Is schizophrenia a serious brain disorder?
Schizophrenia--a brain disease? A critical review of structural and functional cerebral abnormality in the disorder Schizophrenia is characterised by minor structural abnormality which, in the case of lateral ventricular enlargement, may be better understood as a …
What are three brain abnormalities in schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia as a progressive brain disease There is convincing evidence that schizophrenia is characterized by abnormalities in brain volume. At the Department of Psychiatry of the University Medical Centre Utrecht, Netherlands, we have been carrying out neuroimaging studies in schizophrenia since 1995. We focused our research on three main …
What are 5 causes of schizophrenia?
Evidence That Schizophrenia is a Brain Disease. Data from scientific research proves that schizophrenia is clearly a biological disease of the brain, just like Alzheimer's Disease and Bipolar Disorder. Schizophrenia is now known to be partially caused by genetics and to be inherited. Non-invasive brain imaging techniques such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and …
What area of the brain is affected by schizophrenia?
Nov 20, 2012 · Schizophrenia is a leading cause of disability worldwide. 1 Kraepelin originally characterized the illness as having a course that led almost inevitably to severe cognitive and behavioral decline, 2 and many clinicians and neuroscientists still consider it to be a progressive brain disease that leads to chronicity and social incapacity. 3, 4 This view has been reinforced …

What makes schizophrenia a brain disease?
Schizophrenia is a complex brain disorder. It often runs in families and can cause troubling symptoms. It's caused by a chemical imbalance and other changes in the brain. Symptoms include hearing voices, feeling that people are out to get you, and having false beliefs that are not based in reality.
Is schizophrenia a form of brain damage?
Some researchers believe that problems with brain development may be partly responsible for schizophrenia. Others believe that inflammation in the brain may damage cells that are used for thinking and perception. Many other things could also play a role, including: Exposure to viruses before birth.
What part of the brain is damaged in schizophrenia?
Summary: The cerebellum is among the most affected brain regions in schizophrenia, new research has found. Compared to healthy individuals, cerebellar volume was smaller in patients with schizophrenia.Jun 21, 2017
Is schizoaffective a brain disease?
Schizoaffective disorder is a serious mental health condition. It has features of two different disorders: “Schizo” means the psychotic symptoms of schizophrenia. This brain disorder changes how a person thinks, acts and expresses emotions.May 24, 2021
Does schizophrenia worsen with age?
Schizophrenia does not typically get better as you get older. The symptoms of schizophrenia may become worse over time, or they may remain the same for some people. Schizophrenia is a chronic illness that can be managed with medication and therapy, but it does not typically go away as you get older.Feb 28, 2022
How long can a schizophrenic live?
Average life expectancy with schizophrenia According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the decline in life expectancy among people with more severe mental illness ranges from 10–25 years . Most studies of schizophrenia show a life expectancy reduction of 10–20 years.Dec 21, 2021
Can schizophrenia go away?
Like many of the mental issues we treat, schizophrenia never truly goes away in the sense that we have a cure for it. The good news is that individuals diagnosed as schizophrenic have gone on to live successful, productive lives after seeking treatment.Jul 26, 2021
Can schizophrenia be cured?
There is no known cure for schizophrenia, but the outlook for people who have this illness is improving. There are many ways to treat schizophrenia, ideally in a team approach. These include medication, psychotherapy, behavioral therapy, and social services, as well as employment and educational interventions.
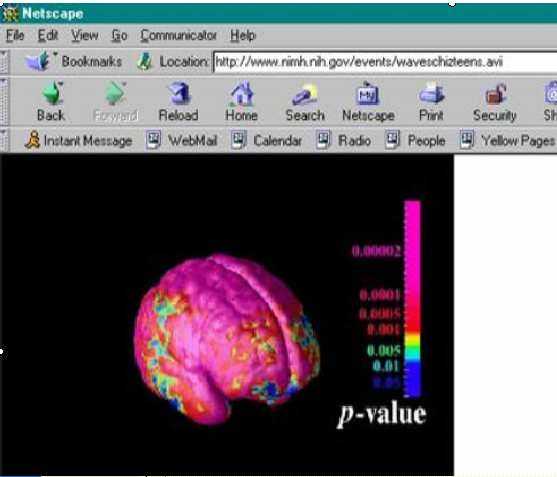
Does schizophrenia show on a brain scan?
Brain scans are not currently used to make a positive diagnosis of schizophrenia. If brain scans are ordered it is likely that they are for the purpose of looking for or ruling out other conditions.Aug 23, 2021
Does schizophrenia affect intelligence?
