Is Staphylococcus epidermidis Gram positive or negative?
Staphylococcus epidermidis is a coagulase-negative, gram-positive cocci bacteria that form clusters. It is also a catalase-positive and facultative anaerobe. They are the most common coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species that live on the human skin. In its natural environments such as the human skin or mucosa, they are usually harmless.[1]
Is Staphylococcus epidermidis coagulase negative?
Coagulase Negative Staphylococci Staphylococci other than S aureuscan cause infections in man. S epidermidisis the most important coagulase-negative staphylococcus (CNS) species and is the major cause of infections associated with prosthetic devices and catheters.
What causes Staphylococcus epidermidis bacteremia?
Bacteremia from the Staphylococcus epidermidisand other coagulase-negative staphylococcus species arise most commonly by indwelling medical device contamination.[5] When placing a prosthetic device in a human body, the bacteria from the human skin can colonize the medical devices and enter the bloodstream. Epidemiology
What is the difference between Staphylococcus aureus and S epidermidis?
Friedrich Julius Rosenbach distinguished S. epidermidis from S. aureus in 1884, initially naming S. epidermidis as S. albus. He chose aureus and albus since the bacteria formed yellow and white colonies, respectively. S. epidermidis is a very hardy microorganism, consisting of nonmotile, Gram-positive cocci, arranged in grape-like clusters.

Is Staphylococcus catalase positive or negative?
Staphylococcus aureus is a gram positive, catalase and coagulase positive coccus and by far the most important pathogen among the staphylococci.
Why is Staphylococcus epidermidis catalase positive?
So, if catalase is present, like in staph epidermidis, it makes the hydrogen peroxide dissociate into water and oxygen, causing the mixture to foam. Staph epidermidis is also urease positive, meaning it produces an enzyme called urease that dissociates urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia.
Is catalase present in Staphylococcus epidermidis?
From the present findings, it appears that catalase activity is involved in both S. epidermidis biofilm and planktonic cells' tolerance against NaCl, NaOCl or H2O2-exposure.
Is Staphylococcus catalase negative?
Staphylococcus species are catalase positive and facultatively anaerobic, except for S. aureus subsp. anaerobius and S. saccharolyticus, which are catalase negative and anaerobic.
Are all Staphylococcus catalase positive?
All Staphylococcus species produce catalase except for S. aureus subsp. anaerobius and S. saccharolyticus (9).
How do you identify Staphylococcus epidermidis?
As species identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci by fatty acid analyses and biochemical tests is known to be difficult ERIC- and BOX-PCR seem to be excellent tools for the identification of Staphylococcus epidermidis isolates.
What organisms are catalase negative?
coli, Enterobacter, Klebsiella, Shigella, Yersinia, Proteus, Salmonella, Serratia), Pseudomonas, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Aspergillus, Cryptococcus, and Rhodococcus equi. If not, the organism is 'catalase-negative'. Streptococcus and Enterococcus spp. are catalase-negative.
How is Staphylococcus aureus distinguished from Staphylococcus epidermidis?
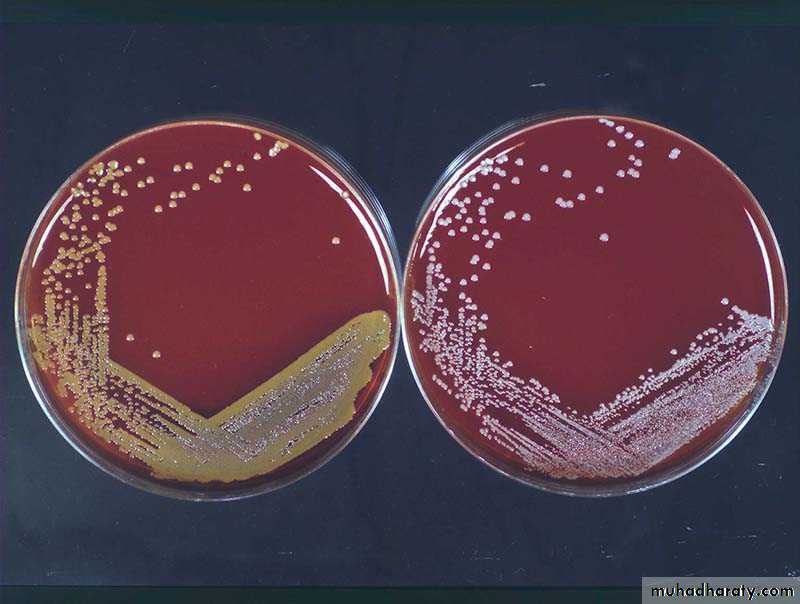
Staphylococcus aureus forms a fairly large yellow colony on rich medium; S. epidermidis has a relatively small white colony. S. aureus is often hemolytic on blood agar; S.
