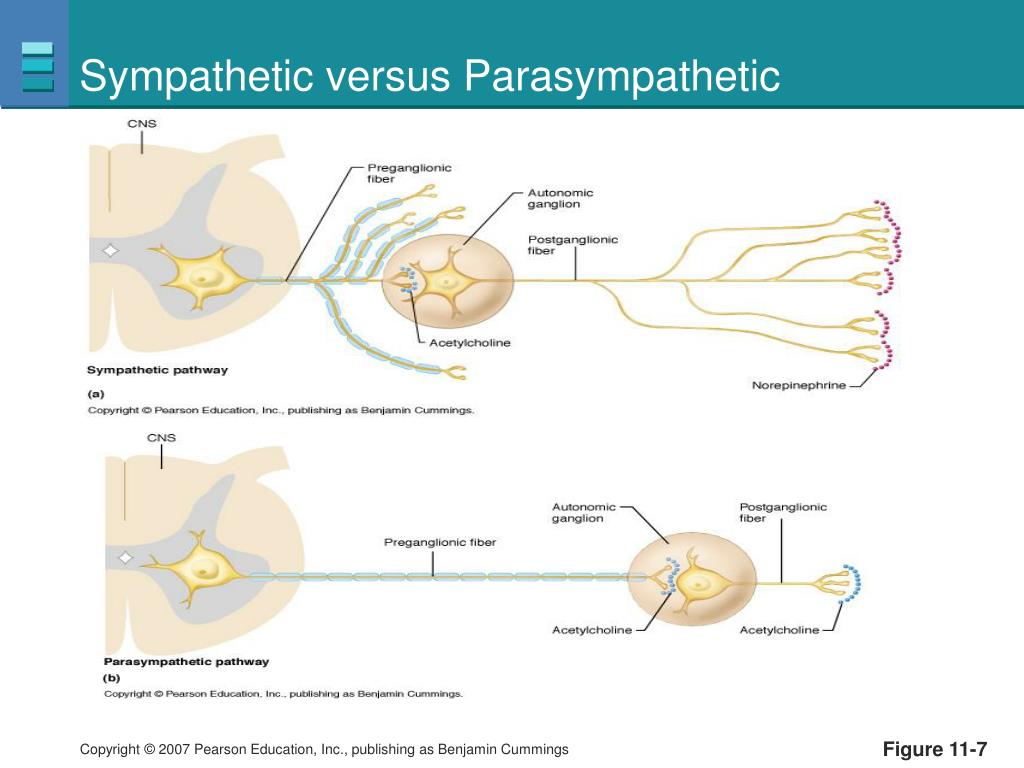
When considering the Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic Nervous System
Parasympathetic nervous system
The parasympathetic nervous system is one of the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the other being the sympathetic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system is responsible for regulating the body's unconscious actions. The parasympathetic system is responsible for stimulation of "rest-and-digest" or "feed and breed" activities that occur when the body is at rest, especially after …
What is the difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic?
Sympathetic is the nervous system responsible for your “fight or flight” responses in times of emergencies. It controls the body’s responses to stress, injuries, or perceived threats. Parasympathetic is the nervous system responsible for your “rest and digest” responses in times of non-emergencies.
How does the sympathetic nervous system work with other systems?
While it typically communicates with the central nervous system through the sympathetic or parasympathetic nervous systems, it can function completely on its own. The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for preparing the body’s reactions to stress, injury, or perceived threats.
What happens to the parasympathetic nervous system when we are at rest?
Once the perceived threat is gone the parasympathetic nervous system takes back over in order to counteract the effects of the sympathetic nervous system’s responses. The parasympathetic nervous system is always at work when the body is at rest.
What is an example of the parasympathetic nervous system?
A common example is body temperature: regardless of the weather the human body always strives to maintain an internal temperature of 98.6 degrees Fahrenheit. The parasympathetic nervous system is commonly referred to as your “rest and digest” response. It is also an involuntary reaction and happens in non-emergency situations.

Why is the sympathetic nervous system faster?
Also, the neurons of the SNS have shorter axons in comparison to those of the parasympathetic nervous system, thus they act a lot quicker, sometimes the responses happen before a person is consciously aware of them.
Which system is faster PNS or SNS?
