
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a gram-positive, catalase-negative cocci that has remained an extremely important human bacterial pathogen since its initial recognition in the late 1800s. The term pneumococcus gained widespread use by the late 1880s, when it was recognized as the most common cause of bacterial lobar pneumonia.
Is Streptococcus catalase positive?
Streptococci are facultatively anaerobic, Gram-positive organisms that often occur as chains or pairs (figures 1 and 2) and are catalase-negative (in contrast, staphylococci are catalase positive) (figure 3). Streptococci are subdivided into groups by antibodies that recognize surface antigens (figure 4).
What is the catalase test for Enterococcus?
oxygen is given off as bubbles in the liquid. The catalase test is primarily used to differentiate between gram-positive cocci. Members of the genus Staphylococcus are catalase-positive, and members of the genera Streptococcus and Enterococcus are catalase-negative.
What are the antigens of Streptococcus pneumoniae?
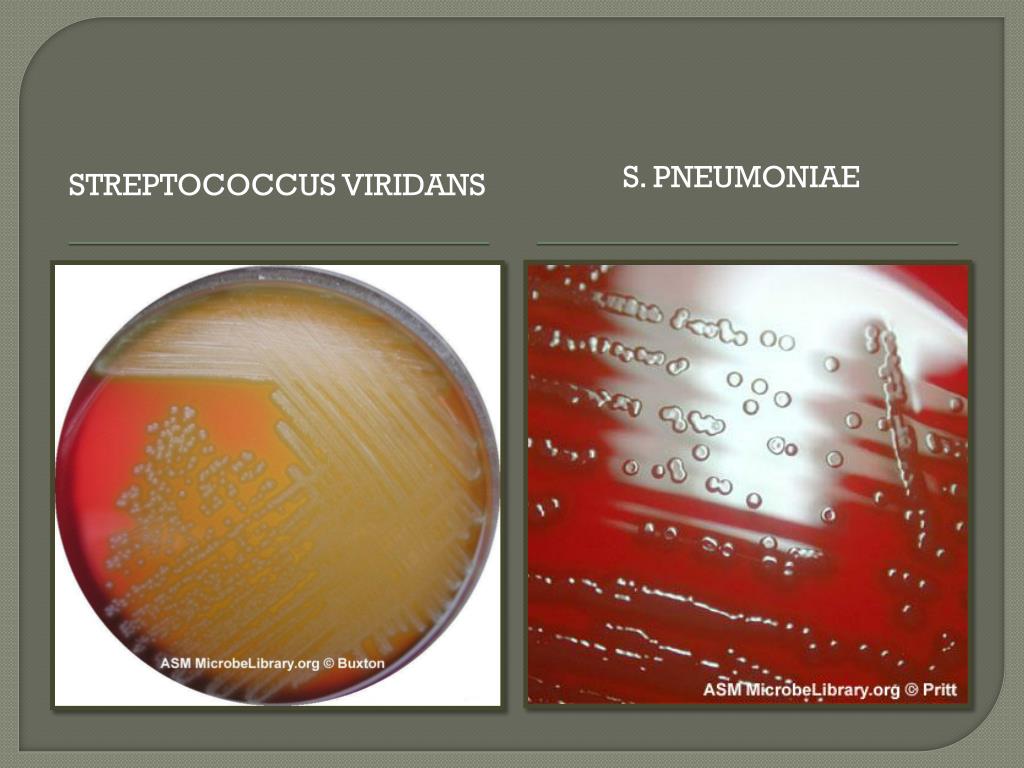
Streptococcus pneumoniae(a major cause of human pneumonia) and Streptococcus mutansand other so-called viridans streptococci (among the causes of dental caries) do not possess group antigens. Three types of hemolysis reaction (alpha, beta, gamma) are seen after growth of streptococci on sheep blood agar.
Which Streptococcus are bile-esculin positive and which are Pyr positive?
eLeuconostoc and Weisella are often coccobacillary, sometimes appearing rod like in chains. f All strains of S. bovis and approximately 10% of viridans streptococci are bile-esculin positive. g All strains of S. pyogenes and most strains of S. porcinus and S. iniae are PYR positive. Other streptococci are all negative
See more
Is Streptococcus pneumoniae catalase positive or negative?
catalase-negativeAll streptococci are catalase-negative. S. pneumoniae strains are sensitive to the chemical optochin (ethylhydrocupreine hydrochloride). Optochin sensitivity allows for the presumptive identification of alpha-hemolytic streptococci as S.
Are all streptococci catalase negative?
Staphylococcus and Micrococcus spp. are catalase positive, whereas Streptococcus and Enterococcus spp. are catalase negative.
Does Streptococcus pneumoniae produce hydrogen peroxide?
