuring the level of glucose (sugar) in a person's blood. Normal blood glucose level (while fasting) range within 70 to 99 mg/dL (3.9 to 5.5 mmol/L). Higher ranges could indicate pre-diabetes or diabetes.
What is 2 hour plasma glucose test?
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) The OGTT is a two-hour test that checks your blood glucose levels before and two hours after you drink a special sweet drink. It tells the doctor how your body processes sugar.
Which is more accurate A1c or fasting glucose?
Measurements of hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) more accurately identify persons at risk for clinical outcomes than the commonly used measurement of fasting glucose, according to a new study. HbA1c levels accurately predict future diabetes, and they better predict stroke, heart disease and all-cause mortality as well.
What causes elevated glucose levels?
eating too much, such as snacking between meals. a lack of exercise. dehydration. missing a dose of your diabetes medication, or taking an incorrect dose.
What is mean plasma glucose in hba1c?
What's a Normal Hemoglobin A1c Test? For people without diabetes, the normal range for the hemoglobin A1c level is between 4% and 5.6%. Hemoglobin A1c levels between 5.7% and 6.4% mean you have prediabetes and a higher chance of getting diabetes. Levels of 6.5% or higher mean you have diabetes.
What blood test results indicate diabetes?
The A1C test is a blood test that provides information about your average levels of blood glucose, also called blood sugar, over the past 3 months. The A1C test can be used to diagnose type 2 diabetes and prediabetes.
What does a low blood glucose level mean?
A low blood sugar level, also called hypoglycaemia or a "hypo", is where the level of sugar (glucose) in your blood drops too low. It mainly affects people with diabetes, especially if they take insulin. A low blood sugar level can be dangerous if it's not treated quickly, but you can usually treat it easily yourself.
What does a glucose level of 200 mean?
A glucose level greater than 200 mg/dL may indicate diabetes, especially if the test is repeated at a later time and shows similar results.
What happens during a glucose test?
During a blood glucose test, blood will be drawn and sent to a lab for analysis.
How to confirm type 2 diabetes?
To confirm the diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, your doctor will order a fasting plasma glucose test or a casual plasma glucose.
What does it mean if your glucose level is 140?
Two hours after the glucose drink your plasma glucose normally is less than 140 mg/dl. Values from 140mg/dl to 199 mg/dl indicate that you have pre-diabetes. You have diabetes if the plasma glucose levels are equal to or greater than 200 mg/dl.
What is a casual glucose test?
The casual plasma glucose test is another method of diagnosing diabetes. During the test, blood sugar is tested without regard to the time since the person's last meal. You are not required to abstain from eating prior to the test.
Is fasting blood sugar higher than postprandial blood sugar?
Since your fasting blood sugar is taken before eating a meal and your postprandial blood sugar is taken after the meal, your fasting level should be lower than your postprandial level. But if the numbers are reversed and your fasting blood sugar levels are higher than your postprandial levels, it could indicate a serious health prob
What is the liquid medium of blood?
The colourless liquid medium of blood, in which red blood cells (carrying oxygen), white blood cells (fighting microbes and viruses) and fat particles (cholesterol, lipids) swim about is known as plasma. It also contains proteins and other nutrients absorbed from your stomach after digestion and being transported to the cells, and also the waste materials, medicines you have taken etc.
What is the blood glucose level of a diabetic?
Diabetes is generally defined as having a fasting blood glucose (or plasma glucose) > 126 mg/dl, or by having a positive glucose tolerance test. Please speak to your doctor for more information about performing a glucose tolerance test.
How to test for glucose?
There are many ways to describe blood tests for glucose. These include fingerstick glucose, blood glucose, and plasma glucose. Fingerstick glucose can be measured at home or in a doctor's office, and uses a drop of whole blood from your finger.
Why Is Plasma Glucose Higher Than Whole Blood Glucose?
These factors might interfere with the blood glucose reading. Although plasma is part of the whole blood, it has higher water content and consequently has more dissolved glucose than whole blood. This is the reason the glucometers nowadays give you the plasma glucose concentration instead of the blood glucose. To convert from whole-blood glucose, multiplication by 1.15 has been shown to generally give the serum/plasma level. Continue reading >>
Why is my blood glucose meter called a plasma?
Because the results of blood samples taken from your vein at your doctor's office or lab are reported as plasma. By having the meter record results as plama glucose, you and your healthcare team can more easily compare your lab tests with your blood glucose meter results.
