| Insulin Type | Onset | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Rapid-acting inhaled | 10 to 15 minutes | 3 hours |
| Regular/short acting | 30 minutes | 3 to 6 hours |
| Intermediate acting | 2 to 4 hours | 12 to 18 hours |
| Long acting | 2 hours | Up to 24 hours |
Is regular insulin and NPH insulin the same thing?
Two of these concentrations are the regular and NPH insulin. NPH insulin, or Insulin Isophane Suspension, is a transitional form of insulin which has the ability to extend its capacity for a longer time in contrast with regular ones. The regular insulin, or Insulin Injection Regular, is described to be a drug with short-acting effects.
What is the peak time for regular insulin?
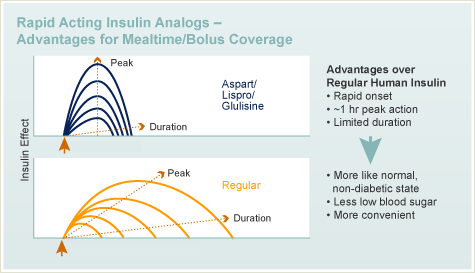
Regular Human Insulin which has an onset of action of 1/2 hour to 1 hour, peak effect in 2 to 4 hours, and duration of action of 6 to 8 hours. The larger the dose of regular the faster the onset of action, but the longer the time to peak effect and the longer the duration of the effect.
How fast does regular insulin acts?
There are several different types of insulin available for people who have diabetes:
- Rapid-acting: This type of insulin starts to work 10 minutes after injection. ...
- Regular-acting: Also called short-acting insulin, this begins to work 30 minutes after injection and its peak time is between two to four hours. ...
- Intermediate-acting: This starts to take effect one to three hours after injection. ...
Which is the fastest acting insulin?
- Fiasp, a new, ultra-fast acting mealtime insulin is available for the treatment of diabetes in adults
- The Scoop on Raw Diets for Pets | ADW Diabetes
- New diabetes treatment could eliminate need for insulin injections
See more

Is regular insulin fast-acting?
Regular insulin is a short-acting insulin that helps people with diabetes control their blood sugar. Take this medication about 30 minutes before a meal. If your healthcare provider has prescribed regular insulin, don't change your dose or stop taking this medication without talking to them.
Is regular insulin slow acting?
Regular insulin (Novolin R, Humulin R) is an example of short-acting insulin.
Which insulin is slow acting?
insulin glargine (Lantus), lasts up to 24 hours. insulin detemir (Levemir), lasts 18 to 23 hours. insulin glargine (Toujeo), lasts more than 24 hours. insulin degludec (Tresiba), lasts up to 42 hours.
What insulins are fast-acting?
Humalog is a fast-acting insulin that starts working faster and works for a shorter period of time than regular human insulin. Humalog is taken within 15 minutes before eating or right after eating a meal.
What is the action of regular insulin?
Regular insulin is a short acting form of the synthetic hormone. It helps move glucose from the blood into the body's cells. The cells then use this sugar for energy. Regular insulin typically starts to work within 30 minutes to 1 hour of an injection.
What's the difference between regular insulin and NPH?
NPH (Neutral Protamine Hagedorn) is a longer-acting human insulin that is used to cover blood sugar between meals, and to satisfy your overnight insulin requirement. A fish protein, protamine, has been added to the Regular human insulin to delay its absorption.
What are the 4 types of insulin?
The types of insulin include:Rapid-acting, which starts to work within a few minutes and lasts a couple of hours.Regular- or short-acting, which takes about 30 minutes to work fully and lasts 3 to 6 hours.Intermediate-acting, which takes 2 to 4 hours to work fully. ... Long-acting, which can work for an entire day.More items...•
What is the duration of regular insulin?
Terms To KnowInsulin TypeOnsetDurationRegular/short acting30 minutes3 to 6 hoursIntermediate acting2 to 4 hours12 to 18 hoursLong acting2 hoursUp to 24 hoursUltra-long acting6 hours36 hours or longer3 more rows•Mar 25, 2021
What is the most common type of insulin?
Insulin is available in different strengths; the most common is U-100.
What are the 5 types of insulin with examples?
The 5 types of insulin are: rapid-acting insulin. short-acting insulin. intermediate-acting insulin....Rapid-acting insulinFiasp and NovoRapid® (insulin aspart)Humalog® (insulin lispro)Apidra® (insulin glulisine).
What are regular insulin names?
Regular- or short-acting products generally use insulin regular, including: Humulin R. Humulin R U-500. Humulin R U-500 KwikPen....Brands of insulininsulin aspart (NovoLog)insulin glulisine (Apidra)insulin lispro (Humalog)
What type of insulin has the most rapid onset of action?
Because insulin lispro begins to exert its effects within 15 minutes of administration, patients must eat within this time period. Compared with insulin lispro, regular human insulin has a slower onset of action.
How quickly does regular insulin work?
