Deviation means change or distance. But change is always followed by the word 'from'. Hence standard deviation is a measure of change or the distance from a measure of central tendency - which is normally the mean.
What are the different measures of central tendency?
What are the Measures of Central Tendency?
- Mean. Mean is an approach that is generally used in Statistics. ...
- Median. The data of the middlemost observation that is achieved after modifying the data in ascending order is termed the median of the data.
- Mode. ...
- Relationship Between Mean, Median and Mode. ...
- Range. ...
What is the measure of central tendency?
Measures of central tendency: The mean
- CENTRAL TENDENCY. Central tendency is defined as “the statistical measure that identifies a single value as representative of an entire distribution.”
- MEAN. Mean is the most commonly used measure of central tendency. ...
- ADVANTAGES. ...
- DISADVANTAGES. ...
- DEGREE OF VARIATION BETWEEN THE MEANS. ...
- Footnotes
- REFERENCES. ...
What is the definition of central tendency?
In statistics, a central tendency is a central value or a typical value for a probability distribution. It is occasionally called an average or just the center of the distribution. The most common measures of central tendency are the arithmetic mean, the median and the mode.
What is central tendency in statistics?
In statistics, the central tendency is the descriptive summary of a data set. Through the single value from the dataset, it reflects the centre of the data distribution. Moreover, it does not provide information regarding individual data from the dataset, where it gives a summary of the dataset.

What are the 4 measures of central tendency?
There are three main measures of central tendency: the mode, the median and the mean. Each of these measures describes a different indication of the typical or central value in the distribution.
Is Mean Deviation is not a measure of central tendency?
Mean Deviation formula is also a measure of central tendency which can be calculated using Arithmetic Mean, median, or Mode. It lets us know on average how far all the observations can be from the middle.
What kind of measure is standard deviation?
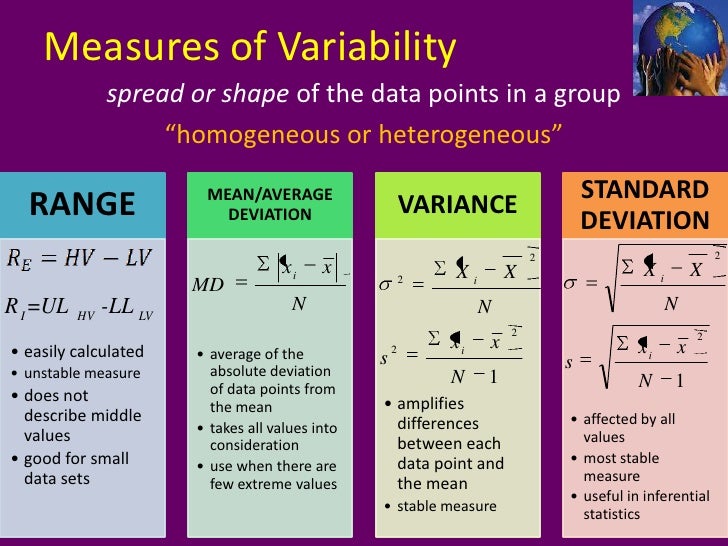
A standard deviation (or σ) is a measure of how dispersed the data is in relation to the mean. Low standard deviation means data are clustered around the mean, and high standard deviation indicates data are more spread out.
Is variance a measure of central tendency?
The parameter that is not a measure of central tendency is (c) variance. The variance is one of the measures of dispersion in a given data set. The parameters that belong to central tendency are the mean, median, and mode.
Which is not measure of central tendency?
Standard deviation is not a measure of central tendency.
Which is not a central tendency?
Mean deviation is deviation from the mean. It is not the central tendency.
What does standard deviation fall under?
Standard deviation is a statistic that measures the dispersion of a dataset relative to its mean and is calculated as the square root of the variance. The standard deviation is calculated as the square root of variance by determining each data point's deviation relative to the mean.
Which best describes standard deviation?
The standard deviation is the average amount that scores in a distribution deviate from the mean of that distribution. The standard deviation is a measure of variability.
Where of standard deviation is called?
Hence, Variance is the square of the standard deviation.
Which of the following is a measure of central tendency?
Mean, median and mode are used as measures of central tendency.
What is the best measure of central tendency?
MeanMean is generally considered the best measure of central tendency and the most frequently used one. However, there are some situations where the other measures of central tendency are preferred. There are few extreme scores in the distribution.
Where are measures of central tendency?
Measures of central tendency help you find the middle, or the average, of a data set. The 3 most common measures of central tendency are the mean, median and mode. The mode is the most frequent value. The median is the middle number in an ordered data set.