Why Is My Finger Stick Often Different That The Laboratory Glucose Test?
Most of my old blogs were lost during the hacking attack and other website changes. I plan to update and repeat some of the previous blogs . We all use home glucose test to manage our diabetes . Home glucose testing has been one of the major improvements in the day to day management of diabetes. It is not perfect but it is still a fantastic improvement when I think about the old urine glucose test that we previously used to make treatment decisions. We assume that our home glucose test are accurate and we feel comfortable making management decisions based on those results. I believe that our home glucose test meet the requirements needed for very good glucose management. However, have you ever wondered why you finger stick capillary test is often different than the venous glucose test done in a laboratory. Lets take a little closer look at the glucose test processes. The meter you are using is require to have an error rate of < 20% at glucose levels of 30 to 400mg/dl. so our result could be somewhere between 65 and 95 mg/dl assuming an error rate of 19%. From my own personal experience in the hospital, where I frequently compared finger stick results with hospital lab. results, I believe the error rate on most meters is small and not a major issue. What else effects the results? The source of the blood effects the results. Arterial blood is about 5% higher than capillary blood and 10% higher than venous blood. You are not likely to be using arterial blood but you will be comparing capillary blood ( finger stick sample) to venous blood that is usually taken from your arm by a lab. Tech. This means ,that if you did a fingerstick test ( capillary blood )at the same time as a laboratory test ( venous blood) , your result may be a little higher than the lab result by about 5% Continue reading >>
Why is relating HbA1C to glucose important?
HbA1c: A "Weighted" Average Many studies have shown that HbA1c is an index of average glucose (AG) over the preceding weeks-to-months. Erythrocyte (red blood cell) life-span averages about 120 days. The level of HbA1c at any point in time is contributed to by all circulating erythrocytes, from the oldest (120 days old) to the youngest. However, HbA1c is a "weighted" average of blood glucose levels during the preceding 120 days, meaning that glucose levels in the preceding 30 days contribute substantially more to the level of HbA1c than do glucose levels 90-120 days earlier. This explains why the level of HbA1c can increase or decrease relatively quickly with large changes in glucose; it does not take 120 days to detect a clinically meaningful change in HbA1c following a clinically significant change in AG. How does HbA1c relate to average glucose (AG)? In the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial or DCCT (New Engl J Med 1993;329:977-986) study of patients with Type 1 diabetes, quarterly HbA1c determinations were the principal measure of glycemic control; study subjects also performed quarterly 24-hour, 7-point capillary-blood glucose profiles. Blood specimens were obtained by subjects in the home setting, pre-meal, 90 minutes post-meal, and at bed-time. In an analysis of the DCCT glucose profile data (Diabetes Care 25:275-278, 2002), mean HbA1c and AG were calculated for each study subject (n= 1439). Results showed Continue reading >>
Why do glucometers give you glucose?
Although plasma is part of the whole blood, it has higher water content and consequently has more dissolved glucose than whole blood. This is the reason the glucometers nowadays give you the plasma glucose concentration instead of the blood glucose.
What does a glucose meter read?
Until the last couple of years, all blood glucose (blood sugar) meters read the glucose level in your blood sample as whole blood. Then several years ago one manufacturer developed a meter calibrated to read the blood glucose sample as if it were plasma. Why? Because the results of blood samples taken from your vein at your doctor's office or lab are reported as plasma. By having the meter record results as plama glucose, you and your healthcare team can more easily compare your lab tests with your blood glucose meter results. Several other meter manufacturers subsequently followed suit, so that today most newer meters provide blood glucose (sugar) readings as plasma glucose readings. What's the difference?" you might ask. The difference is that plasma numbers read about 10 - 12% higher than the older whole blood numbers. So if your fasting and pre-meal blood glucose target is 90 - 130 mg/dl plasma glucose, it would be 80 - 120 mg/dl if your meter reads whole blood. So, it's important for you to know what your meter reads, and then what your targets are for the meter you are using. Check your instruction book, contact the manufacturer of your meter, or ask a diabetes educator to find out how your meter reads. As of July, 2002, the Joslin Web site is listing target blood glucose levels on its Online Diabetes Library as plasma glucose levels to reflect this change. For individuals who use the Online Diabetes Library as a resource to refer to on a regular basis, this is the reason for slight changes in certain target levels presented in this material. Continue reading >>
What is the target glucose for a pre meal?
