The original ideal gas law uses PV =nRT, PM = dRT, where P is pressure measured in atmospheres (atm), T is temperature measured in kelvin (K), and R is the ideal gas law constant0.0821 atm(L)mol(K), just like the original formula, but M is now the molar mass (gmol).
How do you find the unknown variable in PV = nRT?
The Ideal Gas Law Calculator finds the unknown variable in the equation PV = nRT when three of the variables are known. The ideal gas law formula states that pressure multiplied by volume is equal to moles times the universal gas constant times temperature. The gas constant R is a constant of units of energy per temperature increment per mole.
What is the PV nRT formula?
Applications of PV nRT formula. Updated: 08/06/2021 The ideal gas equation, PV=nRT, represents the relationship between pressure (P), volume (V), amount of gas (n), and temperature (T).
What is the universal gas constant of PV?
i.e. v∝ n v ∝ n ……………………………… (iii) where R is the Universal gas constant, which has a value of 8.314 J/mol-K What is ideal gas equation and derive it mathematically? The ideal gas equation is formulated as: PV = nRT.
What is the PV of ideal gases?
An introduction to ideal gases and the ideal gas law: pV = nRT IDEAL GASES AND THE IDEAL GAS LAW This page looks at the assumptions which are made in the Kinetic Theory about ideal gases, and takes an introductory look at the Ideal Gas Law: pV = nRT.

Is PV nRT in Kelvin or Celsius?
Yes, the formula relies on absolute temperature (generally in Kelvins). But by adding 273 to the temperature in degrees Celsius, you are converting to Kelvin, which is the only change you need to make the formula work.
Is ideal gas law in Kelvin?
The Ideal Gas Law: The only constant about the constant is that the temperature scale in all is KELVIN. When using the Ideal Gas Law to calculate any property of a gas, you must match the units to the gas constant you choose to use and you always must place your temperature into Kelvin.
What is the unit for PV nRT?
In SI units, p is measured in pascals, V is measured in cubic metres, n is measured in moles, and T in kelvins (the Kelvin scale is a shifted Celsius scale, where 0.00 K = −273.15 °C, the lowest possible temperature). R has for value 8.314 J/(mol·K) = 1.989 ≈ 2 cal/(mol·K), or 0.0821 L⋅atm/(mol⋅K).
Does Charles law have to be in Kelvin?
and is called Charles' law. For this law to be valid, the pressure must be held constant, and the temperature must be expressed on the absolute temperature or Kelvin scale .
What is K in gas constant?
The Boltzmann constant (kB or k) is the proportionality factor that relates the average relative kinetic energy of particles in a gas with the thermodynamic temperature of the gas.
Is PV nRT in liters?
A PV = nRT problem So, the volume of an ideal gas is 22.41 L/mol at STP. This, 22.4 L, is probably the most remembered and least useful number in chemistry.
What does N stand for in PV nRT?
The ideal gas law is: pV = nRT, where n is the number of moles, and R is universal gas constant. The value of R depends on the units involved, but is usually stated with S.I.
Why is the Celsius scale not appropriate for gas law problems?
In order for gas laws to work, temperature has to be calculated on an absolute scale. Celsius, on the other hand, has an arbitrary 0 degree point, which is the temperature when water melts. Another problem with Celsius is that negative degrees are very possible, which may cause confusing results.
What is ideal gas temperature?
One mole of an ideal gas has a volume of 22.710947(13) litres at standard temperature and pressure (a temperature of 273.15 K and an absolute pressure of exactly 105 Pa) as defined by IUPAC since 1982.
What law is P1V1 T1 P2V2 T2?
Combined gas lawCombined gas law: P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2 Use the gas laws for pressure, volume and temperature calculations. Avagadro's law – Equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal numbers of molecules.
What does the ideal gas law assume?
For a gas to be “ideal” there are four governing assumptions: The gas particles have negligible volume. The gas particles are equally sized and do not have intermolecular forces (attraction or repulsion) with other gas particles. The gas particles move randomly in agreement with Newton's Laws of Motion.
What is the N in PV nRT?
The amount of the gas (n) is measured in moles. Sometimes it will be given in grams, in which case the amount of gas should be converted into moles...
