What are the 10 most spoken languages in Europe?
Top 10 Languages By Total Number Of Speakers
- English
- Mandarin Chinese
- Hindi
- Spanish
- Standard Arabic
- Bengali
- French
- Russian
- Portuguese
- Urdu. Illustrations by Victoria Fernandez. This article was originally published in 2015. It has been updated with more recent data and information.
What is the origin of Sanskrit language?
- Khalkha ( Xalx ), or the Khalkha group of dialects, are spoken centrally in the country of Mongolia, but some dialects, e.g. ...
- Khorchin ( Xorcen ), or the Khorchin group of dialects, are spoken to the east, in the eastern part of Inner Mongolia and Manchuria.
- Ordos ( Ordes ), is spoken to the south, in the Ordos city of Inner Mongolia.
What are non Indo European languages?
What are the top five languages spoken in Spain?
- Spanish (99%)
- Catalan (8%)
- Valencian (4%)
- Galician (3%)
- Basque (1%)
- Aranese (0,007%)
- Extremaduran (0,4%)
Where does Sanskrit originate?
- It’s an ancient language. Every one speak either solely Sanskrit derived language or Sanskrit mixed language. ...
- Government promoted Hindi after independence not Samskrtuam. Even today government promote samskrutam only for the sake of it. They really love Hindi than sanskrutam. ...
- The best way to learn lan
See more
Why is Sanskrit an Indo-European language?
Sanskrit traces its linguistic ancestry to Proto-Indo-Iranian and ultimately to Proto-Indo-European languages, meaning that it can be traced historically back to the people who spoke Indo-Iranian, also called the Aryan languages, as well as the Indo-European languages, a family of several hundred related languages and ...
Is Sanskrit Mother of European languages?
Sanskrit belongs to the Indo-European languages family. The meaning of the word "Sanskrit" is refined, decorated and produced in perfect form. This is the oldest language ever attested on Earth.
Is Sanskrit originated from Europe?
Newer scholarship has shown that even though Sanskrit did indeed share a common ancestral homeland with European and Iranian languages, it had also borrowed quite a bit from pre-existing Indian languages in India.
Which language is an Indo-European language?
It turns out that Sanskrit, Greek, Latin, Hittite, Old Irish, Gothic, Old Bulgarian, Old Prussian, and other languages share surprising attributes, meaning that most European languages and many of the languages of Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and India belong to the Indo-European family.
Who invented Sanskrit?
PaniniClassical Sanskrit has its origin in the end of the Vedic period when the Upanishads were the last sacred texts to be written down, after which Panini, a descendant of Pani and a grammar and linguistic researcher, introduced the refined version of the language.
Is Sanskrit the mother of Tamil?
Tamil is not the mother of Sanskrit. Although, many believe Tamil is the mother of all languages. Sanskrit is the Divine language of Hinduism.
Is Sanskrit an Aryan language?
Sanskrit language, (from Sanskrit saṃskṛta, “adorned, cultivated, purified”), an Old Indo-Aryan language in which the most ancient documents are the Vedas, composed in what is called Vedic Sanskrit.
Which European language is closest to Sanskrit?
Romani, because it's descended from Sanskrit like Italian is descended from Latin. The next closest European relative of Sanskrit is Ossetian, an Eastern Iranian Language. It has an ancestor in common with Sanskrit, and that's Proto-Aryan.
Is Sanskrit closest to Proto Indo European?
vedic sanskrit is considered closest to proto indo european language, the 70 words of sanskrit are considered part of proto indo european more than any other known language.
What are the 4 Indo-European languages?