So if your fasting and pre-meal blood glucose target is 90 - 130 mg/dl plasma glucose, it would be 80 - 120 mg/dl if your meter reads whole blood. So, it's important for you to know what your meter reads, and then what your targets are for the meter you are using.
What does a glucose level of 200 mean?
A glucose level greater than 200 mg/dL may indicate diabetes, especially if the test is repeated at a later time and shows similar results.
What happens during a glucose test?
During a blood glucose test, blood will be drawn and sent to a lab for analysis.
What is a glycated hemoglobin test?
The glycated heamoglobin, or HbA1c test, is a measure of the percentage of haemoglobin that is glycated. It has NOTHING to do with a measurement of BG (Blood Glucose) - average, or otherwise. That said… the more glucose there is in your bloodstream, the more of your haemoglobin will glycate. That’s where the “average BG” myth comes from. There IS a relationship - but it is NOT as exact as medicos will have you believe… and it’s riddled with inaccuracies. As others have noted… regular BG testing will tell you what effect different types and amounts of food have on your BG levels, as well as exercise. The HbA1c test has been used as an indicator of how well or poorly your BG control has been. BUT… to actually control your BG, you must perform regular testing - AND MODIFY YOUR BEHAVIOURS based on the results of that testing. Remember when you were in school - you took regular exams, and submitted papers/reports, all of which were graded. At the end of the semester, you got a report card with a grade on it. Think of BG tests as classroom tests - and the HbA1c test as the end-of-semester grade. You MUST do well on the tests to get a good grade - there’s nothing you can do with the HbA1c test to improve your BG control.
How to confirm type 2 diabetes?
To confirm the diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, your doctor will order a fasting plasma glucose test or a casual plasma glucose.
What is a casual glucose test?
The casual plasma glucose test is another method of diagnosing diabetes. During the test, blood sugar is tested without regard to the time since the person's last meal. You are not required to abstain from eating prior to the test.
Can you have a glucose tolerance test if you are diabetic?
However, if you have normal fasting blood sugar, but you have risk factors for diabetes or symptoms of diabetes, your doctor may decide to do a glucose tolerance test (see below) to be sure that you do not have diabetes.
Can fasting blood sugar be high?
These people may have impaired glucose tolerance. If their blood sugar levels are high enough, they may be diagnosed with diabetes .
What is a blood glucose test?
A blood glucose test is a blood test that screens for diabetes by measuring the level of glucose (sugar) in a person’s blood.
How does the pancreas respond to the increase in glucose?
The pancreas responds by releasing enough insulin to handle the increased level of glucose — moving the glucose out of the blood and into cells. This helps return the blood glucose level to its former, lower level.
What does it mean if your glucose is 100?
If your blood glucose level is 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L). . . What it means: You have an impaired fasting glucose level (pre-diabetes**) . . . If your blood glucose level is 126 mg/dl (7.0 mmol/L ) or higher on more than one testing occasion. What it means: You have diabetes.
Why is my blood sugar low?
Too low a level of blood sugar, a condition called hypoglycemia, can be caused by the presence of too much insulin or by other hormone disorders or liver disease.
What is the blood pressure of a woman with diabetes?
Women who developed diabetes while they were pregnant or gave birth to large babies (9 pounds or more) Individuals with high blood pressure (140/90 or higher) Individuals with high-density lipoprotein (HDL, the "good cholesterol level") below 25 mg/dl or triglyceride levels at or above 250 mg/dl.
Where does sugar come from?
The sugar comes from the foods you eat and is released from storage from your body’s own tissues. Insulin is a hormone made by the pancreas. Its job is to move glucose from the bloodstream into the cells of tissues. After you eat, the level of glucose in the blood rises sharply. The pancreas responds by releasing enough insulin to handle ...
Does the pancreas make insulin?
The pancreas does not make enough insulin. The insulin does not work properly. As a result of either of these situations, the blood sugar level remains high, a condition called hyperglycemia or diabetes mellitus.
How much glucose is in the blood?
As a result, glucose remains in the blood, where levels can rise to over 1000 mg/dL, or 10 times the upper limit of normal. When this happens, some of the glucose present in the blood enters the urine. Advertisement.
Where does glucose go when it is broken down?