The sympathetic nervous system is a faster system as it moves along very short neurons. When the system is activated, it activates the adrenal medulla to release hormones and chemical receptors into the bloodstreams. The target glands and muscles get activated.
How are sympathetic and parasympathetic systems different?
The sympathetic system controls “fight-or-flight” responses. In other words, this system prepares the body for strenuous physical activity. The events that we would expect to occur within the body to allow this to happen do, in fact, occur. The parasympathetic system regulates “rest and digest” functions.
Does the parasympathetic nervous system speed up or slow down the heart?
The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) releases the hormone acetylcholine to slow the heart rate. Such factors as stress, caffeine, and excitement may temporarily accelerate your heart rate, while meditating or taking slow, deep breaths may help to slow your heart rate.
What is the major difference between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems quizlet?
The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) controls homeostasis and the body at rest and is responsible for the body's "rest and digest" function. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) controls the body's responses to a perceived threat and is responsible for the "fight or flight" response.
What are 3 differences between the parasympathetic and the sympathetic division?
Sympathetic Nervous System: Sympathetic nervous system increases heart beat, blood level, and metabolic rate. Parasympathetic Nervous System: Parasympathetic nervous system decreases heart beat, blood level, and metabolic rate.
How do you remember parasympathetic and sympathetic?
One of the best ways to remember their differences is to look at the beginning letters of the words. The sympathetic nervous system responds to stress and is your “fight or flight” response. While the parasympathetic nervous system responds to peace and is your “rest and digest” response.
Can the parasympathetic and sympathetic work at the same time?
The parasympathetic and sympathetic systems do not work entirely separately, but rather work at the same time, often in opposition to one another.
What are parasympathetic activities?
Your parasympathetic nervous system is a network of nerves that relaxes your body after periods of stress or danger. It also helps run life-sustaining processes, like digestion, during times when you feel safe and relaxed.
Does parasympathetic stimulation increase heart rate?
In contrast, parasympathetic stimulation decreases heart rate and constricts the pupils. It also increases secretion of the eye glands, increases peristalsis, increases secretion of salivary and pancreatic glands, and constricts bronchioles.
Does parasympathetic increase blood pressure?
This study indicates the importance of behavioural modification in hypertension and that increased parasympathetic function is associated with success in reduction of BP.
What happens when parasympathetic nervous system is stimulated?
The parasympathetic nervous system decreases respiration and heart rate and increases digestion. Stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system results in: Construction of pupils. Decreased heart rate and blood pressure.
What is the difference between ANS and SNS?
The SNS consists of motor neurons that stimulate skeletal muscles. In contrast, the ANS consists of motor neurons that control smooth muscles, cardiac muscles, and glands. In addition, the ANS monitors visceral organs and blood vessels with sensory neurons, which provide input information for the CNS.
How does the central nervous system compare with the peripheral nervous system?
The central nervous system (CNS) includes the brain and spinal cord, while the peripheral nervous system includes all of the nerves that branch out from the brain and spinal cord and extend to other parts of the body, including muscles and organs.
What is the difference between PNS and ANS?
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the division of the PNS that governs the internal activities of the human body, including heart rate, breathing, digestion, salivation, perspiration, urination, and sexual arousal.
How does the sympathetic division compare to the parasympathetic division quizlet?
The parasympathetic division has short axons with relatively few branches and ganglia located close to or within the wall of the organ. The sympathetic division has long axons with many branches and ganglia located in the sympathetic trunk or prevertebral ganglia.
What is the major difference between the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems?
The parasympathetic nervous system restores the body to a calm and composed state and prevents it from overworking. The sympathetic nervous system,...
What are the hormones released by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems?
The sympathetic nervous system releases the hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine that accelerate the heart rate. The parasympathetic nervous sys...
What actions are controlled by the parasympathetic nervous system?
Salivation, urination, lacrimation, defecation and digestion are the important body activities stimulated by the parasympathetic nervous system.
What are parasympathetic ganglia?
These are the autonomic ganglia of the parasympathetic nervous system that lie near or within the organs they innervate.
What are the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system composed of?
The parasympathetic nervous system is composed of cranial and spinal nerves. The sympathetic nervous system comprises cell bodies that lie within t...
Is slow heart rate sympathetic or parasympathetic?
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) releases the hormones (catecholamines - epinephrine and norepinephrine) to accelerate the heart rate. The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) releases the hormone acetylcholine to slow the heart rate.