Terms To KnowInsulin TypeOnsetDurationRegular/short acting30 minutes3 to 6 hoursIntermediate acting2 to 4 hours12 to 18 hoursLong acting2 hoursUp to 24 hoursUltra-long acting6 hours36 hours or longer3 more rows•Mar 25, 2021
How long does it take regular insulin to work?
Short-acting insulin (such as regular insulin) starts working in 30 to 60 minutes and lasts 5 to 8 hours. Intermediate-acting insulin (such as insulin NPH) starts working in 1 to 3 hours and lasts 12 to 16 hours.
Which insulin has the shortest time duration?
The types of insulin include: Rapid-acting, which starts to work within a few minutes and lasts a couple of hours. Regular- or short-acting, which takes about 30 minutes to work fully and lasts 3 to 6 hours. Intermediate-acting, which takes 2 to 4 hours to work fully.
What is the peak time for regular insulin?
Rapid-acting insulin has a peak time of roughly 30–90 minutes. Short-acting insulin has a peak time of two to three hours. Intermediate-acting insulin has a peak time of anywhere from four to 10 hours. Basal insulin can lower blood glucose levels at a relatively steady pace over a roughly 24-hour period.
How long does slow acting insulin last?
The duration differs and it is determined by the specific type of slow-acting insulin used. However, it should last between 22 and 24 hours. Highlighted below are the types of slow-acting insulin and the duration it takes for each product to last:
Why is fast acting insulin used?
Fast-acting insulin is used due to its fast peak. The insulin acts within a short time to reduce the level of sugar in the blood. Slow-acting insulin, on the other hand, is preferred for its long duration. Its effect in reducing the level of sugar in the blood lasts for several hours.
How long does it take for insulin to be absorbed into the bloodstream?
Fast-acting insulin is absorbed into the bloodstream within a short period, usually within minutes, to act like bolus insulin (i.e. the surge of insulin that the pancreas releases when food is ingested). As a result, this form of insulin is injected just before taking meals or snacks.
What is the term for the amount of time it takes for insulin to reach the bloodstream?
Onset: This refers to the length of time it takes insulin to reach the bloodstream and reduce the blood sugar level.
How much insulin is needed to lower sugar levels?
Generally, one unit of fast-acting insulin is required to lower the level of sugar in the blood by 50 mg/dl.
Why do people use insulin pumps?
Most people use an electronic insulin pump to administer slow-acting insulin thereby eliminating the need for manual injections. However, those that don’t have access to pumps or decide not to use a pump due to their lifestyles may go for injections.
How long does it take for insulin to peak?
Fast-acting insulin has a peak time of about 1 to 3 hours after it is injected. Slow-acting insulin, on the other hand, does not have a peak time. It helps to regulate the sugar levels in the blood at a fairly stable rate.
What do you need to know about insulin?
Insulin Chart: What You Need to Know About Insulin Types and Timing. Medically reviewed by Deborah Weatherspoon, Ph.D., R.N., CRNA — Written by Heather Grey — Updated on March 4, 2019. If you have type 2 diabetes, your doctor might prescribe insulin therapy to help manage your blood sugar levels. Insulin is a hormone that’s produced in the pancreas.
What factors should be considered when taking insulin?
For example, your doctor may consider: your blood glucose. levels. how long you’ve lived. with type 2 diabetes. any current medications. you take.
Why can't you take insulin in pill form?
Insulin can’t be taken in pill-form because your digestive system would break it down in the same way that you digest food. That means the insulin wouldn’t make it to your bloodstream where it’s needed. Depending on your health history, your doctor might prescribe one type of insulin or multiple types of insulin.
How many different types of insulin are there?
Although there are four main types of insulin, there are far more prescription brands that offer the medication in its main forms. These brands may vary by the type of insulin, dosing, and how it is delivered, among other factors. Here’s an overview of the different brands and insulin products available:
Why do people with type 2 diabetes need insulin?
It regulates blood sugar levels and allows your body to convert sugar into energy. People with type 2 diabetes are still able to make insulin, but the body doesn’t use it effectively. That’s why some people with type 2 diabetes need to take prescription insulin.
Does insulin need to change over time?
your lifestyle and. overall health. your insurance coverage. Over time, your insulin needs may change and your doctor may suggest trying something new. It’s normal for your treatment plan to shift over time. If you have questions about why your doctor recommends a certain type of insulin, talk to them.
How long does insulin take to work?
Includes: NPH Human Insulin which has an onset of insulin effect of 1 to 2 hours, a peak effect of 4 to 6 hours, and duration of action of more than 12 hours.
How long does it take for insulin to peak?
Regular Human Insulin which has an onset of action of 1/2 hour to 1 hour, peak effect in 2 to 4 hours , and duration of action of 6 to 8 hours. The larger the dose of regular the faster the onset of action, but the longer the time to peak effect and the longer the duration of the effect. Intermediate-acting insulin:
What is insulin analog?
