Why is smooth muscle voluntary?
Smooth muscle cannot be controlled consciously and thus acts involuntarily. The non-striated (smooth) muscle cell is spindle-shaped and has one central nucleus. Smooth muscle contracts slowly and rhythmically.
Is involuntary muscle smooth muscle?
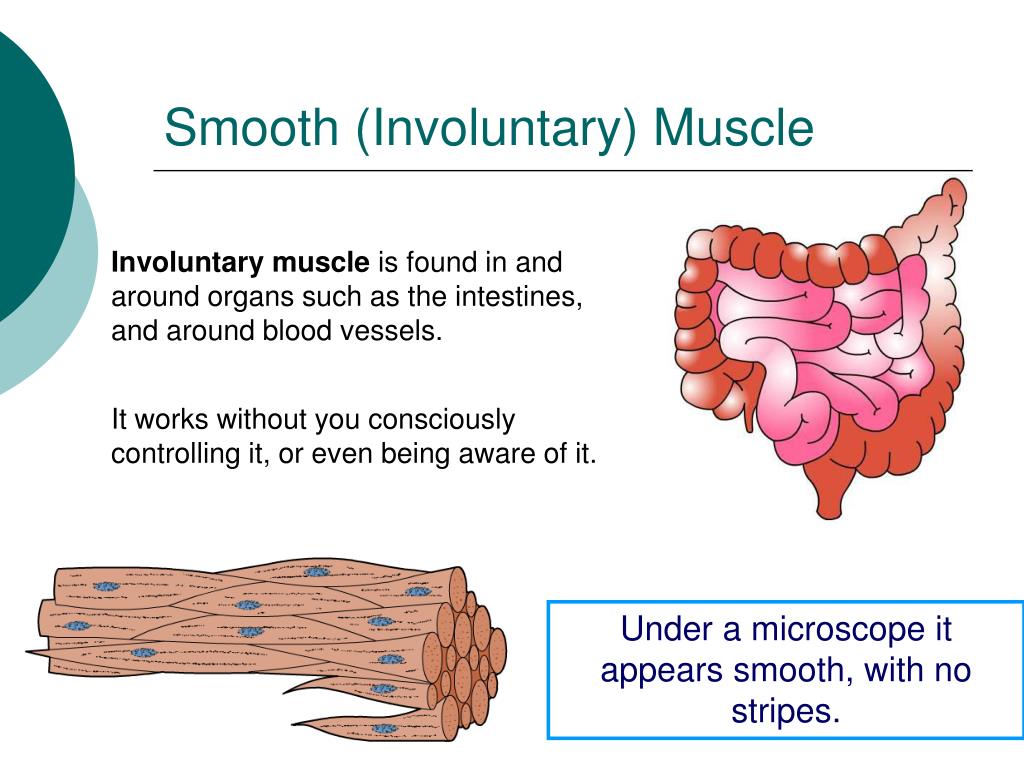
smooth muscle, also called involuntary muscle, muscle that shows no cross stripes under microscopic magnification. It consists of narrow spindle-shaped cells with a single, centrally located nucleus. Smooth muscle tissue, unlike striated muscle, contracts slowly and automatically.
Does smooth muscle work voluntarily?
Unlike voluntary muscles, these muscles act without conscious control in the human body and cannot be controlled willingly. Involuntary muscles are also known as smooth muscles. Muscles found in the heart, digestive system, respiratory system works automatically.
What are 3 involuntary muscles?
Involuntary muscles of the heart, respiratory and digestive systems work automatically. These operations are triggered by nerves and the nerves are stimulated by complex chemical fluids (such as acetylcholine and norepinephrine) that surround them and other living cells.
Which muscles are involuntary?
One very important involuntary muscle is your heart, which keeps beating all day and night. Other involuntary muscles help digest food and are found in your stomach and intestines. It takes guts to be an involuntary muscle!
What type of muscle is voluntary?
Skeletal muscleSkeletal muscle: Skeletal muscles are voluntary muscles, meaning you control how and when they move and work. Nerves in your somatic nervous system send signals to make them function.
What muscle is both voluntary and involuntary?
1:012:11Voluntary and Involuntary muscles - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd your heart rate.MoreAnd your heart rate.
Why are involuntary muscles not under conscious control?
Involuntary muscles are not under our conscious control which means we can't make them contract when we think about it. Voluntary muscles are under our conscious control so we can move these muscles when we want to. These are the muscles we use to make all the movements needed in physical activity and sport.
What are the different types of muscles?
There are three types of muscle in the body: 1 smooth muscle – found in the internal organs and blood vessels - this is involuntary 2 cardiac muscle – found only in the heart - this is involuntary 3 skeletal muscle – attached to the skeleton - this is voluntary
What muscles do you use to kick a ball?
Hip extension (moving the femur backwards) Pulling leg back at the hip before kicking a ball. Quadriceps. Extension of the knee (straightening the leg) Kicking a ball (execution and recovery phase) Hamstrings. Flexion of the knee (bending the leg)
What is shoulder horizontal extension?
Shoulder horizontal extension (moving the arms backwards at shoulder level) Preparation phase of an overarm throw or badminton smash. Pectorals. Adduction of the shoulder (moving the arm towards the body); Shoulder horizontal flexion (moving the arms forwards in front of the body)
What muscle is used to block a volleyball?
Deltoid. Lifting the arm at the shoulder (the deltoid muscle has different parts which flex, extend and abduct the shoulder joint) Lifting the arms to block in volleyball; upward arm swing when trampolining. Trapezius.
Which muscle is involuntary?
smooth muscle – found in the internal organs and blood vessels - this is involuntary. cardiac muscle – found only in the heart - this is involuntary. skeletal muscle – attached to the skeleton - this is voluntary. Involuntary muscles are not under our conscious control which means we can't make them contract when we think about it.
What are the organs that are involved in contraction?
Voluntary muscles are associated with the skeletal system. Involuntary muscles are also known by the name non-striated muscle or smooth muscle. Striated or skeletal muscles are also called as Voluntary muscle. Location of involuntary muscle is stomach, intestine, hearts cardiac muscle, urinary bladder and blood vessel.
What are some examples of involuntary muscles?
Involuntary muscles are under our control, whereas voluntary muscles are under our control. Examples of involuntary muscles are smooth muscles and cardiac muscle. These two same muscles are also example of voluntary muscle; however, they differ from each other.
What is the difference between voluntary and involuntary muscle?
Muscles which are under our control are called as Voluntary muscle, whereas those which cannot be controlled by ourselves are called as involuntary muscle. These muscles are under the control of autonomic nervous system. Functions such as contraction, expansion and other functions are involuntary. An example is heart which is controlled by involuntary muscle. To perform the involuntary action, autonomic nervous system, stimulates the nerves and other signal transferring molecule to carry out the function. However, in other cases stretching of muscle can also trigger contraction.
What is the cause of cardiac muscle contraction?
Thus, action potential gets generated and in the sarcoplasmic reticulum, calcium ions get deposited. Due to huge amount of calcium ions, excitation occurs and muscles get contracted.
What muscle is responsible for goosebumps?
e) In cold conditions or in fear, involuntary muscle preset on the skin called the arector pili are responsible for goosebumps.
What is the difference between a single unit muscle and a multi unit muscle?
They are of two type: single unit smooth muscle which contract and relax together, whereas multi-unit smooth muscle contract and expand differently, as they are not electrically coupled. Example digestive system contraction is an example of single unit muscle.
What are the two types of muscle?
There are two types such as Cardiac and Smooth muscle.