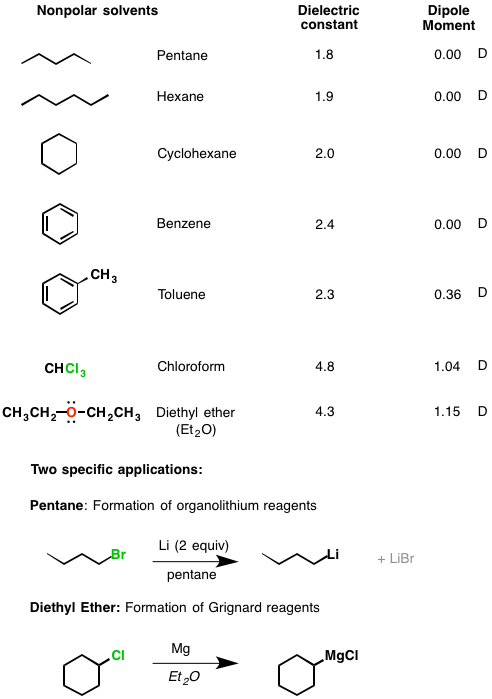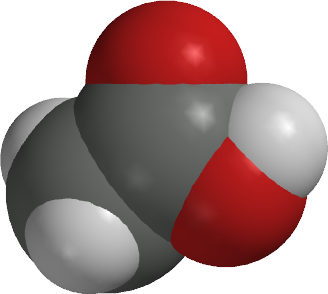
Is propionic acid polar or nonpolar?
Is propionic acid polar? - Answers yes, it is a polar molecule because the carboxylic acid group (COOH) on the end is electron-rich. it also fairly easily loses the proton from the -OH of the carboxylic acid to make it an ion in solution (called propionate). it is also miscible with water, which is a hint that it is polar as well.
Are amino acids polar or nonpolar?
Polar amino acids with a negative charge have more carboxyl groups compared to amine groups. Then the amino acid becomes more acidic. The negative charge of these amino acids can be found in the “R” group. Examples of this group include aspartic acid and glutamic acid. What are Nonpolar Amino Acids?
What is the formula for propanoic acid?
PubChem CID 1032 Structure Find Similar Structures Chemical Safety Laboratory Chemical Safety Summary (LCSS ... Molecular Formula C3H6O2or CH3CH2COOH Synonyms propionic acid Propanoic acid 79-09-4 et ... 3 more rows ...
What is the difference between polar and non-polar substances?
In non-polar substances, there are dispersion forces between each molecule. These dispersion forces are relatively weak and hence only require little energy to break them. In polar substances, there are dipole dipole and hydrogen bonding (depending on the substance) between each molecule.
What is the color of propionic acid?
Where does propionic acid come from?
How many people are exposed to propionic acid?
What is the concentration of propionic acid in mussels?
What was the average propionic acid concentration in 1980?
What is the pesticide code for propionic acid?
How is propionic acid released?
See 4 more
About this website
Is propanoic acid soluble in water?
HSDB and the SRC Physical Properties database database reports that propionic acid has a water solubility of 1000 g/l at 25 °C.
What type of bond is propanoic acid?
Propanoic acid is a three carbon acid with no carbon-carbon double bonds. Notice that there is an ionic bond between the sodium and the propanoate group.
Is propanoic acid most soluble in water?
Answer and Explanation: Propanoic acid has the least number of carbons and it also has a carboxylic acid group. Therefore, it will be the most soluble in water among the three organic compounds.
Is propanoic acid hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Carboxylic acids are compounds containing a carboxylic acid group with the formula -C(=O)OH. Propionic acid is a very hydrophobic molecule, practically insoluble (in water), and relatively neutral.
Why is propanoic acid soluble in water?
In propanoic acid, there is only one alkanoic group(COOH) that make dipole dipole attraction with water for the purpose of solubility, While in propandioic acid there are two alkanoic groups(COOH) that makes bonds with water for solubility, That's why propandioic acid is more soluble in water than propanoic acid.
Is propanoic acid weak or strong?
We can conclude that propanoic acid is weaker than acetic acid in aqueous media, but stronger than that in non-aqueous media.
Which acid is most soluble in water?
1 Answer. All the molecules contain a polar group. However, the molecule that should be most soluble in water is propanoic acid.
What is the structure of propanoic acid?
C₃H₆O₂Propionic acid / Formula
Why is butanoic acid polar?
Butanoic acid in water. Carboxylic acids are categorised by their functional -COOH (carboxyl) group. This functional group is highly polar and allows the carboxylic acid to form strong intermolecular forces with other polar molecules.
Does propanoic acid have hydrogen bonding?
Propanoic acid has hydrogen bonds which are much stronger than the induced-dipole forces in hex-1-ene.
What is the difference between propanoic acid and propionic acid?