What enzymes does Staphylococcus epidermidis use?
epidermidis produces an extracellular slime that enables it to form adherent biofilms on plastic surfaces. We found that a biofilm-releasing enzyme produced by the gram-negative periodontal pathogen Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans rapidly and efficiently removed S. epidermidis biofilms from plastic surfaces.
What does it mean to be catalase negative?
Catalase is an enzyme that converts hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen gas. The test is easy to perform; bacteria are simply mixed with H2O2. If bubbles appear (due to the production of oxygen gas) the bacteria are catalase positive. If no bubbles appear, the bacteria are catalase negative.
What is the shape of Staphylococcus epidermidis?
S. epidermidis cells are spherical (0.5–1.5 μm in diameter) and gram-positive.
Is Staphylococcus Saprophyticus catalase positive?
Staphylococcus saprophyticus is known to cause urinary tract infections and other staphylococci are infrequent pathogens. Staphylococci are nonmotile, nonspore-forming, catalase-positive, facultatively anaerobic cocci, except for Staphylococcus saccharolyticus, which is a true anaerobe.
What is the morphology of Staphylococcus epidermidis?
Morphology of Staphylococcus epidermidis epidermidis is a Gram-positive bacterium that appears spherical with an average diameter of 0.5–1.5 µm on light microscopy. The cells of old cultures (>48 h) are often gram-variable to nearly gram-negative.
Is Staphylococcus epidermidis methyl red positive or negative?
This led to further testing of Methyl Red and Catalase. The results from these tests concluded that the Gram-positive bacteria were Staphylococcus epidermidis.
What is the colony morphology of Staphylococcus epidermidis?
Cellular morphology and biochemistry S. epidermidis is a very hardy microorganism, consisting of non-motile, Gram-positive cocci, arranged in grape- like clusters. It forms white, raised, cohesive colonies about 1–2 mm in diameter after overnight incubation, and is not haemolytic on blood agar.
Is Staphylococcus epidermidisis a gram positive or negative?
Staphylococcus epidermidisis a coagulase-negative, gram- positive cocci bacteria that form clusters. It is also a catalase-positive and facultative anaerobe. They are the most common coagulase-nega tive Staphylococcusspecies that live on the human skin. In its natural environments such as the human skin or mucosa, they are usually harmless.
Is staph a coagulase negative organism?
In its natural environments such as the human skin or mucosa, they are usually harmless. Many times, these coagulase-negative staph species invade the human body via prosthetic devices, at which point a small number of microbes travel down the prosthetic device to the bloodstream.
Is Staphylococcus epidermidis a cocci?
In its natural environments such</span> …. <span><i>Staphylococcus epidermidis</i> is a coagulase-negative, gram-positive cocci bacteria that form clusters. It is also a catalase-positive and facultative anaerobe.
What is a staphylococcus epidermidis?
Staphylococcus epidermidis, 1000 magnification under bright field microscopy. S. epidermidis is a very hardy microorganism, consisting of nonmo tile, Gram-positive cocci, arranged in grape-like clusters. It forms white, raised, cohesive colonies about 1–2 mm in diameter after overnight incubation, and is not hemolytic on blood agar.
How to detect S. epidermidis?
epidermidis is by using appearance of colonies on selective media, bacterial morphology by light microscopy, catalase and slide coagulase testing. On the Baird-Parker agar with egg yolk supplement, colonies appear small and black.
What is the biofilm that protects P. acnes from innate immunity?
Moreover, S. epidermidis biofilm formation by releasing the exopolysaccharide intercellular adhesion (PIA) provides the susceptible anaerobic environment to P. acnes colonisation and protects it from the innate human immunity molecules.
What is the main bacterium that causes acne vulgaris?