Intelligence Decline (ID) in Schizophrenia The disorder is characterized by a wide spectrum of symptoms, such as delusions, hallucinations, blunted affect and withdrawal, cognitive impairments, as well as subtle decline in intelligence.Dec 22, 2017
What is schizophrenia considered?
Schizophrenia is a serious mental disorder in which people interpret reality abnormally. Schizophrenia may result in some combination of hallucinations, delusions, and extremely disordered thinking and behavior that impairs daily functioning, and can be disabling.Jan 7, 2020
Is schizoaffective worse than bipolar?
2:549:21What is Schizoaffective Disorder- Is It Worse Than Bipolar Disorder?YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipNow you can become psychotically depressed or you can have mania with psychotic symptoms. In thisMoreNow you can become psychotically depressed or you can have mania with psychotic symptoms. In this case though the psychosis is a measure of the intensity of the illness in cycle.
What are the symptoms of schizophrenia?
Considered as a group and compared to those without the condition, people with schizophrenia show observable functional deficits as well. Functional deficits are problems people have in performing basic mental and physical tasks and activities. This may include: 1 remembering things - compared to those without schizophrenia, they may be less able to remember things they learned 5-minutes ago, but have no problem remembering long-term memories from the past 2 being able to flexibly shift between various tasks (known as executive functioning) 3 making judgment, etc.) 4 figuring out rules from consequences 5 reduced hand grip strength 6 reduced memory attention span and reaction time 7 being more distractible 8 having a harder time engaging in problem solving and planning
What is the dopamine hypothesis?
The "dopamine hypothesis" of schizophrenia believes that schizophrenia is caused by excess dopamine or extra sensitivity to dopamine. Support for this idea comes from several main sources. First, drugs known to block the effects of dopamine in the brain are also known to be useful as antipsychotic medications.
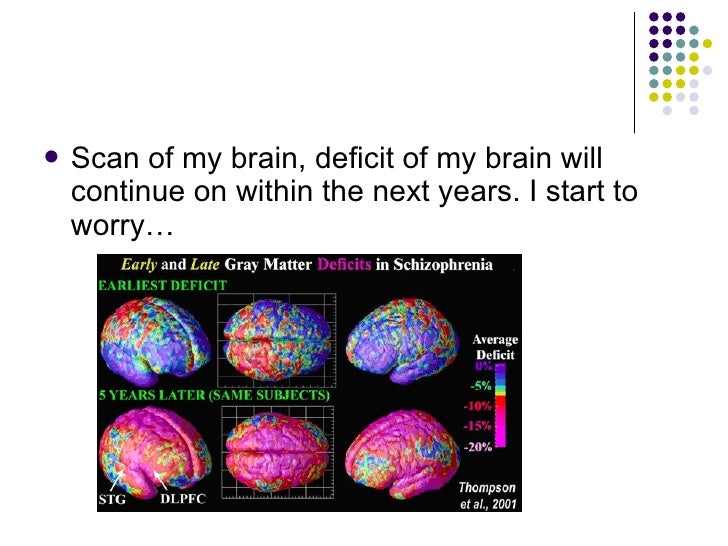
How much gray matter does schizophrenia have?
People with schizophrenia have up to 25% less volume of gray matter in their brains, especially in the temporal and frontal lobes. These areas are known to be important for coordination of thinking and judgment. People demonstrating the worst brain tissue losses also tend to show the worst symptoms.
Is schizophrenia a brain disease?
Evidence That Schizophrenia is a Brain Disease. Data from scientific research proves that schizophrenia is clearly a biological disease of the brain, just like Alzheimer's Disease and Bipolar Disorder. Schizophrenia is now known to be partially caused by genetics and to be inherited. Non-invasive brain imaging techniques such as Magnetic Resonance ...
How do neurotransmitters help the brain?
By providing a way for allowing neurons to communicate with one another, neurotransmitters literally allow the brain to function. There are millions and millions of individual synapses, or gaps, in the brain. The neurotransmitter traffic and activity happening inside those gaps is constant and complicated.
Can antipsychotics cause tardive dyskinesia?
Chronic use of antipsychotic medications (which block dopamine) can result in a Parkinson's-like condition called tardive dyskinesia. The dopamine hypothesis has been dominant for a long time. However, after a lot of recent research, it is no longer so clear that dopamine alone is responsible for causing schizophrenia.
Why is early intervention important?
In Parkinson’s Disease, Alzheimer’s Disease and other diseases of the brain, early intervention is considered important. Early intervention is also important in schizophrenia. However, many people suffer for years while the disease progresses before they are sick enough to qualify for evaluation without consent.
What is schizophrenia?