Then In Propenoic acid, the C atom is attached to the −COOHgroup and H+has to be removed from it. The hybridization is sp2, In this, the s character is 33.33%. In the case of propionic acid, the C atom is attached to the −COOHgroup and H+has to be removed from it.
Why is propanoic acid a weak acid?
Propionic acid, CH3CH2COOH , is a weak acid, which means that it does not ionize completely in aqueous solution to produce hydronium cations, H3O+ , and propionate anions, CH3CH2COO− .
Does propanoic acid have hydrogen bonding?
Propanoic acid has hydrogen bonds which are much stronger than the induced-dipole forces in hex-1-ene.
What is the structure of propanoic acid?
C₃H₆O₂Propionic acid / Formula
How many covalent bonds are present in propanoic acid?
The propionic acid molecule contains a total of 10 bond(s) There are 4 non-H bond(s), 1 multiple bond(s), 1 rotatable bond(s), 1 double bond(s), 1 carboxylic acid(s) (aliphatic) and 1 hydroxyl group(s).
What is the functional group for propanoic acid?
The functional group of propanoic acid is the carboxyl group -COOH. The carboxyl group is basically the combination of two functional groups: the hydroxyl -OH and the carbonyl group -C=O.
Propionic Acid Technical Data Sheet - Dow Chemical Company
Water in solvent . 100% : 100 % . Hansen solubility parameters (J/cm3)½ : _Total. _Non-polar . _Polar . _Hydrogen bonding -- -- -- -- Partition Coefficient, n ...
Propionic Acid MATERIAL SAFETY DATA SHEET CAS No 79-09-4 SDS/MSDS
SECTION 1: Identification of the substance/mixture and of the company/undertaking 1.1 Product identifiers Product name : Propionic Acid CAS-No. : 79-09-4 1.2 Relevant identified uses of the substance or mixture and uses advised against
Propionic Acid: Toxicity, Uses & Safety | Study.com
This lesson goes over a tasty (in a way) compound called propionic acid. You'll learn about its uses, its potentially toxic effects and its various important safety issues.
Propionic Acid - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
S.C. Gad, in Encyclopedia of Toxicology (Third Edition), 2014 Abstract. Propionic acid, CASRN 79-09-4, also known as propanoic acid, is a ubiquitous fatty acid present in many processed foods as well as animal feedstocks.It has a long history of use in this capacity, is a natural intermediate and metabolite in many biological processes, and is a useful intermediate in several chemical ...
Propionic Acid - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Bankole A. Johnson DSc, MD, MB, ChB, MPhil, DFAPA, FRCPsych, FACFEI, ABDA, in Addiction Medicine: Science and Practice, 2020 Alpha-Amino-3-Hydroxy-5-Methylisoxazole-4-Propionic Acid and Kainate Glutamate Receptor Antagonist—Topiramate. Topiramate, a sulfamate-substituted fructopyranose derivative, has six important mechanisms of action.
Why can't nonpolar molecules dissolve in water?
The hydrophobic effect can better explain why some nonpolar molecules can't dissolve in water: The hydrophobic effect is the observed tendency of nonpolar substances to aggregate in aqueous solution and exclude water molecules.
What forces do nonpolar solutes need to break?
Non-polar Solute and Solvent. For the solute to dissolve, the dispersion forces between the molecules in the solute and solvent need to break. This only requires very little energy. However when the solute dissolves into the solvent, they are able to be make dispersion forces with each other.
Is the polarity of a solute or solvent important in determining solubility?
In a conclusion, I would say "yes, the polarity of the solute/solvent plays an important rule in determining solubility or insolubility. But that's not the half of it.".
Does "like dissolves like" explain nitrates?
Note that "like dissolves like" or any similar rules can't explain this. Actually, the impressive delocalization of the electron in the nitrate ion can explain the massive range of soluble nitrates.
Can nonpolar solutes dissolve in polar solvents?
That " nonpolar doesn't dissolve in polar" isn't accurate. Nonpolar solutes are generallyinsoluble in polar solvents. We can easily think of exceptions. Bromine wateris an example for a start, but certainly not the most remarkable example.
What is the difference between polar and nonpolar amino acids?
The difference between polar and nonpolar amino acids is that polar amino acids have polarity whereas polarity is absent in nonpolar amino acids.
What are Nonpolar Amino Acids?
Nonpolar amino acids are amino acids that have no polarity. That is because these amino acids have equal numbers of carboxylic acid groups and amine groups. This makes these nonpolar amino acids to have a neutral charge. They have no charge on the “R” group.
Which amino acids have no charge?
Polar amino acids with no charge have no charge on the “R” group (side chain). These amino acids can be found participating in the hydrogen bond formation in protein molecules. Example, amino acids for this group, are serine, threonine, tyrosine, cysteine, glutamine, and asparagine. Figure 01: Classification of Amino Acids.