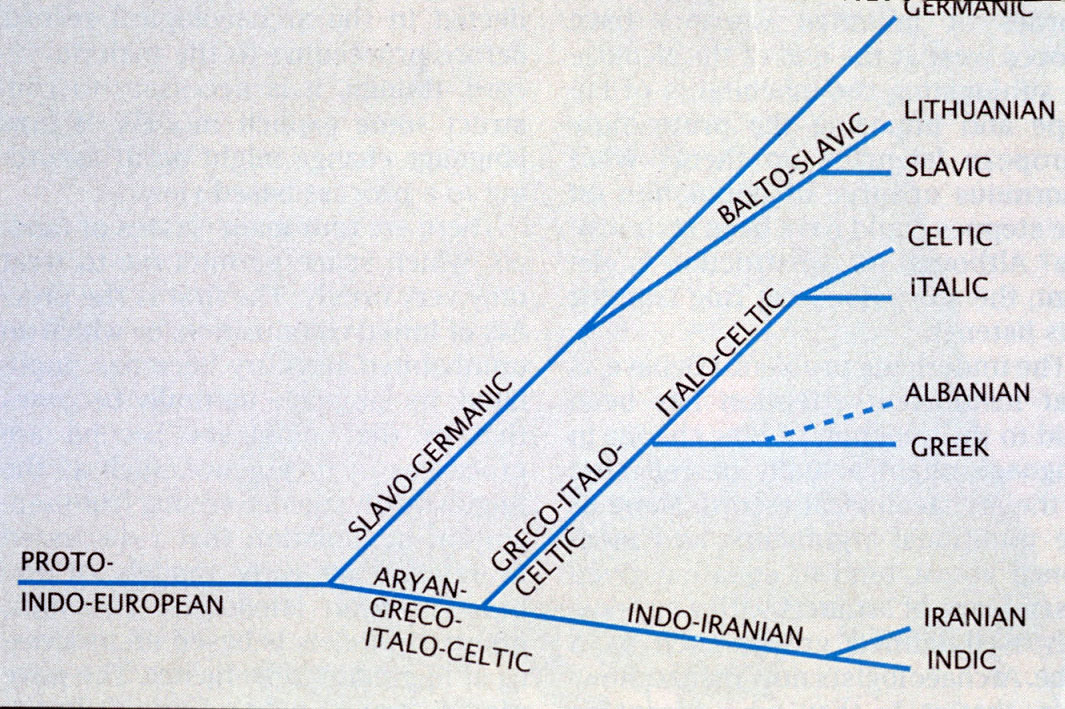
Branches. The Indo-European language family has four main living branches: Indo-Iranian, Balto-Slavic, Germanic, and Italic.
What are the six Indo-European languages?
There are six Indo-European languages spoken by millions of people in Europe today, including: Hellenic (Greek); Romance (Latin-based languages of the Mediterranean and Romanian); Celtic (largely extinct, but Gaelic, Welsh, and Breton); Germanic (Scandinavian languages, modern German, Dutch, and English); Balto- ...
Is Tamil Indo-European?
Kannada, Malayalam, Tamil, and Telugu, the four major languages spoken there, are Dravidian languages. They are structurally unrelated to the languages of northern India, which are Indo-European.
Which language is called mother of all languages?
SANSKRIT is one of the official languages of India, and is popularly known as a classical language of the country. Considered to be the Mother of all Languages, it belongs to the Indic group of language family of Indo-European and its descendents, which are Indo-Iranian and Indo-Aryan.
Which European language is closest to Sanskrit?
Romani, because it's descended from Sanskrit like Italian is descended from Latin. The next closest European relative of Sanskrit is Ossetian, an Eastern Iranian Language. It has an ancestor in common with Sanskrit, and that's Proto-Aryan.
Who said Sanskrit is the mother of all languages?
Once Sri Aurobindo said, “Sanskrit language, as has been universally recognized by those competent to form a judgment, as one of the most magnificent, the most perfect, the most prominent and wonderfully sufficient literary instruments developed by the human mind. “
Is Sanskrit the root of all languages?
Sanskrit is a language which belongs to the Indo-Aryan group and is the root of many, but not all Indian languages. "If you know Sanskrit, you can easily understand many Indian languages such as Hindi, Bengali and Marathi," says Vaishnav, a grade 11 student at Laxman Public School.
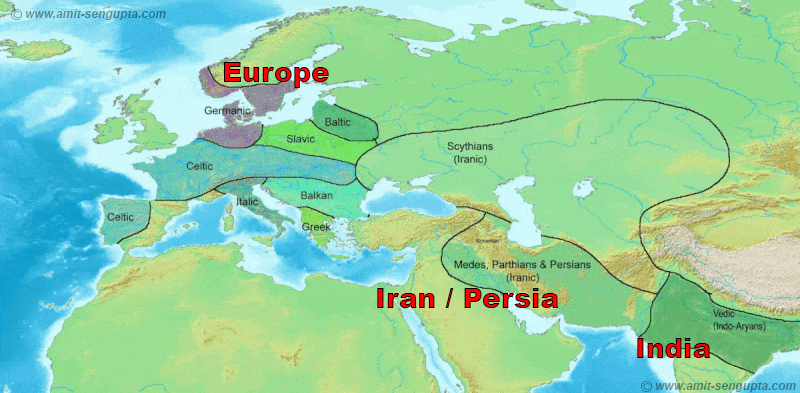
Where are Indo-European languages native to?
t. e. The Indo-European languages are a language family native to western and southern Eurasia. It comprises most of the languages of Europe together with those of the northern Indian subcontinent and the Iranian Plateau.
