
Normal Red Reflex. Moreover, the infant might not keep the eyes open. In such cases, pupils might have to be dilated, provided the infant is older than 2 weeks. While observing the change in the color, the change in the level of pigmentation of the fundus in children from different ethnic groups should be considered.
What is a normal red reflex?
To be considered normal, a red reflex should emanate from both eyes and be symmetric in character. Dark spots in the red reflex, a markedly diminished reflex, the presence of a white reflex, or asymmetry of the reflexes (Bruckner reflex) are all indications for referral to an ophthalmologist who is experienced in the examination of children.
What age does red reflex disappear?
What age does red reflex disappear? This is a normal and transient reflex that disappears by 6 to 12 months of age. Click to see full answer. Moreover, what age do you stop checking red reflex?
What is the absence of a red reflex?
The absence of red reflex during an eye test indicates an abnormality and the need for treatment. A red reflex test is recommended for all infants and should ideally be performed for the first time between the first two weeks and two months of life.
What is a positive red reflex?
The red reflex was documented as positive or abnormal if the reflex was white, yellow, nonuniform, absent, asymmetric, markedly diminished, unusually brighter, or having spots in it. Comprehensive eye examinations, serving as the reference standard, included external inspection, pupil examination, hand-held slit lamp examination, and RetCam imaging.
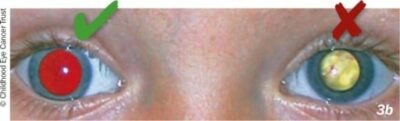
What does red reflex indicate?
Examination of pupil reflections, also known as the red reflex text, can reveal problems in the cornea, lens and sometimes the vitreous, and is particularly useful in young children. These photographs show what can occur in the case of certain major eye conditions, the most serious of which is retinoblastoma.
Is red reflex normal?
To be considered normal, a red reflex should be seen in both eyes symmetrically and equivalent in color, intensity, and clarity. An absent or black reflex may indicate an obstruction that is preventing light from reflecting back to the examiner.
What does red reflex absent mean?
An absent red reflex usually suggests sight-threatening pathology (cataract) and may mean life-threatening pathology (retinoblastoma).
What causes abnormal red reflex?
An abnormal red reflex can result from mucus or other foreign bodies in the tear film, corneal opacities, aqueous opacities, iris abnormalities affecting the pupillary aperture (pupil), cataracts, vitreous opacities, and retinal abnormalities including tumors or chorioretinal colobomata.
At what age do you stop checking red reflex?
For the well-baby check up at 1 month, check for the red reflex. For visits from 2 to 18 months of age, in addition to the red reflex, you need to check for the corneal light reflexes and ocular mobility, as well as to perform cover- uncover tests.
What if red reflex is white?
The red reflex is either absent or white with leukocoria. This occurs because of abnormal reflection or blockage of light coming out of the eye. Pediatricians will refer patients with “abnormal red reflex” on their exam for a more thorough exam by a pediatric ophthalmologist.
What is a white reflex?
Leukocoria (also white pupillary reflex) is an abnormal white reflection from the retina of the eye. Leukocoria resembles eyeshine, but leukocoria can also occur in animals that lack eyeshine because their retina lacks a tapetum lucidum. Leucocoria. Other names. Leucocoria, white pupillary reflex.
How do you assess red reflex in children?
0:513:44Fundal Reflex (a.k.a. Red Reflex) Assessment in Children - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAt the same time look for any signs of wobbly eyes squint red eye or white pupil. Then prepare theMoreAt the same time look for any signs of wobbly eyes squint red eye or white pupil. Then prepare the Arc Light by selecting the brightest light setting with three clicks. Make sure the lens rack is at
Why do my baby's pupils look red?
Redness in the eye area of a newborn can be caused by a blocked tear duct, irritation, or infection. Newborn conjunctivitis can be serious, so talk with your pediatrician right away.
What is the cause of the red reflex quizlet?