ABSTRACT. Aerobic growth of Streptococcus pneumoniae results in production of amounts of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) that may exceed 1 mM in the surrounding media.
Is Streptococcus pneumoniae methyl red positive or negative?
BIOCHEMICAL TESTS FOR STREPTOCOCCUS PNEUMONIAETESTSRESULTSMR (Methyl Red)+VE (POSITIVE)VP (Voges Proskauer)-VE (NEGATIVE)Coagulase-VE (NEGATIVE)Catalase-VE (NEGATIVE)10 more rows
Why is catalase test negative for Streptococcus?
Catalase-negative bacteria may be anaerobes, or they may be facultative anaerobes that only ferment and do not respire using oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor (ie. Streptococci).
Is Strep pneumoniae alpha hemolytic?
Historically, Streptococcus pneumoniae and other streptococci of the viridians group are classified as alpha-hemolytic bacteria on the basis of a greenish halo that surrounds colonies when grown aerobically on blood agar plates (1, 2).
Is Streptococcus pneumoniae beta-hemolytic?
Streptococcus pneumoniae, or pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, spherical bacteria, alpha-hemolytic (under aerobic conditions) or beta-hemolytic (under anaerobic conditions), aerotolerant anaerobic member of the genus Streptococcus. They are usually found in pairs (diplococci) and do not form spores and are non motile.
Is Streptococcus coagulase positive or negative?
Gram-positive cocci include Staphylococcus (catalase-positive), which grows clusters, and Streptococcus (catalase-negative), which grows in chains. The staphylococci further subdivide into coagulase-positive (S. aureus) and coagulase-negative (S. epidermidis and S.
Does Streptococcus pneumoniae grow on MacConkey Agar?
Hence, it does not grow on MacConkey agar (MA) due to the absence of blood as well as due to the presence of high concentration of bile in the medium which is inhibitory to the growth of S. pneumoniae.
What color is Streptococcus pneumoniae?
pneumoniae appear as small, grey, moist (sometimes mucoidal), colonies and characteristically produce a zone of alpha-hemolysis (green) (Figure 1).
What are the characteristics of Streptococcus pneumoniae?
Streptococcus pneumoniae is a gram-positive, catalase-negative, facultatively anaerobic organism that grows as a single coccus, as diplococci often identifiable because of their lancet shape, and in chains of variable length. Growth is enhanced in 5% carbon dioxide or anaerobic conditions.
Is Streptococcus agalactiae catalase positive or negative?
NegativeBiochemical Test and Identification of Streptococcus agalactiaeBasic CharacteristicsProperties (Streptococcus agalactiae)CatalaseNegative (-ve)CoagulaseNegative (-ve)FlagellaNon-flagellatedGram StainingPositive (+ve)41 more rows•Aug 15, 2019
How often should you check a bottle for catalase?
Opened bottles should be checked against a known catalase positive organism every 6 months.
What is a positive Neufeld reaction?
A positive quellung or Neufeld reaction is the result of the binding of the capsular polysaccharide of pneumococci with type specific antibody contained in the typing antiserum. Pneumococcal typing sera are commercially available as pooled, group, or serotype-specific (see http://www.ssi.dk/English.aspx). It is recommended to initially test with pooled antisera in succession until a positive reaction is observed. Typing should then proceed by testing with individual group and serotype-specific antisera included in the antisera pool that gave a positive reaction to determine the serogroup and serotype. An antigen-antibody reaction causes a change in the refractive index of the capsule so that it appears “swollen” and more visible. After the addition of a counter stain (methylene blue), the pneumococcal cells stain dark blue and are surrounded by a sharply demarcated halo which represents the outer edge of the capsule. The light transmitted through the capsule appears brighter than either the pneumococcal cell or the background. Single cells, pairs, chains, and even clumps of cells may have positive quellung reactions.
Is ATCC 49619 inhibited by optochin?
The growth of S. pneumoniae strain ATCC 49619 is inhibited by optochin and growth of S. mitis strain ATCC 49456 is not inhibited by optochin.
Is S. pneumoniae gram positive?