Which language family is linked to Indo-European?
Proposals linking the Indo-European languages with a single language family include: Indo-Uralic, joining Indo-European with Uralic. Pontic, postulated by John Colarusso, which joins Indo-European with Northwest Caucasian.
What languages are palatovelars?
In the satem languages, which include the Balto-Slavic and Indo-Iranian branches, as well as (in most respects) Albanian and Armenian, the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European palatovelars remained distinct and were fricativized, while the labiovelars merged with the 'plain velars'.
What is the PIE language?
The proposed Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) is also the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European languages, spoken by the Proto-Indo-Europeans. From the 1960s, knowledge of Anatolian became certain enough to establish its relationship to PIE.
How many languages are native speakers?
Of the 20 languages with the largest numbers of native speakers according to Ethnologue, 10 are Indo-European: Spanish, English, Hindustani, Portuguese, Bengali, Russian, Punjabi, German, French, and Marathi, accounting for over 1.7 billion native speakers.
What is the Indo-Hittite hypothesis?
The Indo-Hittite hypothesis proposes that the Indo-European language family consists of two main branches: one represented by the Anatolian languages and another branch encompassing all other Indo-European languages.
How many people speak Indo-European?
In total, 46 percent of the world's population (3.2 billion) speaks an Indo-European language as a first language, by far the highest of any language family.
What is the name of the ancient language of Indo-European?
Coeditor of Indo-European and Indo-Europeans. Sanskrit language, (from Sanskrit saṃskṛta, “adorned, cultivated, purified”), an Old Indo-Aryan language in which the most ancient documents are the Vedas, composed in what is called Vedic Sanskrit. Although Vedic documents represent the dialects then found in the northern midlands ...
What is Sanskrit used for?
Sanskrit was also used as the medium for composing treatises of various philosophical schools, as well as works on logic, astronomy, and mathematics. Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content. Subscribe Now. Sanskrit is not restricted to Hindu compositions.
What is the language of India?
India: Indo-European languages. …the family all derive from Sanskrit, the language of the ancient Aryans. Sanskrit, the classic language of India, underwent a process of systematization and grammatical refinement at an early date, rendering it unique among Indo-Aryan languages in its degree of linguistic cultivation.
What is the first poem written in Sanskrit?
The two epics Rāmāyaṇa (“Life of Rāma”) and Mahābhārata (“Great Tale of the Bhāratas”) were also composed in Sanskrit, and the former is esteemed as the first poetic work ( ādikāvya) of India. The Pañcatantra (“Treatise in Five Chapters”) and Hitopadeśa (“Beneficial Instruction”) are major representatives of didactic literature.
How many genders are there in Sanskrit?
It is an inflected language. For instance, the Sanskrit nominal system—including nouns, pronouns, and adjectives—has three genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), three numbers (singular, dual, and plural), and seven syntactic cases (nominative, accusative, instrumental, dative, ablative, genitive, and locative), in addition to a vocative.
Is Sanskrit literature published in regional scripts?
Sanskrit texts continue to be published in regional scripts, although in fairly recent times Devanāgarī has become more generally used. There is a large corpus of literature in Sanskrit covering a wide range of subjects. The earliest compositions are the Vedic texts.
How many people speak Sanskrit?
Despite this, it has experienced a slight revival, and today, around 14,000 people claim to speak the language natively. Further, Sanskrit is an Indo-European language, part of the Indo-Aryan Languages branch, relating it to other languages like Gujarati and Hindi. Sanskrit is a highly inflected language: it has three grammatical genders, ...
Which language gave rise to all Indo-European languages?
So, what was Proto-Indo-European like?
When did Sanskrit become extinct?
While it was spoken pretty widely in the Indus Valley Civilizations, it was almost completely extinct by the seventh century AD.
Which language is the mother of all IE languages?
Schlegel’s hypothesis that Sanskrit is the mother of all IE languages is based on the fact that when Sanskrit was first studied by European scholars in the 19th century, they discovered that it was not only a very old language, but it shared a surprising amount of linguistic similarity to other Indo-European languages.
Who was the mother of all Indo-European languages?