The red glow filling the person's pupil is the red reflex. This is caused by the reflection of the ophthalmoscope light off the inner retina.
Why do human eyes reflect red?
Let us explain. The problem with red pupil reflex in photography is a common one, especially in children because of their relatively large pupils. It occurs when the flash reflects off of the blood-rich retina. If both eyes show up red, that can indicate that all is well (normal).
What is the cause of the red reflex quizlet?
The red glow filling the person's pupil is the red reflex. This is caused by the reflection of the ophthalmoscope light off the inner retina.
How do you assess red reflex in children?
0:513:44Fundal Reflex (a.k.a. Red Reflex) Assessment in Children - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAt the same time look for any signs of wobbly eyes squint red eye or white pupil. Then prepare theMoreAt the same time look for any signs of wobbly eyes squint red eye or white pupil. Then prepare the Arc Light by selecting the brightest light setting with three clicks. Make sure the lens rack is at
What is the white reflex?
Leukocoria, meaning “white pupil,” originates from the Greek words “leukos” (white) and “kore” (pupil). It refers to the reflection of white light seen upon direct illumination of the fundus through the pupil, in contrast to the usual red glow. Leukocoria of the right eye due to retinoblastoma.
How often is the red reflex done?
The red reflex is undertaken twice using an ophthalmoscope: Once in the first week: during the full newborn examination within the first 48 hours or later in the first week. This is usually completed by the LMC, maternity or paediatric staff. Subsequently at the 6 week assessment. This is usually completed by the general practitioner or LMC.
Where to check for red reflex?
Checking for the red reflex is best done in a darkened room to allow the pupils to dilate. Either the parent/caregiver or the examiner hold the baby.
What to do if there is uncertainty at first red reflex check?
If there is uncertainty at the first red reflex check, more often in babies with pigmented skin and where there is poor pupil dilatation, request a second red reflex exam from a colleague, the local paediatric team or GP before referral to ophthalmology.
What to do if reflex is poor?
If the reflex is poor, move the light from side to side and ensure you are in a dark room.
What is the difference between red and orange reflexes?
In babies with pigmented skin the reflex is less red, more yellow-orange.
How to open a baby's eyes?
Often this can be achieved by holding the baby vertically or by gently opening the eyes with clean fingers. Using a direct hand-held ophthalmoscope with lens focus set between zero and plus 2 (black 2) or for your eye requirements, hold the ophthalmoscope to your eye at a distance of ~40-50cm from the baby’s eye.
How many red reflexes does a 6 week old have?
A baby seen at 6 weeks of age has one red reflex and one absent reflex. No mention of abnormal reflexes has been made in the neonatal discharge. A parent brings their child aged <2 years with a squint in the eye. They have noticed a ‘glint’ in the eye in certain lighting conditions. The eye is turning outwards slightly.
What does a baby's reflexes look like at 6 weeks?
A baby born to black and minority ethnic (BME) parents is seen for a 6-week check. The red reflexes appear more yellowy white than orange. (They may be almost absent if the pupil is very small.)
How to treat red reflexes in the eye?
Instil a drop of tropicamide 0.5% into both eyes and reassess the red reflexes through dilated pupils. If the red reflex is still absent then an urgent referral should be made to the local paediatric ophthalmologist. Occasionally, a white reflex is seen instead of a dark one. This kind of reflex is the hallmark of a retinoblastoma in the eye; and it is the light reflecting from the tumour’s white surface that can be seen when light reflects from a certain angle ( Figure 3 ).
What does it mean when a paediatric ophthalmologist says there is no red reflex?
The single most important piece of clinical information that a paediatric ophthalmologist requires is the presence or absence of a red reflex. An absent red reflex usually suggests sight-threatening pathology (cataract) and may mean life-threatening pathology (retinoblastoma).
What is the BME reflex?