Does the parasympathetic nervous system speed up or slow down heart rate?
Parasympathetic Nervous System Helps us Switch Off Increased parasympathetic activity causes the heart rate and respiration to slow down and heart rate variability to increase. Normally, this happens when we rest, but sometimes the system doesn't work like it should.
How do the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems differ?
The sympathetic nervous system is involved in preparing the body for stress-related activities; the parasympathetic nervous system is associated with returning the body to routine, day-to-day operations. The two systems have complementary functions, operating in tandem to maintain the body's homeostasis.
Is sympathetic or parasympathetic more important?
The sympathetic division initiates the fight-or-flight response and the parasympathetic initiates the rest-and-digest or feed-and-breed responses. The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are important for modulating many vital functions, including respiration and cardiac contractility.
What is the role of sympathetic and parasympathetic?
Parasympathetic. Involved in the fight or flight response. Involved in maintaining homeostasis and also, permits the rest and digest response. The sympathetic system prepares the body for any potential danger. The parasympathetic system aims to bring the body to a state of calm.
What is Sympathetic And Parasympathetic Nervous System?
Sympathetic Autonomic Nervous System: It is the part of the autonomic nervous system, located near the thoracic and lumbar regions in the spinal cord. Its primary function is to stimulate the body’s fight or flight response. It does this by regulating the heart rate, rate of respiration, pupillary response and more.
Why is the autonomic nervous system called the autonomic nervous system?
The autonomic nervous system is named so, because it works autonomously, i.e., without a person’s conscious effort. The primary function of the autonomic nervous system is homeostasis. Apart from maintaining the body’s internal environment, it is also involved in controlling and maintaining the following life processes: Digestion. Metabolism.
Where is the parasympathetic nervous system located?
Parasympathetic Autonomic Nervous System: It is located in between the spinal cord and the medulla. It primarily stimulates the body’s “rest and digest” and “feed and breed” response. Read on to explore more differences between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system.
Which system prepares the body for fight and flight response?
The parasympathetic nervous system restores the body to a calm and composed state and prevents it from overworking. The sympathetic nervous system , on the other hand, prepares the body for fight and flight response.
Which system activates the fight or flight response during a threat or perceived danger?
The sympathetic nervous system activates the fight or flight response during a threat or perceived danger, and the parasympathetic nervous system restores the body to a state of calm. Learn more about the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, or other related topics at BYJU’S Biology.
What is the difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system?
Sympathetic vs. Parasympathetic Nervous System. The human nervous system is a sprawling network of nerves and cells which , together , regulate all of the vital functions that take place in our bodies. The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) and the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) are both components of the autonomic nervous system (ANS).
What Does the Parasympathetic Nervous System Do?
Put simply, the PSNS keeps your bodily functions working as they should. It keeps your heart rate and blood pressure steady while stimulating activities related to digestive and sexual function. These include the production of saliva, tears, and urine, digestion, defecation, and sexual arousal.
What is the Autonomic Nervous System?
The SNS and PSNS are the two main parts of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which controls the functions of our internal organs. All of the functions of the ANS are involuntary and reflexive, so we don’t always notice its effects on our bodies.
Sympathetic Nervous System: Fight or Flight
The ANS directs your body’s rapid and involuntary response to strain, such as danger, disease, and exercise. It sends messages to organs, muscles, and glands to increase heart rate, dilate the bronchial tubes to your lungs, increase perspiration, and cause pupil dilation.
Parasympathetic Nervous System: Rest and Digest
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) works in opposition to the sympathetic system, controlling the body’s ability to relax. It mainly functions to downregulate the body using the vagus nerve, which sends impulses from the brain to the body and back.
Autonomic Nervous System and Heart Rate Variability
Heart rate variability (HRV) is a measure of how the SNS and PSNS affect your heart beat. When your nervous system is balanced, your heart is constantly being told to beat slower by your parasympathetic system, and to beat faster by your sympathetic system. These mixed messages result in a constant state of variation in your heart rate.
WHOOP Calculates HRV to Help Monitor Your ANS
WHOOP monitors your heart rate and calculates your HRV on a nightly basis using a dynamic average during sleep. It is weighted towards your last stage of slow wave sleep when you’re in your deepest period of sleep and your body is most at rest.