Once it is broken down in your small intestine, it is absorbed into the bloodstream, where it travels throughout your body and can enter the cells of every major organ. Within your cells, glucose undergoes chemical reactions called glycolysis and the Krebs Cycle, in which it is broken down and combined with oxygen to produce ATP, ...
Why does glucose spill out of urine?
However, in conditions such as diabetes, blood glucose levels can become elevated, causing glucose to spill out into your urine.
What is the normal blood glucose level?
Blood Glucose. The normal range for blood glucose is from 70 to 115 mg/dL, according to "Maxwell Quick Medical Reference.". To keep the glucose you consume within this range, your pancreas secretes the hormone insulin, which drives glucose into your cells, where it can be used for fuel.
What are the sources of glucose?
Other sources of glucose include fruits and vegetables. Grains, legumes, nuts and seeds contain large molecules of glucose known as starch. Sweeteners such as maple syrup, honey, high-fructose corn syrup and molasses also contain abundant quantities of glucose.
Does glucose disappear from urine after delivery?
No treatment is necessary, and glucose generally disappears from the urine after delivery. Advertisement.
Is there a condition where blood glucose is not in urine?
Healthy individuals are able to maintain blood glucose within normal range and so no excess appears in the urine. Exceptions exist, however. Nondiabetic glycosuria, also known as renal glycosuria, is a benign condition in which glucose appears in the urine despite normal blood levels.
How is glucose transferred from the capillary endothelium to the IF?
Glucose is transferred from the capillary endothelium to the IF by simple diffusion across a concentration gradient without the need of an active transporter.20Blood flow to the area dictates the amount of glucose delivered.
What is the equation for glucose transport?
As shown in Figure 1b, the equation characterizing IF glucose was described as follows: dV2G2/dt = K21V1G1 − (K12 + K02)V2G2, where G1 =plasma glucose concentration, G2 = IF glucose concentration, K12 = forward flux rate for glucose transport across the capillary, K21 = reverse flux rate for glucose transport across the capillary, K02 = glucose uptake into the subcutaneous tissue, V1 = volume of the plasma, and V2 = volume of the IF.
How does continuous glucose monitoring work?
Current continuous glucose monitoring systems have the advantage of direct insertion of electrochemical sensors into the IF space rather than transporting the sampled fluid outside the body to detect glucose concentrations . Software programs have been designed to accommodate the lag in IF glucose readings. Despite the advances in the making of sensors with new and improved designs and materials, sensor insertion causes trauma to the insertion site. It can disrupt the tissue structure, provoking an inflammatory reaction that can consume glucose followed by a repair process.38–40The interaction of the sensor with the traumatized microenvironment warrants the need for a waiting period for the sensor signal to stabilize, and that period varies depending on the sensor type.21
When was self monitoring of glucose first used?
Self-monitoring of blood glucose was described as one of the most important advancements in diabetes management since the invention of insulin in 1920 . Recent advances in glucose sensor technology for measuring interstitial glucose concentrations have challenged the dominance of glucose meters in diabetes management, while raising questions about the relationships between interstitial and blood glucose levels. This article will review the differences between interstitial and blood glucose and some of the challenges in measuring interstitial glucose levels accurately.
Does blood glucose correlate with arterial blood glucose?
Capillary blood glucose levels at the fingertip have been shown to correlate well with systemic arterial blood glucose levels.11During times of blood glucose stability, identical glucose levels were demonstrated from alternate sites (e.g., forearm) as compared with finger tip samples.12However, at times of rapid change, mainly due to blood flow variability, levels from alternate sites differ considerably.12,13Capillary blood glucose measured from the forearm is lower than fingertip values at times of rapid increases (>2 mg/dL/min) in systemic blood and higher during rapid decreases.12Samples from the dorsal forearm have been shown to correspond better to fingertip values when compared with volar forearm samples.14The only exception for the alternate site testing is the palm. The skin type of the palm is in the same skin category, hairless or glabrous skin, as the fingertip, and they share the same amount of blood flow, which is considerably more (five to 20 times) than the blood flow to most alternate sites like the forearm. In that respect, blood flow to forearm and abdomen upper dermal region has been reported to be comparable.11
Is all blood glucose equal?
Not All Blood Glucose Is Created Equal
Is palm skin the same as fingertip?
The skin type of the palm is in the same skin category, hairless or glabrous skin, as the fingertip, and they share the same amount of blood flow, which is considerably more (five to 20 times) than the blood flow to most alternate sites like the forearm.