In a BME baby, it is symmetrical and similar to the red reflexes of the parents. It is often more like the sun than orange, but the parents should have similar reflexes. In a dilated pupil, the white reflex seen by photographic flash picture of the optic disc is swamped by a normal orange retinal reflex.
What is the white reflex in the eye?
Occasionally, a white reflex is seen instead of a dark one. This kind of reflex is the hallmark of a retinoblastoma in the eye; and it is the light reflecting from the tumour’s white surface that can be seen when light reflects from a certain angle ( Figure 3 ). Download figure. Open in new tab. Download powerpoint.
Is a red reflex state considered urgent?
Referrals from general practice are semi-urgent and need assessment within the week. In children <2 years of age, referrals that do not mention the red reflex state make it difficult to assess the degree of urgency. Inevitably, this means that some children may have a worse outcome as a result of delayed diagnosis.
What is the red reflex?
The term 'red reflex' refers to the reddish-orange glow or the reflection of light that is observed from the eye's retina during direct ophthalmoscopy. This AptParenting write-up provides information on the causes of the absence of red reflex in newborns.
Why is it important to check the red reflex?
This condition can also be present at birth. However, the cataract in newborns might be so small that it might not affect the vision. Thus, checking red reflex is extremely important to rule out cataract.
What does it mean when your eyes are red?
In case of healthy eyes where there is no obstruction in the optical pathway, red reflex is present, which means that a reddish-orange reflection of light from the retina would be observed. Absence of red reflex is indicative of certain serious eye conditions, which is why, this test is conducted in newborns to rule out vision-related problems.
Why is my red reflex absent?
If the reddish-orange reflection of the light is not observed in one or both eyes, it implies that the red reflex is absent. This indicates the presence of an obstruction or abnormalities in the structures located at the back of the eye. In some cases, lack of symmetry in the red reflex might be indicative of unequal or high refractive errors.
Is the red reflex absent in infants?
Red reflex is absent. White reflex is present (retinal reflection) The test must be conducted properly, as the pupils in infants can sometimes be small. Moreover, the infant might not keep the eyes open. In such cases, pupils might have to be dilated, provided the infant is older than 2 weeks.
Can high refractive errors cause redness?
High refractive errors could sometimes cause an asymmetrical red reflex . Sometimes, both eyes might have a red reflex; however, there might be difference in the level of brightness. This could be indicative of anisometropic amblyopia that occurs due to different refractions.
Is a red reflex normal?
Normal Red Reflex. The test will be considered normal under the following circumstances: The red or orange glow must be observed in both the eyes. The reflection should be symmetrical in terms of color, intensity, and clarity. The pediatrician should make a referral to an ophthalmologist in the following cases:
What is the red reflex text?
Examination of pupil reflections, also known as the red reflex text, can reveal problems in the cornea, lens and sometimes the vitreous, and is particularly useful in young children. These photographs show what can occur in the case of certain major eye conditions, the most serious of which is retinoblastoma.
When to test for red reflexes?
It is essential to test the red reflex after birth, at the age of six weeks and also during routine consultations or when parents are concerned about the child's vision or the appearance of her or his eyes.
How to teach a child to see red?
Encourage the child to look at the light source and direct the light at the child's eyes individually and together. You should see an equal and bright red reflex from each pupil.
How to open eyes when breastfeeding?
For the child that won’t open his/her eyes: try picking/sitting them up or rocking them from sitting to lying. Having a parent hold them on their shoulder (as if winding them) and looking from behind often works. A feeding child will often open his/her eyes, although breast feeding then makes looking in the eyes logistically tricky.
Should low birth weight infants have ROP screening?
Low birth-weight/premature infants (at high risk of retinopathy of prematurity): Should have had ROP screening and follow-up arranged as necessary by neonatal unit.
Can a child with darker skin tones have a pale retina?
Children with darker skin tones may have pale retina . If retinal vessels can be seen and followed to the disc and the reflex is equal bilaterally then this is reassuring. Comparison with parents’ red reflexes may also help.