Casey Meserve
Casey Meserve is a writer at WHOOP. Prior to joining WHOOP, they were an SEO Strategist at TechTarget, an editor at Patch.com, and a reporter for the Old Colony Memorial in Plymouth, Mass.
Where does the parasympathetic nervous system originate?
The parasympathetic nervous system is always at work when the body is at rest. It originates in the spinal cord and the medulla oblongata (the medulla of the brain, not the adrenal medulla).
Why does the sympathetic nervous system have a short neuron pathway?
The sympathetic nervous system has short neuron pathways and a faster system. This is because they must react quickly in times of stress and danger.
What is the autonomic nervous system?
Autonomic Nervous System in Depth. The autonomic nervous system is the one that pertains to sympathetic vs parasympathetic. The autonomic nervous system has three divisions: the enteric nervous system, the sympathetic nervous system, and the parasympathetic nervous system.
What are the two parts of the peripheral nervous system?
The peripheral nervous system can be further broken down into two components: the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system .
Why does the sympathetic nervous system decrease saliva production?
The sympathetic nervous system decreases your stomach movement and your saliva production. This is because they are considered non-essential during moments of danger.
What is the nervous system responsible for your fight or flight response?
Sympathetic is the nervous system responsible for your “fight or flight” responses in times of emergencies. It controls the body’s responses to stress, injuries, or perceived threats.
What is the nervous system?
Humans have a nervous system which is responsible for detecting environmental changes, controlling the body, and transmitting signals to and from different parts of the body. The nervous system is made up of the brain, the spinal cord, sensory organs, and nerves (that transmit impulses).
What happens if your parasympathetic nervous system doesn't work?
Your PSNS is a vital part of your body’s key functions. When it doesn’t work properly, you can face a number of bodily dysfunctions that affect your health. If you think you may be having trouble with one of your body’s parasympathetic nervous system functions, talk to your doctor to find out how you can get help.
Where do parasympathetic nerves come from?
Trusted Source. of all parasympathetic nerve fibers in the body come from this nerve. This nerve has branches in many key organs, including the stomach, kidneys, liver, pancreas, gallbladder, bladder, anal sphincter, vagina, and penis.
What is the acronym for parasympathetic response?
Examples of parasympathetic responses. An easy acronym to remember how and where the PSNS works is SLUDD. This stands for: Salivation: As part of its rest-and-digest function, the PSNS stimulates production of saliva, which contains enzymes to help your food digest.
What is the nervous system?
Your nervous system is a wild and wonderful network of nerves that act in different key functions to keep your body moving, responding, sensing, and more. This article is going to examine the parasympathetic nervous system, one of two majors divisions of the larger autonomic system. In the simplest terms, the parasympathetic ...
Where does the parasympathetic nervous system start?
Parasympathetic nervous system function. Your PSNS starts in your brain and extends out via long fibers that connect with special neurons near the organ they intend to act on. Once PSNS signals hit these neurons, they have a short distance to travel to their respective organs.
What is the difference between resting heart rate and sympathetic nervous system?
This means they’re responsible for helping you maintain your resting heart rate. For most people, the resting heart rate is between 60 and 100 beats per minute. On the other hand, the sympathetic nervous system (SNS) increases heart rate. A faster heart rate (usually) pumps more oxygen-rich blood to the brain and lungs.
Which nerves are responsible for many movements and sensations that take place in your body's head and neck?
Parasympathetic cranial nerves. The cranial nerves are paired nerves that are responsible for many movements and sensations that take place in your body’s head and neck. The nerves all start in the brain.
Does the parasympathetic nervous system speed up or slow down heart rate?
Increased parasympathetic activity causes the heart rate and respiration to slow down and heart rate variability to increase. Normally, this happens when we rest, but sometimes the system doesn’t work like it should.
How do the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems differ?
The sympathetic nervous system is involved in preparing the body for stress-related activities; the parasympathetic nervous system is associated with returning the body to routine, day-to-day operations. The two systems have complementary functions, operating in tandem to maintain the body’s homeostasis.
Is sympathetic or parasympathetic more important?
The sympathetic division initiates the fight-or-flight response and the parasympathetic initiates the rest-and-digest or feed-and-breed responses. The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems are important for modulating many vital functions, including respiration and cardiac contractility.