Is skin color an example of incomplete dominance?
Yes, skin colour is an example of incomplete dominance. It is controlled by multiple genes and therefore shows a polygenic inheritance. The polygenic trait is controlled by three or more genes and each gene contributes to the expression of the phenotype.
What is an example of codominance?
Concept of Codominance. This trait generally occurs in case of coat color of organisms. For example, the roan coat color observed in horses is the result of the roan gene inherited by its progeny. In horses, three types of roans exist - namely, red roan, bay roan and blue roan. All of these coat colors follow similar codominance patterns.
What is codominance in blood?
If a person has a single copy of the sickle cell allele, then half their red blood cells become abnormally shaped. If this happens, codominance occurs because both normal and sickled shapes are mixed and seen in the blood. 3. Horse color The roan coat color of a horse is due to codominance.
Is skin color polygenic inheritance?
Polygenic inheritance can be seen in skin color. At least three genes are considered to influence skin colour, and other genes may potentially play a role. The amount of the dark colour pigment melanin in the skin determines skin color.
Is skin color a codominant trait?
Yes, skin colour is an example of incomplete dominance. It is controlled by multiple genes and therefore shows a polygenic inheritance. The polygenic trait is controlled by three or more genes and each gene contributes to the expression of the phenotype.
What are examples of codominance?
Examples of codominance in animals include speckled chickens, which have alleles for both black and white feathers, and roan cattle, which express alleles for both red hair and white hair. Codominance is also seen in plants.
What type of dominance is skin color?
incomplete dominanceInheritance of Skin Color Each gene has two forms: dark skin allele (A, B, and C) and light skin allele (a, b, and c). Neither allele is completely dominant to the other, and heterozygotes exhibit an intermediate phenotype (incomplete dominance).
Which is not an example of codominance?
D. A flower offspring of red and white flowers, which has both red and white petals. C is correct. This is not an example of codominance, because the child does not express both parents' traits.
Is this an example of codominance or incomplete dominance?
An example of codominance is the roan cow which has both red hairs and white hairs. In incomplete dominance a heterozygous individual blends the two traits. An example of incomplete dominance is the pink snapdragon, which receives a red allele and white allele.
What is incomplete and codominance?
Codominance and Incomplete dominance are two types of genetic inheritance. Codominance essentially means that no allele can block or mask the expression of the other allele. On the other hand, incomplete dominance is a condition in which a dominant allele does not completely mask the effects of a recessive allele.
What is skin color called?
Your skin gets its color from a pigment called melanin. Special cells in the skin make melanin. When these cells become damaged or unhealthy, it affects melanin production.
Is eye color Codominance?
For example, do some humans have one blue eye and one green eye, or are these traits just incomplete dominance? There are definitely codominant traits in people. But having two different colored eyes is not one of them.
Where does skin color come from?
Melanin is produced within the skin in cells called melanocytes and it is the main determinant of the skin color of darker-skin humans. The skin color of people with light skin is determined mainly by the bluish-white connective tissue under the dermis and by the hemoglobin circulating in the veins of the dermis.
What traits are codominant?
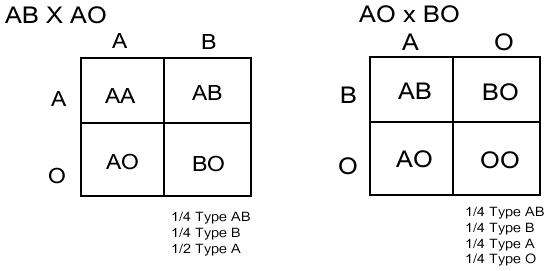
A trait resulting from an allele that is independently and equally expressed along with the other. An example of codominant trait is blood type, i.e. a person of blood type AB has one allele for blood type A and another for blood type B.
What is an example of codominant inheritance in humans?
An example of a codominant trait is blood type. There are four blood types, A, B, AB and o. Type A and B are both dominant to o, but when a person has an allele for A blood and an allele for B blood, both A and B sugars are expressed and the person has type AB blood.
Which of the following describes codominance?
Correct answer: Codominance suggests that both phenotypes are dominant, but cannot be expressed at the same time. The result of codominance would be regions of dominant red expression and regions of dominant white expression, resulting in spots rather than blending.
Which is an example of codominance quizlet?
Codominance is the type of inheritance that occurs when a heterozygote displays both alleles equally. An example would be AB blood type in humans or a red and white striped flower.
What traits are codominant?
A trait resulting from an allele that is independently and equally expressed along with the other. An example of codominant trait is blood type, i.e. a person of blood type AB has one allele for blood type A and another for blood type B.