The idea that Sanskrit could be the mother for all Indo-European languages can be traced back to the scholar Fredriech Schlegel in the 1800s. He is often deemed a pioneer of comparative linguistics (the study of how languages are related), and his work led to much development in modern linguistics, including Grimm’s Law.
Is Sanskrit a descendent of Indo-European?
There are many other such examples of Sanskrit’s relation to other Indo-European languages. For the scientific standards of that time, this was enough for many to believe that Sanskrit was in fact the mother of all Indo-European languages—or at least a very, very close descendent of proto-Indo-European.
Is Armenian a new language?
Armenian, un like Sanskrit, is a relatively new language. The first written account of Armenian dates back to 500 AD—almost 3500 years after the first written accounts of Sanskrit. Further, Armenian occupies is own branch of the Indo-European language family, and today there are an estimated 12 million speakers of Armenian in Armenia and abroad. Armenian has a fairly large consonant inventory, chalking in around 34 individual consonant sounds compared to English’s 24 consonant sounds. Further, there are even more consonant sounds in some Armenian dialects. Grammatically, Armenian also has a subject-object-verb word order, no grammatical gender, and seven noun cases.
Who discovered that Sanskrit is a language?
Scientists who studied linguistics focusing on Sanskrit have discovered there is a strong relationship between Sanskrit and languages spoken in Europe. William Jones (1746 -1794), an English philologist, Orientalist, and jurist suggested that many languages sprang from a common source. Williams discovered that many Sanskrit words ...
Where did Sanskrit originate from?
It is derived from the ancient mother of Assamese language that was already existing in India,” says Devy. Yet another instance of Sanskrit borrowing from pre-existing languages in India is that of ‘sandhi’, or compound words. “Take the example of ‘nava’ and ‘uday’ it becomes ‘navyodaya’.
What is the mysterious PIE language?
Mysterious Ancient PIE Language. You may have heard about the mysterious PIE language from which half of all languages originate. Ancient Pages wrote earlier that the “ancient language PIE is not a universal language, but it is the common ancestor of the Indo-European languages, the most widely spoken language family in the world.
What is the Sanskrit name for father?
The Sanskrit for ‘father’, ‘pitar’ for instance, has remarkable phonetic relations across European languages. It is ‘pater’ in Greek and Latin, ‘padre’ in Spanish, ‘pere’ in French, and ‘vader’ in German.
What is the Sanskrit word for snake?
Similarly, the Sanskrit for ‘snake’, is ‘sarpa’, which shares a phonetic link with ‘serpens’ in Latin. He also found similarities in other European languages, like the words ‘mata’ or mother in Sanskrit, is ‘mutter’ in German. ‘Dan’ or ‘to give’ in Sanskrit is ‘donor’ in Spanish.
When did Sanskrit come to India?
Medieval language. Credit: Public Domain. “Sanskrit arrived in the subcontinent around 1800 BCE at a time when there were already pre-existing languages here.
When did the first language emerge?
Historians think the first language emerged approximately between 200,000 years ago and 60,000 years ago, but the topic is difficult to study and reliable answers cannot be given because of the lack of direct evidence.
Where did Sanskrit originate from?
It is derived from the ancient mother of Assamese language that was already existing in India,” says Devy. Yet another instance of Sanskrit borrowing from pre-existing languages in India is that of ‘sandhi’, or compound words. “Take the example of ‘nava’ and ‘uday’ it becomes ‘navyodaya’.
Who discovered the Indo-European language?
First is the Kurgan hypothesis, formulated in the 1950s by a Lithuanian-American archaeologist, Marija Gimbutas.
What is the Sanskrit name for father?
The Sanskrit for ‘father’, ‘pitar’ for instance, has remarkable phonetic relations across European languages. It is ‘pater’ in Greek and Latin, ‘padre’ in Spanish, ‘pere’ in French, and ‘vader’ in German. William Jones established himself as an authority on ancient Indian language and culture.
What is the Sanskrit word for snake?
Similarly, the Sanskrit for ‘snake’, is ‘sarpa’, which shares a phonetic link with ‘serpens’ in Latin. As he studied the languages further, it became clearer that apart from Greek and Latin, Sanskrit words could be found in most other European languages. For instance, ‘mata’ or mother in Sanskrit, is ‘mutter’ in German.
What did Jones believe about the relationship between Sanskrit and Latin?
Jones’ claim rested on the evidence of several Sanskrit words that had similarities with Greek and Latin. For instance, the Sanskrit word for ‘three’, that is ‘trayas’, ...