Human Insulin and Insulin Analogs are available for insulin replacement therapy. Insulins also are classified by the timing of their action in your body – specifically, how quickly they start to act, when they have a maximal effect and how long they act.Insulin analogs have been developed because human insulins have limitations when injected ...
How are insulins categorized?
Insulins are categorized by differences in: Onset (how quickly they act) Peak (how long it takes to achieve maximum impact) Duration (how long they last before they wear off) Concentration (Insulins sold in the U.S. have a concentration of 100 units per ml or U100. In other countries, additional concentrations are available.
How long does insulin detemir last?
The insulin effect plateaus over the next few hours and is followed by a relatively flat duration of action that lasts 12-24 hours for insulin detemir and 24 hours for insulin glargine.
What is the difference between pre-mixed insulin and pre-mixed insulin?
Very small doses will have an earlier peak effect and shorter duration of action, while higher doses will have a longer time to peak effect and prolonged duration. Pre-Mixed Insulin which is NPH pre-mixed with either regular human insulin or a rapid- acting insulin analog. The insulin action profile is a combination of the short ...
Where is insulin injected?
Insulin is usually injected into the fatty tissue just under the skin. This is also called subcutaneous tissue. See a table of insulin action below and a graphic illustration of onset of action, peak effect and duration of action of the different insulins.
What is fast acting insulin?
Rapid-acting, or fast-acting insulin is insulin that is generally taken before or after you eat a meal. When your pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin, you may have post-meal blood sugar spikes that keep you from good management of your diabetes.
How long does it take for insulin to peak?
They will peak at anywhere from 30 to 90 minutes, and they have a duration of about 1 to 5 hours, depending on whether it’s Lispro, Aspart, or Glulisine. The way that you can differentiate the types of insulin available are to look at the onset, peak, and the duration of the particular insulin.
How many types of rapid insulins are there?
There are three main types of rapid or fast acting insulin. They are listed in the chart above, and they are Lispro (Humalog), Aspart (Novolog), and Glulisine (Apidra). There are a few other versions of rapid acting insulin, which we will discuss.
What insulin does Christie use?
For Christie, she uses Humalog lispro insulin. She gets a little bit of this rapid or fast acting insulin continually through her pump via a basal. She also gets some of this insulin through her pump, in a bolus dose every time she eats a meal.
What happens when there is no insulin?
When there is no insulin, or not enough insulin, the goal is to try to simulate what the body normally does to bring down blood sugars through injections of insulin, inhaled insulin, or via an insulin pump. To do this, rapid or fast acting insulin must be taken in relation to food that is eaten in many cases.
What insulin is used for diabetes?
Humulin U-500. When a person with diabetes needs even more concentrated rapid acting insulin, there is Humulin U-500. Again, this insulin allows for larger doses to be given in a smaller amount of units to control post-meal blood sugar spikes.
How to make insulin lower blood sugar?
Counting carbohydrates that are contained in your meals and snacks, so that you bolus enough insulin before or with your meal will make a difference. It’s better to correct a blood sugar before it gets high, than to try to shoot darts of insulin at it after it has already risen too high. This way you prevent high blood sugars, rather than react to them. As it turns out, once blood sugar gets high, it’s tough to bring it back down.
What is a combination of insulins that are usually administered 30 minutes before a meal and contain?
Combination insulins that are usually administered 30 minutes before a meal and contain: A short-acting insulin. An intermediate-acting insulin. These pre-mixed insulins simplify dosing in people needing insulin because they already have a short-acting and an intermediate-acting insulin in them.
What happens when you inject insulin?
Changes in eyesight. Low potassium levels – may be felt as muscle pain, cramps or weakness or a funny heartbeat. Mood changes. A rash – usually just where you inject the insulin although some people may develop one over their whole body. Lumps or scars where you inject the insulin.
How long does humulin R last?
Humulin R is a short-acting insulin that starts to work within 30 minutes and lasts for 8 hours.
What is the name of the insulin that is used to treat diabetes?
Humulin is the brand name for four different types of insulin, each with a different speed of effect and length of time they work for.
Why are humulin N and humulin R the same?
Humulin N and Humulin R have the same side effects because they are both insulins. Side effects of insulin include:
When was insulin first discovered?
Without insulin, we cannot survive, and death from diabetes was a common occurrence until insulin was discovered in the early 1900s by Frederick Banting and Charles Best. There are several different types of Humulin and each one has been made to last for a specific length of time, for example: Humulin R: Short-acting insulin.
Is Humulin discontinued?
Humulin L and Humulin U have been discontinued.
What is the role of insulin in the body?
The main role of insulin is to allow cells throughout the body to uptake glucose (sugar) and convert it into a form that can be used by these cells for energy. Without insulin, we cannot survive, and death from diabetes was a common occurrence until insulin was discovered in the early 1900s by Frederick Banting and Charles Best.
What is the name of the bacterium that makes insulin?
To make insulin glargine, scientists have genetically modified a bacterium called Escherichia coli to produce insulin that is very similar to human insulin.