Is a zebra an example of codominance?
Codominance: Examples in Nature You have no doubt noticed various animals that have stripes or spots on their fur or skin, such as zebras and leopards. This is an archetypal example of codominance.
Are pink flowers codominance?
This type of allelic relationship was termed codominance. It appears as if the red and white alleles are interacting in the heterozygote to generate the pink flowers. Another example of codominance can be seen by looking at a biochemical phenotype.
What would happen if two plants were crossed to produce a yellow and blue flower?
If two plants were crossed to produce a yellow and blue flower, and if the alleles of the gene responsible for petal color were dominant in nature, the flower produced by the progeny plant would either be yellow with blue spots or blue with yellow spots. Related Links: Examples. Science Examples.
What is codominance in biology?
Codominance Examples. Codominance. A person's appearance, and often how they act, is due to the genes located on segments of chromosomes. Genes are the units of hereditary information that are responsible for many of a person's characteristics. These genes for a specific trait, such as eye color, may exist in different forms known as alleles.
What are some examples of alleles?
For a flower, an example of an allele or gene may be for its color. The alleles may make the flower red, pink, violet, etc.
What is it called when both alleles are expressed?
Finally, when both alleles are expressed or appear in some situations it is called codominance.
What happens when you have both an A and a B allele?
There are several combinations of blood types that can result, but when a person has both an A and a B allele, it will lead to blood types visible in the blood, AB. 2. Sickle-Cell Anemia. Sickle cell anemia is a disease where red blood cells become thin and stretched out.
What are some examples of codominance?
Examples of Codominance: 1. AB Blood Type. People with this blood type have A and B proteins at the same time. The ABO gene determine what blood type a person has, and everyone has two copies of this gene, one from each parent.
Why do horses roan?
The roan coat color of a horse is due to codominance. Roan is the result when a color appears in conjugation with white. It is the graying out of a color, and in horses there are actually three types of roans: red, bay, and blue. All of the colors follow similar co-dominance patterns.
What is codominance in genetics?
The National Human Genome Research Institute defines it as ‘a relationship between two versions of a gene, where neither allele is recessive and the phenotypes of both alleles are expressed.‘. In codominance scenarios, simple dominant Mendelian inheritance is not followed.
What are some examples of roan coats?
In horses, three types of roans exist – namely, red roan, bay roan and blue roan. All of these coat colors follow similar codominance patterns. ╬ Other examples of codominance in animals include, roan cattle, agouti mice, and tabby cats.
Why is it important to understand dominant and recessive traits?
Understanding the patterns of dominant and recessive traits and their inheritability are crucial in the study of gene behavior and genetic interactions. This understanding can be practically applied by people involved in the selective breeding of animals and the crossing of plants to produce new and better varieties that have superior traits as compared to their parental organisms.
What is incomplete dominance?
In incomplete dominance, the term itself suggests that the dominance is incomplete, hen ce there is room, so to speak, for the expression of the recessive allele as well. This results in the production of a phenotype that is neither like the dominant nor like the recessive but rather an intermediate form of the two.
When two different alleles of a specific single-gene trait are both expressed simultaneously, what is the answer?
Codominance is observed when two different alleles of a specific single-gene trait are both expressed simultaneously. It follows non-Mendelian inheritance patterns. This article explains this phenomenon with the help of examples.
What are some examples of codominance?
Red and white flowers of Camellia are examples of codominance. ╬ It can be observed very distinctly in case of plants, and can be easily discerned from a case of incomplete dominance. The most commonly observed examples are that of the color of the flowers.
Is a gene dominant or recessive?
According to the Mendelian laws of inheritance, an allele for any given gene (coding for a specific trait), is either dominant or recessive with regards to the end phenotype presented by it. However, in cases where a gene may have multiple alleles, all the alleles may not necessarily follow simple dominance, since one or more alleles of the gene may be dominant or recessive.
Which allele is more likely to be healthy?
C) Most individuals carrying a lethal dominant allele have the disorder and die before they reproduce, whereas individuals carrying a lethal recessive allele are more likely to be healthy and reproduce.
Which is more severe, dominant or recessive?
A) Lethal disorders caused by dominant alleles are usually more severe than lethal disorders caused by recessive alleles.
What color is a finch's beak?
Imagine that beak color in a finch species is controlled by a single gene. You mate a finch homozygous for orange (pigmented) beak with a finch homozygous for ivory (unpigmented) beak and get numerous offspring, all of which have a pale, ivory-orange beak.
Which chromosome is more fragile?
C) the male chr omosome is more fragile than the female chromosome.
Where is the color vision gene found?
C) The gene for color vision is found on the X chromosome.