S. pneumoniae may occur intracellularly or extracellularly as gram-positive lanceolate diplococci, but can also occur as single cocci or in short chains of cocci. S. pneumoniae is a fastidious bacterium, growing best at 35-37°C with ~5% CO2 (or in a candle-jar). It is usually cultured on media that contain blood, but can also grow on a chocolate agar plate (CAP). On a blood agar plate (BAP), colonies of S. pneumoniae appear as small, grey, moist (sometimes mucoidal), colonies and characteristically produce a zone of alpha-hemolysis (green) (Figure 1). The alpha-hemolytic property differentiates this organism from many species, but not from the commensal alpha-hemolytic (viridans) streptococci. Differentiating pneumococci from viridans streptococci is difficult as young pneumococcal colonies appear raised, similar to viridans streptococci. However, once the pneumococcal culture ages 24-48 hours, the colonies become flattened, and the central portion becomes depressed, which does not occur with viridans streptococci (Figure 2). A microscope (30-50X) or a 3X hand lens can also be a useful tool in differentiating pneumococci from viridans streptococci. Prior to identification and characterization testing procedures, isolates should always be inspected for purity of growth and a single colony should be re-streaked, when necessary, to obtain a pure culture. For the following identification and characterization procedures, it is essential to test alpha-hemolytic colonies that are less than a day old, typically grown overnight at 35-37°C with ~5% CO2 (or in a candle-jar).
Is serotyping necessary for pneumococci?
Although serotyping of pneumococci is not usually necessary for a clinical response, capsular serotype determination is a critical component of successful pneumococcal disease surveillance efforts. Effective current multivalent vaccines target combinations of key serotypes. Determination of serotype distributions associated with disease in certain regions provides information regarding the potential usefulness of applying existing vaccines and is also critical for assessing vaccine impact.
How to identify streptococci?
The most convenient way to begin to identify the streptococci is to determine the hemolysis of the bacteria on blood agar plates. As mentioned earlier the techniques for determining hemolysis is described in detail in; Isolation and Identification of streptococci, Part 1. Collection, transport, and determination of hemolysis, Annex 1. Once the streptococci are divided into ß-hemolytic and non-ß-hemolytic categories differentiation into species, groups, and categories can be made. The identification of most ß-hemolytic strains is performed by determining the antigenic characteristics of the culture; but, identification of the non-ß-hemolytic strains is performed by determining antigenic and physiologic characteristics of the culture
How to identify a nutritionally variant streptococci?
Nutritionally variant streptococci (NVS) can be identified by demonstrating that the strain requires pyridoxal or grows on an agar plate only when a bacteria that satellites is present. In addition to this requirement, NVS also give positive PYR tests, which helps to differentiate these strains from viridans streptococci.
What is the origin of gram positive cocci?
The origin of this genus is from a collection of viridans-like streptococci that most closely resembled Streptococcus uberis. What makes Globicatella distinct from the viridans streptococci is that all the Globicatella strains were PYR positive, LAP negative and grow in broth containing 6.5% NaCl while all viridans species are PYR negative, LAP positive and fail to grow in 6.5% NaCl. All strains identified to date have been sensitive to vancomycin, PYR positive, LAP negative, grow in 6.5% NaCl broth, do not grow at 10ΕC or 45ΕC, are nonmotile, and are α-hemolytic.
Why were the vagococci and pediococci split?
The tetragenococci were split from the Pediococcus genus because it too is genetically different from the other members of the genus. The Leuconostoc s and pediococci were considered non-pathogenic until the mid 1980s.
What is the VP test for?
Most species can only be identified to viridans species group. The VP test aids in the identification and differentiation of the viridans streptococcal species and is a key reaction for the S. anginosus group. The urea test is particularly useful in the identification of Streptococcus salivarius. Table 6.
What are the two species of helocococci?
H. kurzii is the only one isolated from humans. These bacteria have been isolated from wound infections. Like the Alloiococci and Gemella e these bacteria grow very slowly on blood agar media. The physiologic characteristics of helocococci are similar to the aerococci in that they are PYR positive, LAP negative, and grow in broth containing 6.5% NaCl. These bacteria grow more slowly and are not α-hemolytic on blood agar while the aerococci grow readily and are α-hemolytic on blood agar. Like the Aerococci these strains are vancomycin sensitive, do not form gas in MRS broth and fail to grow at 10ΕC and 45ΕC. All isolates have been non-motile.
What are ß-hemolytic streptococci?
There are other ß-hemolytic streptococci but they are rarely found in human infections. Some of the strains are associated with infections of swine and they have specific group antigens. Using DNA-DNA homology the taxonomist have suggested that those ß-hemolytic strains with group E, P, U, V, and other experimental group antigens be called S. porcinus. ß-hemolytic strains with group L antigen have been associated with avian sources (chicken), it is suggested that these strains be called S. dysgalactiae. ß-hemolytic strains with group M antigen are not well studied and there is no suggested taxonomic name for these strains. A ß-hemolytic strain with a yet to be named group antigen (suggested X) isolated from fresh water dolphins, and occasionally in human infections, is called S. iniae. This bacterium may be submitted as a group A streptococci because it may react with the group A antibody in the latex slide agglutination assay. It is also PYRase positive but is not sensitive to bacitracin. Whenever a latex agglutination group A positive bacterium is submitted that is not sensitive to bacitracin the group reaction should be confirmed using the Lancefield extraction procedure.