EMAIL. COMMENTS. Source: Pixabay. Schizophrenia is a physical disease of the brain characterized by an imbalance of neurotransmitters and damaged brain tissue. Other diseases of the brain, such as Parkinson’s Disease, Alzheimer’s Disease, stroke and brain tumors also involve changes in brain tissue.
Is Parkinson's disease a mental illness?
About 50% of individuals with Parkinson’s Disease struggle with psychosis that often looks like schizophrenia. Schizophrenia commonly presents like an early onset Alzheimer’s Disease, with a break from reality and cognitive deficits. Despite these similarities, schizophr enia is still called a mental illness while other brain diseases are classified ...
Is a seizure a mental illness?
Seizures used to be called a mental illness. Women with behavioral effects from hormonal changes were often diagnosed with “female hysteria,” which is no longer considered a disease. People with Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease and stroke, which are all considered physical illnesses are generally not held responsible for odd ...
Is schizophrenia a negative word?
The word schizophrenia has such negative connotations, evo king fear and even terror in people who do not actually know someone who has schizophrenia. I think that it is this reaction of fear and terror that perpetuates the stigma. Reclassifying and renaming schizophrenia would do a great deal towards minimising stigma.
What are the symptoms of schizophrenia?
Considered as a group and compared to those without the condition, people with schizophrenia show observable functional deficits as well. Functional deficits are problems people have in performing basic mental and physical tasks and activities. This may include: 1 remembering things - compared to those without schizophrenia, they may be less able to remember things they learned 5-minutes ago, but have no problem remembering long-term memories from the past 2 being able to flexibly shift between various tasks (known as executive functioning) 3 making judgment, etc.) 4 figuring out rules from consequences 5 reduced hand grip strength 6 reduced memory attention span and reaction time 7 being more distractible 8 having a harder time engaging in problem solving and planning
Is schizophrenia a biological disease?
Data from scientific research proves that schizophrenia is clearly a biological disease of the brain, just like Alzheimer's Disease and Bipolar Disorder. Schizophrenia is now known to be partially caused by genetics and to be inherited. Non-invasive brain imaging techniques such as Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computerized Tomography (CT), ...
Can dopamine cause Parkinson's?
It is also known that too little dopamine is responsible for Parkinson's disease .
What is the space between two neurons called?
In between two linked neurons is a tiny space or gap called a synapse. In a simple scenario, one cell sends a neurotransmitter message across this gap and the next cell receives the signal by catching the messenger chemical as it floats across the gap.
How do neurotransmitters help the brain?
By providing a way for allowing neurons to communicate with one another, neurotransmitters literally allow the brain to function. There are millions and millions of individual synapses, or gaps, in the brain. The neurotransmitter traffic and activity happening inside those gaps is constant and complicated.
Can antipsychotics cause tardive dyskinesia?
Chronic use of antipsychotic medications (which block dopamine) can result in a Parkinson's-like condition called tardive dyskinesia. The dopamine hypothesis has been dominant for a long time. However, after a lot of recent research, it is no longer so clear that dopamine alone is responsible for causing schizophrenia.
What is the dopamine hypothesis?
The "dopamine hypothesis" of schizophrenia believes that schizophrenia is caused by excess dopamine or extra sensitivity to dopamine. Support for this idea comes from several main sources. First, drugs known to block the effects of dopamine in the brain are also known to be useful as antipsychotic medications.
Is schizophrenia a genetic disease?
For one thing, schizophrenia is now known to be partially caused by genetics and to be inherited.
What is the brain's chemical messenger?
The brain uses a number of chemical messengers, called neurotransmitters, to communicate among its millions of individual neurons. At the most basic level, schizophrenic brains appear to be differentially sensitive to the neurotransmitter dopamine compared to normal brains. The "dopamine hypothesis" of schizophrenia holds ...
Which neurotransmitter is involved in schizophrenia?
Today, it appears more likely that other neurotransmitters are involved in creating conditions for schizophrenia and psychosis, including serotonin (implicated in depression and anxiety), and glutamate (which is known to be implicated in the hallucinatory effects of the drug PCP ("angel dust").
Can cocaine cause hallucinations?
Second, stimulant drugs like cocaine and methamphamine, which are known to either mimic the action of dopamine, or to cause dopamine to become more active in the brain, are know to be capable of causing hallucinations and delusions in non-schizophrenic people (if enough of those substances are taken). It is also known that too little dopamine is ...
What is the dopamine hypothesis?
The "dopamine hypothesis" of schizophrenia holds that schizophrenia is caused by excess dopamine (or excessive sensitivity to dopamine). Support for this hypothesis comes from several main sources.