Is standard deviation nominal or ordinal?
In the 1940s, Stanley Smith Stevens introduced four scales of measurement: nominal, ordinal, interval, and ratio....More videos on YouTube.OK to compute....Mean, standard deviation, standard error of the meanNominalNoOrdinalNoIntervalYesRatioYes4 more columns•Oct 3, 2019
Is standard deviation a measure of precision or accuracy?
precisionThe standard deviation measures the precision of a single typical measurement. It is common experience that the mean of a number of measurements gives a more precise estimation than a single measurement.
Is standard deviation A statistical measure?
Standard Deviation is a statistical term used to measure the amount of variability or dispersion around an average. Technically it is a measure of volatility. Dispersion is the difference between the actual and the average value. The larger this dispersion or variability is, the higher is the standard deviation.
What is the standard measurement called?
Many kinds of units of measurements have been used indigenously in different places over different periods of time and new units have been introduced as and when needed. But the need for universal conformity gave birth to the standard system of measurements, what is known as the S.I. unit today.
What are the three common measures of central tendency?
In statistics, there are three common measures of central tendency: The mean. The median. The mode. Each of these measures finds the central location of a dataset using different methods. Depending on the type of data you’re analyzing, one of these three measures may be better to use than the other two.
How to find median?
You can find the median by arranging all the individual values in a dataset from smallest to largest and finding the middle value. If there are an odd number of values, the median is the middle value.
What measure the central location of a dataset?
We’ve seen that the mean, median, and mode all measure the central location, or the “typical value,” of a dataset in very different ways:
Why is central tendency important?
Takeaway: A measure of central tendency is useful because it provides us with a single value that describes the “center” of a dataset. This helps us understand a dataset much more quickly compared to simply looking at all of the individual values in the dataset.
How much does a typical person make in a year?
In this particular example, the mean tells us that the typical individual earns about $47,000 per year in this town while the median tells us that the typical individual only earns about $32,000 per year, which is much more representative of the typical individual.
What is the median of two middle values?
Since we have an even number of values, the median is simply the average of the two middle values: 13.5.
What would happen if a couple looked at the individual home prices in each neighborhood?
If the couple just looked at the individual home prices in each neighborhood, they might have a tough time determining which neighborhoods best fit their budget because they might see something like this:
What is Central Tendency?
Central tendency is a descriptive summary of a dataset through a single value that reflects the center of the data distribution. Along with the variability (dispersion) of a dataset, central tendency is a branch of descriptive statistics.
What is the median of a dataset?
Median: The middle value in a dataset that is arranged in ascending order (from the smallest value to the largest value). If a dataset contains an even number of values, the median of the dataset is the mean of the two middle values. Mode: Defines the most frequently occurring value in a dataset.
Is the mode the only central tendency measure?
The selection of a central tendency measure depends on the properties of a dataset. For instance, the mode is the only central tendency measure for categorical data, while a median works best with ordinal data. Although the mean is regarded as the best measure of central tendency for quantitative data, that is not always the case.
Does a dataset have multiple modes?
In some cases, a dataset may contain multiple modes, while some datasets may not have any mode at all. Even though the measures above are the most commonly used to define central tendency, there are some other measures, including, but not limited to, geometric mean. Geometric Mean The geometric mean is the average growth ...
Is the mean a good measure of central tendency?
Although the mean is regarded as the best measure of central tendency for quantitative data, that is not always the case. For example, the mean may not work well with quantitative datasets that contain extremely large or extremely small values. The extreme values may distort the mean. Thus, you may consider other measures.
What is the midpoint of 15?
The midpoint of 15 is the 8 th score because there are 7 scores above it and 7 scores below it. The teacher then counts down or up to the 8 th score to determine the midpoint, or median. In the case of Illustration 11, the median is 29. Note that, for this data set, 29 is also the mode.
What is mode in math?
The mode is defined as the most frequently occurring score. If the data are arranged in a frequency distribution similar to illustration 4, then the mode is easy to identify. In illustration 4 the mode is 89. Why is the mode 89? Because there were four students who scored an 89, and that was the largest number of students who scored at the same level on this assessment.
How to find the mean of a data point?
In fact, when most people think of average, they are imagining the mean. The mean is easy to calculate and most people have been doing it since elementary school. To calculate the mean, add up all of the data points and divide that result by the total number of data points. Consider the following ordered array of test scores on a 25 point quiz from a typical middle school class of 20 students.
Why can't a child get a mean of 10?
In fact, the child could never get an average of 10 because there is no way to recoup the mathematical effects of the low score. The mean has limitations as a statistic and this is a classic example of the most common one.