What are the elements that make up an amino acid?
Therefore, an amino acid is formed from four basic chemical elements; C, H, O and N. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins.
What is the color of propionic acid?
Propionic acid is a colorless liquid with a sharp rancid odor. Produces irritating vapor. (USCG, 1999) CAMEO Chemicals. Propionic acid is a short-chain saturated fatty acid comprising ethaneattached to the carbonof a carboxy group.
Where does propionic acid come from?
PROPIONIC ACID WAS ISOLATED FROM BOILED BEEF IN SLURRY, DRY CURED HAM. /FROM TABLE/
How many people are exposed to propionic acid?
NIOSH (NOES Survey 1981-1983) has statistically estimated that 31,092 workers (8,489 of these are female) are potentially exposed to propionic acid in the US (1). The NOES Survey does not include farm workers. Occupational exposure to propionic acid may occur through dermal contact or inhalation with this compound at workplaces where propionic acid is produced or used (SRC). Monitoring data indicate that the general population may be exposed to propionic acid via inhalation of ambient air, ingestion of food and drinking water, and dermal contact with this compound (SRC).
What is the concentration of propionic acid in mussels?
Two samples of mussels (Mytilus edulis) from the Oarai Coast, Japan contained propionic acid at concentrations of 2.73 and 0.50 ug/g (1).
What was the average propionic acid concentration in 1980?
URBAN/SUBURBAN: The average and maximum propionic acid concns for the ambient air over the Netherlands in 1980 was reported to be 0.15 and 2.0 ppb (1). Propionic acid was detected in the ambient air of Los Angeles, CA from July to Sept, 1984 at concn ranging from 0.019 to 0.305 ppb (2). On Sept 24-5, 1984, propionic acid was detected in the ambient air of Los Angeles, CA at an average concn ranging of 0.139 ppb for 3 samples with a high and low concn of 0.154 and 0.126 ppb (2). Propionic acid was detected in three field studies in Albuquerque, NM at 0.6 ppb (summer 1994), 0.6 ppb (winter 1994), and <1 ppb (winter (1995) (3). On Sept 8-9, 1993 propionic acid was detected in the ambient air during a photochemical smog episode in Los Angeles, CA at an average concn of 1.67 ug/cu m for 6 samples with a high and low concn of 0.08 ug/cu m and 2.03 ug/cu m (4).
What is the pesticide code for propionic acid?
For Propionic acid (USEPA/OPP Pesticide Code: 77702) ACTIVE products with label matches. /SRP: Registered for use in the U.S. but approved pesticide uses may change periodically and so federal, state and local authorities must be consulted for currently approved uses./
How is propionic acid released?
Propionic acid's production and use in animal feed, as a grain preservative, calcium and sodium salt production, cellulose ester production, plastic dispersions, pharmaceuticals, and flavors and fragrances may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams. Propionic acid is formed from various enzymatic and fermentation processes and is produced during anaerobic carbohydrate fermentation in the stomachs of ruminants. It occurs in dairy products in small amounts and its esters are found in some essential oils. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 3.53 mm Hg at 25 °C indicates propionic acid will exist solely as a vapor. Vapor-phase propionic acid will be degraded in the atmosphere by reaction with photochemically-produced hydroxyl radicals; the half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 13 days. Propionic acid is not expected to directly photolyze due to the lack of absorption in the environmental UV spectrum. If released to soil, propionic acid is expected to have very high mobility based upon an estimated Koc of 36. The pKa of propionic acid is 4.87, indicating that this compound will exist primarily in anion form in the environment anions generally do not adsorb more strongly to soils containing organic carbon and clay than their neutral counterparts. Propionic acid in its anionic form would not volatilize from water or moist soil surfaces. Propionic acid is expected to volatilize from dry soil surfaces based upon its vapor pressure. Propionic acid is expected to biodegrade rapidly in most environmental conditions based on the results of a sewage inoculum screening test with theoretical BODs ranging from 23-55%. If released into water, propionic acid is not expected to adsorb to suspended solids and sediment based upon the estimated Koc. A pKa of 4.87 indicates propionic acid will exist almost entirely in the anion form at pH values of 5 to 9 and therefore volatilization from water surfaces is not expected to be an important fate process. An estimated BCF of 3.2 suggests the potential for bioconcentration in aquatic organisms is low. Hydrolysis is not expected to be an important environmental fate process since this compound lacks functional groups that hydrolyze under environmental conditions. Occupational exposure to propionic acid may occur through dermal contact with this compound at workplaces where propionic acid is produced or used. Monitoring data indicate that the general population may be exposed to propionic acid via inhalation of ambient air, ingestion of food and drinking water, and dermal contact with this compound and other consumer products containing propionic acid. Propionic acid was widely detected in landfill leachates and wastewater from industrial areas. (SRC)