Staphylococcus epidermidis enters the sebaceous gland (where Propionibacterium acnes the main bacterium that causes acne vulgaris colonizes) and damages the hair follicles by producing lipolytic enzymes that change the sebum from fraction to dense (thick) form leading to inflammatory effect.
What causes biofilms to grow on plastic devices placed within the body?
Staphylococcus epidermidis stained by safranin. (x1000) As mentioned above, S. epidermidis causes biofilms to grow on plastic devices placed within the body. This occurs most commonly on intravenous catheters and on medical prostheses.
How does S. epidermidis help with acne?
epidermidis can interact to protect the host skin health from pathogens colonisation. But in the case of competition, they use the same carbon source (i.e. glycerol) to produce short chain fatty acids which act as antibacterial agent against each other. Also, S. epidermidis helps in skin homeostasis and reduces the P. acnes pathogenic inflammation by decreasing the TLR2 protein production that induces the skin inflammation.
What is the cause of virulence in S. epidermidis?
Virulence and antibiotic resistance. The ability to form biofilms on plastic devices is a major virulence factor for S. epidermidis. One probable cause is surface proteins that bind blood and extracellular matrix proteins.
What is the most pathogenic organism in the genus Staphylococcus?
Bacteria in the genus Staphylococcus are pathogens of man and other mammals. Traditionally they were divided into two groups on the basis of their ability to clot blood plasma (the coagulase reaction). The coagulase-positive staphylococci constitute the most pathogenic species S aureus.
Which is the most pathogenic species?
The coagulase-positive staphylococci constitute the most pathogenic species S aureus. The coagulase-negative staphylococci (CNS) are now known to comprise over 30 other species. The CNS are common commensals of skin, although some species can cause infections.
Is coagulase a virulence factor?
Coagulase is a marker for S aureus but there is no direct evidence that it is a virulence factor. Also, some natural isolates of S aureus are defective in coagulase. Nevertheless, the term is still in widespread use among clinical microbiologists.

Overview
Cellular morphology and biochemistry
Staphylococcus epidermidis is a very hardy microorganism, consisting of nonmotile, Gram-positive cocci, arranged in grape-like clusters. It forms white, raised, cohesive colonies about 1–2 mm in diameter after overnight incubation, and is not hemolytic on blood agar. It is a catalase-positive, coagulase-negative, facultative anaerobe that can grow by aerobic respiration or by fermentation. So…
Etymology
'Staphylococcus' - bunch of grape-like berries, 'epidermidis' - of the epidermis.
Discovery
Friedrich Julius Rosenbach distinguished S. epidermidis from S. aureus in 1884, initially naming S. epidermidis as S. albus. He chose aureus and albus since the bacteria formed yellow and white colonies, respectively.
Virulence and antibiotic resistance
The ability to form biofilms on plastic devices is a major virulence factor for S. epidermidis. One probable cause is surface proteins that bind blood and extracellular matrix proteins. It produces an extracellular material known as polysaccharide intercellular adhesin (PIA), which is made up of sulfated polysaccharides. It allows other bacteria to bind to the already existing biofilm, creating a multilayer biofilm. Such biofilms decrease the metabolic activity of bacteria within them. This dec…
Disease
As mentioned above, S. epidermidis causes biofilms to grow on plastic devices placed within the body. This occurs most commonly on intravenous catheters and on medical prostheses. Infection can also occur in dialysis patients or anyone with an implanted plastic device that may have been contaminated. It also causes endocarditis, most often in patients with defective heart valves. In som…
The role of Staphylococcus epidermidis in acne vulgaris
Staphylococcus epidermidis in the normal skin is nonpathogenic. But in abnormal lesions, it becomes pathogenic, likely in acne vulgaris. Staphylococcus epidermidis enters the sebaceous gland (colonized by Propionibacterium acnes, the main bacterium that causes acne vulgaris) and damages the hair follicles by producing lipolytic enzymes that change the sebum from fraction to dense (thick) form leading to inflammatory effect.
Identification
The normal practice of detecting S. epidermidis is by using appearance of colonies on selective media, bacterial morphology by light microscopy, catalase and slide coagulase testing. Zobell agar is useful for the isolation of Staphylococcus epidermidis from marine organisms. On the Baird-Parker agar with egg yolk supplement, colonies appear small and black. Increasingly, techniques such as quantitative PCR are being employed for the rapid detection and identificatio…