How do you calculate N in PV nRT?
To calculate the number of moles when all other values are known, known values are plugged into the equation. Then n is solved for algebraically. I...
What are the units for PV nRT?
Pressure (P) is measured in atmospheres (atm). Volume (V) is measured in liters (L). Amount of gas (n) is measured in moles (mol). The gas constant...
What is the R in PV nRT?
The R is the ideal gas constant. The value is 0.082 atm*L/mol*K. This should be converted to different units depending on the units of other variab...
What is ideal gas equation and derive it mathematically?
The ideal gas equation is formulated as: PV = nRT. In this equation, P refers to the pressure of the ideal gas, V is the volume of the ideal gas, n...
What is meant by ideal gas equation?
An equation that equates the product of the pressure and the volume of one mole of a gas to the product of its thermodynamic temperature and the ga...
What is ideal gas example?
Many gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen, noble gases, some heavier gases like carbon dioxide and mixtures such as air, can be treated as idea...
What is an ideal gas explain?
An ideal gas is defined as one in which all collisions between atoms or molecules are perfectly eleastic and in which there are no intermolecular a...
What are ideal gas conditions?
For a gas to be “ideal” there are four governing assumptions: The gas particles have negligible volume. The gas particles are equally sized and do...
What is the equation for the initial volume of a gas?
If P 1 = the initial pressure of a gas, V 1 = the initial volume of a gas.
What is the law of gas at constant temperature?
Boyles law. Boyles law states that at constant temperature, the volume of a particular mass of gas is inversely proportional to its pressure. If the pressure is doubled, the volume is halved. If P 1 = the initial pressure of a gas, V 1 = the initial volume of a gas.
Why do we know that n = 1?
We know that n = 1, because we are trying to calculate the volume of 1 mole of gas.
What is the molar volume of an ideal gas?
The molar volume of an ideal gas is therefore 22.4 dm3at stp.
What is the SI value of R?
A value for R will be given you if you need it, or you can look it up in a data source. The SI value for R is 8.31441 J K-1mol-1.
When p and t are constant, what is the relationship between volume and moles of gas?
When p & T are constant, then the volume of a gas bears a direct relation with the number of moles of gas.
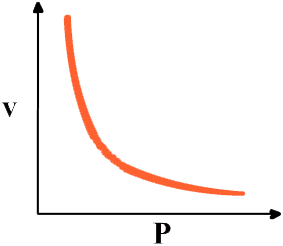
Which law states that gas pressure is inversely proportional to volume?
The laws which deal with ideal gases are naturally called ideal gas laws and the laws are determined by the observational work of Boyle in the seventeenth century and Charles in the eighteenth century. Boyles Law – states that for a given mass of gas held at a constant temperature the gas pressure is inversely proportional to the gas volume.
What is the universal gas constant?
Note: From the SI system the value of the universal gas constant is 8.314 kJ/mole.K
What is the value of R in chemistry?
where R is the Universal gas constant, which has a value of 8.314 J/mol-K
What is the product of pressure and volume of a gas?
The product of Pressure & Volume of a gas bears a constant relation with the product of Universal gas constant and the temperature.
What is the gas constant R?
The gas constant R is a constant of units of energy per temperature increment per mole. It is also known as the universal gas constant, ideal gas constant and molar gas constant.
What is the equation for the ideal gas law?
The Ideal Gas Law Calculator finds the unknown variable in the equation PV = nRT when three of the variables are known.
How to convert temperature to Kelvin?
You can convert your temperature in Celsius or Fahrenheit to Kelvin first, then plug in the result in the formula, or you can modify the formula to do that for you: P V = n R ( T ° C + 273.15) K. Where T ° C is the number of the temperature in Celsius and K just stands for Kelvin.
Can you change a temperature scale to Kelvin?
You could use some simple conversionsto change any temperature scale to Kelvin to work in the ideal gas law.
What is an ideal gas
An ideal gas is a special case of any gas that fulfills the following conditions:
Ideal gas law equation
The properties of an ideal gas are all summarized in one formula of the form:
Ideal gas constant
The gas constant (symbol R) is also called the molar or universal constant. It is used in many fundamental equations, such as the ideal gas law.