How does the median work?
The median divides a distribution exactly in half so that 50% of the scores are at or below the median and 50% of the scores are at or above it. It is the “middle value” in a frequency distribution. When the number of data points is an odd number, the middle score is the median. For example, given 13 scores, the 7 th score would be the median. When the number of data points is even, like 14, then the median is equal to the sum of the two middle scores in a frequency distribution divided by 2.
Why is it important to calculate the mean?
For the teacher, it is helpful to calculate the mean to get a sense of the average score . However, the mean has a major drawback: it is greatly influenced by extreme scores. Consider the data below in illustration 16. Assume the data points are from a single student on a series of 10 point tests.
What are the three main measures of central tendency?
Knowing the center point answers such questions as, “what is the middle score?” or “which student attained the average score?” There are three fundamental statistics that measure the central tendency of data: the mode, median, and mean. All three provide insights into “the center” of a distribution of data points. These measures of central tendency are defined differently because they each describe the data in a different manner and will often reflect a different number. Each of these statistics can be a good measure of central tendency in certain situations and an inappropriate measure in other scenarios. The next section describes each statistic and both its educational value and its limitations.
How to find central tendency?
The central tendency can be found using the formulas of mean, median or mode in most of the cases . As we know, mean is the average of a given data set, median is the middlemost data value and the mode represents the most frequently occurring data value in the set.
What is central tendency in statistics?
In statistics, the central tendency is the descriptive summary of a data set. Through the single value from the dataset, it reflects the centre of the data distribution. Moreover, it does not provide information regarding individual data from the dataset, where it gives a summary of the dataset. Generally, the central tendency of a dataset can be defined using some of the measures in statistics.
Why do analysts use mean?
But most of the times, the analyst uses the mean because it involves all the values in the distribution or dataset. If you have skewed distribution, the best measure of finding the central tendency is the median. If you have the original data, then both the median and mode are the best choice of measuring the central tendency.
What is mean in statistics?
The mean represents the average value of the dataset. It can be calculated as the sum of all the values in the dataset divided by the number of values. In general, it is considered as the arithmetic mean. Some other measures of mean used to find the central tendency are as follows: Geometric Mean. Harmonic Mean.
What are the measures of central tendency?
The four measures of central tendency are mean, median, mode and the midrange. Here, mid-range or mid-extreme of a set of statistical data values is the arithmetic mean of the maximum and minimum values in a data set.
What is the measure of dispersion?
A statistic that tells us how the data values are dispersed or spread out is called the measure of dispersion. A simple measure of dispersion is the range. The range is equivalent to the difference between the highest and least data values.
What is the most frequently repeated value in a given dataset?
Since the mode represents the most common value. Hence, the most frequently repeated value in the given dataset is 5. Based on the properties of the data, the measures of central tendency are selected.
What is mean deviation?
Mean deviation is a measure of dispersion calculated from the arithmetic deviation of different items of a central tendency , such as the mean or the median. The measure of central tendency gives only a single value that represents the whole of the observed data. But, it cannot describe the observation fully, particularly in terms of spread of the data. Hence, the measure of dispersion that helps us to study the variability of the items in the observation. Mean deviation is defined as:
What is standard deviation in math?
4) The standard deviation is the square root of the variance so it is also a measure of how "far" you "typically" are from the middle (where "far" now means the usual distance, but "typically" doesn't exactly mean on average anymore).
What is the difference between central tendency and standard deviation?
Central tendency is a single number (or observation) that is chosen to represent all your data . Standard deviation is a measure of how far apart your data is. So let’s take a series of test scores 75,78,80,91,95 the sample standard deviation is 8.70 this represents how far the data are apart from each other, but there is no score anywhere near the standard deviation.
What is central tendency?
A measure of central tendency attempts to describe what is typical of the distribution with the understanding that typical does not have a single precise meaning. Because the mode gives the peak of the likelihood function for a distribution, it is usually included as a measure of central tendency. Obviously the mode can coincide with the minimum or maximum possible value so it need not be a value near the center. But the same is true of the median. And the mean also follows the direction of the skew, so it can also seem un-central in a way.
What are mean median and mode?
By definition, it follows that averages namely mean, median and mode are measures of Central tendencies and employed to measures of central tendencies they do not throw any light on the variation present in the data.
What is the square of the standard deviation called?
1) The square of the standard deviation is called the variance.
When a distribution is symmetric, the mean, median, mode, and trimmed and winsorized mean are?
When a distribution is symmetric, the mean, median, mode and trimmed and winsorized mean are all the same and the mean is easiest for computers to calculate.