What is the name of the language that originated in the Indo-European migration?
In the middle of the 19th century, linguistic scholarship entered a new phase wherein the Indo-European languages were assumed to be derived from a common ancestral language called ‘proto-Indo-European’ (PIE).
Did Sanskrit have an ancestral homeland?
Yet, newer scholarship has shown that even though Sanskrit did indeed share a common ancestral homeland ...
Introduction
Accuracy of Reconstruction
- Having said that PIE language is reconstructed in modern times, how accurate is the reconstruction? J. P. Mallory and D. R. Adams who are two of the greatest Indo-Europeanists have to say this : “How real are our reconstructions? This question has divided linguists on philosophical grounds. There are those who argue that we are not really engaged in ‘reconstructi…
More Issues with The Reconstructions
- Also, apart from the major Indo-European branches mentioned above, we have very less information about other branches like Illyrian, Thracian, Dacian, Messapian, Paeonian etc. as they are poorly attested. So if we manage to somehow gain more information regarding these languages, it would contribute a lot to the reconstruction. Also we must watch out for more uniq…
Role of Sanskrit
- Of course, among these 4-5 branches, Sanskrit plays a crucial role in understanding the ancestral language. Sanskrit is one of the earliest attested Indo-European language along with Mycenaean Greek and Anatolian (Hittite), also possessing the largest ancient literature in any language of the world. Even early philologists like William Jones from 18th century had to say this about Sanskri…
References
- The Oxford introduction to Proto-Indo-European and the Proto-Indo-European worldby J.P. Mallory & D.Q. Adams p .50.
- Ibid p .107-108.
- Dissertations and Miscellaneous Pieces Relating to the History and Antiquities, the Arts, Sciences and Literature of Asia by William Jones, Volume 1 p .105.
- The Oxford introduction to Proto-Indo-European and the Proto-Indo-European worldby J.P. Mallory & D.Q. Adams p .50.
- Ibid p .107-108.
- Dissertations and Miscellaneous Pieces Relating to the History and Antiquities, the Arts, Sciences and Literature of Asia by William Jones, Volume 1 p .105.
- A History of Ancient Sanskrit Literature So Far as it Illustrates the Primitive Religion of the Brahmansby Max Muller p .14.
Overview
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divide…
Evolution
The proposed Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European languages, spoken by the Proto-Indo-Europeans. From the 1960s, knowledge of Anatolian became certain enough to establish its relationship to PIE. Using the method of internal reconstruction, an earlier stage, called Pre-Proto-Indo-European, has been proposed.
History of Indo-European linguistics
During the 16th century, European visitors to the Indian subcontinent began to notice similarities among Indo-Aryan, Iranian, and European languages. In 1583, English Jesuit missionary and Konkani scholar Thomas Stephens wrote a letter from Goa to his brother (not published until the 20th century) in which he noted similarities between Indian languages and Greek and Latin.
Classification
The various subgroups of the Indo-European language family include ten major branches, listed below in alphabetical order:
• Albanian, attested from the 13th century AD; Proto-Albanian evolved from an ancient Paleo-Balkan language, traditionally thought to be Illyrian, or otherwise a totally unattested Balkan Indo-European language that was closely related to Ill…
Proposed external relations
From the very beginning of Indo-European studies, there have been attempts to link the Indo-European languages genealogically to other languages and language families. However, these theories remain highly controversial, and most specialists in Indo-European linguistics are sceptical or agnostic about such proposals.
Proposals linking the Indo-European languages with a single language family include:
Present distribution
Today, Indo-European languages are spoken by billions of native speakers across all inhabited continents, the largest number by far for any recognised language family. Of the 20 languages with the largest numbers of speakers according to Ethnologue, 10 are Indo-European: English, Hindustani, Spanish, Bengali, French, Russian, Portuguese, German, Persian and Punjabi, each with 100 million speake…
See also
• Grammatical conjugation
• The Horse, the Wheel, and Language (book)
• Indo-European copula
• Indo-European sound laws
Further reading
• Beekes, Robert S. P. (1995). Comparative Indo-European Linguistics. Amsterdam: John Benjamins.
• Chakrabarti, Byomkes (1994). A Comparative Study of Santali and Bengali. Calcutta: K. P. Bagchi & Co. ISBN 978-81-7074-128-2.
• Collinge, N. E. (1985). The Laws of Indo-European. Amsterdam: John Benjamins. ISBN 9789027235305.